Abstract
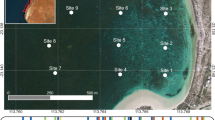
We present the first study of the effects of ocean acidification on settlement of benthic invertebrates and microfauna. Artificial collectors were placed for 1 month along pH gradients at CO2 vents off Ischia (Tyrrhenian Sea, Italy). Seventy-nine taxa were identified from six main taxonomic groups (foraminiferans, nematodes, polychaetes, molluscs, crustaceans and chaetognaths). Calcareous foraminiferans, serpulid polychaetes, gastropods and bivalves showed highly significant reductions in recruitment to the collectors as pCO2 rose from normal (336–341 ppm, pH 8.09–8.15) to high levels (886–5,148 ppm) causing acidified conditions near the vents (pH 7.08–7.79). Only the syllid polychaete Syllis prolifera had higher abundances at the most acidified station, although a wide range of polychaetes and small crustaceans was able to settle and survive under these conditions. A few taxa (Amphiglena mediterranea, Leptochelia dubia, Caprella acanthifera) were particularly abundant at stations acidified by intermediate amounts of CO2 (pH 7.41–7.99). These results show that increased levels of CO2 can profoundly affect the settlement of a wide range of benthic organisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augier H, Boudouresque C-F (1970) Végetation marine de l’ile de Port Cros. Le recif barrière de posidonies. Bull Mus Hist Nat Marseille 30:221–228
Barry JP, Hall-Spencer JM, Tyrell T (2010) In situ perturbation experiments: natural venting sites, spatial/temporal gradients in ocean pH, manipulative in situ pCO2 perturbations. In: Riebesell U, Fabry VJ, Hansson L, Gattuso J-P (eds) Guide to best practices for ocean acidification research and data reporting. Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg
Bellan G (1980) Relationship of pollution to rocky substratum polychaetes on the French Mediterranean coast. Mar Pollut Bull 11(11):318–321
Bijma J, Hönisch B, Zeebe RE (2002) Impact of the ocean carbonate chemistry on living foraminiferal shell weight: comment on ‘Carbonate ion concentration in glacial-age deep waters of the Caribbean Sea’ by Broecker WS, Clark E. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 3(11):1064. doi:10.1029/2009GC000388
Boudouresque CF, Cinelli F (1971) Le peuplement des biotopes sciaphiles superficiels de mode battu de l’île d’Ischia (Golfe de Naples, Italie). Pubbl St Zool Napoli 39:1–43
Boudouresque CF, Cinelli F (1976) Les peuplement algal des biotopes sciaphiles superficiles de mode battu en Mediterranée occidentale. Pubbl St Zool Napoli 40:433–459
Buia MC, Gambi MC, Lorenti M, Dappiano M, Zupo V (2003) Aggiornamento sulla distribuzione e sullo stato ambientale dei sistemi a fanerogame marine (Posidonia oceanica e Cymodocea nodosa) delle isole Flegree. Acc Sc Lett Arti Napoli, Mem Soc Sc Fis Mat 5:163–186
Caldeira K, Wickett ME (2003) Anthropogenic carbon and ocean pH. Nature 425:365
Cozzolino GC, Scipione MB, Lorenti M, Zupo V (1992) Migrazioni nictemerali e struttura del popolamento a crostacei Peracaridi e Decapodi in una prateria a Posidonia oceanica dell’isola d’Ischia (Golfo di Napoli). Oebalia suppl 17:343–346
Dashfield SL, Somerfield PJ, Widdicombe S, Austen MC, Nimmo M (2008) Impacts of ocean acidification and burrowing urchins on within-sediment profiles and subtidal nematode communities. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 365(1):46–52
deFur PL, McMahon BR (1984) Physiological compensation to short term air exposure in red rock crabs, Cancer productus Randall, from littoral and sublittoral habitats: acid-base balance. Physiol Zool 57:151–160
Dupont S, Havenhand J, Thorndyke W, Peck L, Thorndyke M (2008) Near-future level of CO2-driven ocean acidification radically affects larval survival and development in the brittlestar Ophiothrix fragilis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 373:285–294
Ellis RP, Bersey J, Rundle SD, Hall-Spencer JM, Spicer JI (2009) Subtle but significant effects of CO2 acidified sea water on embryos of the intertidal snail, Littorina obtusata. Aquat Biol 5:41–48
Fabry VJ, Siebel BA, Feeley RA, Orr JC 2008. Impact of ocean acidification on marine fauna and ecosystem processes. International council for the exploration of the sea. Oxford Journal 414–432
Feely RA, Sabine CL, Lee K, Berelson W, Kleypas J, Fabry VJ, Millero FJ (2004) Impact of anthropogenic CO2 on the CaCO3 system in the oceans. Science 305:362–366
Findlay HS, Kendall MA, Spicer JI, Widdicombe S (2009) Future high CO2 in the intertidal may compromise adult barnacle Semibalanus balanoides survival and embryonic development rate. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 389:193–202
Gambi MC, Cafiero G (2001) Functional diversity in the Posidonia oceanica ecosystem: an example with polychaete borers of the scales. In: Faranda FM, Guglielmo L, Spezie G (eds) Mediterranean Ecosystems: Structure and Processes. Springer-Verlag, Italy, pp 399–405
Gambi MC, Ramella L, Sella G, Protto P, Aldieri E (1997) Variation in genome size in benthic polychaetes: systematic and ecological relationships. J Mar Biol Ass UK 77:1045–1057
Gambi MC, Zupo V, Buia MC, Mazzella L (2000) Feeding ecology of the polychaete Platynereis dumerilii (Audouin & Milne Edwards) (Nereididae) in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica system: role of the epiphytic flora. Ophelia 53(3):189–202
Gambi MC, De Lauro M, Iannuzzi F (Eds) (2003) Ambiente marino costiero e territorio delle isole Flegree (Ischia Procida Vivara). Acc Sc Lett Arti Napoli. Mem Soc Sc Fis Mat 5:425
Gattuso J-P, Frankignoulle M, Bourge I, Romaine S, Buddemeier RW (1998) Effect of calcium carbonate saturation of seawater in coral calcification. Glob Planet Chan 18:37–46
Gazeau F, Quiblier C, Jansen JM, Gattuso JP, Middelburg JJ, Heip CHR (2007) Impact of elevated CO2 on shellfish calcification. Geophys Res Lett 34:L07603
Gobin J, Warwick RM (2006) Geographical variation in species diversity: a comparison of marine polychaetes and nematodes. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 330:234–244
Green MA, Jones ME, Boudreau CL, Moore RL, Westman BA (2004) Dissolution mortality of juvenile bivalves in coastal marine deposits. Limnol Oceanogr 49:727–734
Guidetti P, Bussotti S (1998) Juveniles of littoral fish species in shallow seagrass beds: preliminary quali-quantitative data. Biol Mar Mediter 5:347–350
Hall-Spencer JM, Rodolfo-Metalpa R, Martin S, Ransome S, Fine M, Turner SM, Rowley SJ, Tedesco D, Buia MC (2008) Volcanic carbon dioxide vents show ecosystem effects of ocean acidification. Nature 454:96–99
Houghton JT, Callander BA, Varney SK (1992) Climate Change: the supplementary report to the IPCC Scientific. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Iglesias-Rodriguez D, Halloran PR, Rickaby REM, Hall IR, Colmenero-Hidalgo E, Gittins JR, Green DRH, Tyrrell T, Gibb S, von Dassow P, Rehm E, Armbrust EV, Boessenkool KP (2008) Phytoplankton calcification in a high-CO2 world. Science 320(5874):336–340
Jokiel PL, Rodgers KS, Kuffner IB, Andersson AJ, Cox EF, Mackenzie FT (2008) Ocean acidification and calcifying reef organisms: a mesocosm investigation. Coral Reefs 27:473–483
Jury C, Whitehead R, Szmant A (2009) Effects of variations in carbonate chemistry on the calcification rates of Madracis auretenra (=Madracis mirabilis sensu Wells, 1973): bicarbonate concentrations best predict calcification rates Global Chan Biol doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02057.x
Keeling CD, Whorf TP (1994) Atmospheric CO2 records from sites in the SIO air sampling network. In: Boden TA, Kaiser DP, Sepanki RJ, Stoss FW (eds) Trends ‘93: a compendium of data on global change. Carbon Dioxide Information Analysis Center, Oak Ridge National Laboratory. Oak Ridge, TN, pp 16–26
Kendall MA, Widdicombe S, Davey JT, Somerfield PJ, Austen MCV, Warwick RM (1996) The biogeography of islands: preliminary results from a comparative study of the isles of Scilly and Cornwall. J Mar Biol Ass UK 76:219–222
Kleypas JA, Feely RA, Fabry VJ, Langdon C, Sabine CL, Robbins LL (2006) Impacts of Ocean Acidification on Coral Reefs and Other Marine Calcifiers: A Guide for Future Research. Report of a workshop held 18–20 April 2005, St. Petersburg, FL
Kuffner IB, Andersson AJ, Jokiel PL, Rodgers KS, Mackenzie FT (2007) Decreased abundance of crustose coralline algae due to ocean acidification. Nat Geosci 1(2):114–117
Kurihara H, Ishimatsu A (2008) Effects of high CO2 seawater on the copepod (Acartia tsuensis) through all life stages and subsequent generations. Mar Pollut Bull 56:1086–1090
Kurihara H, Shirayama Y (2004) Effects of increased atmospheric CO2 on sea urchin early development. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 274:161–169
Kurihara H, Shimode S, Shirayama Y (2004) Sub-lethal effects of elevated concentration of CO2 on planktonic copepods and sea urchins. J Oceanogr 60:743–750
Kurihara H, Kato S, Ishimatsu A (2007) Effects of increased seawater pCO2 on early development of the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Aquat Biol 1:91–98
Lindinger MI, Lauren DJ, McDonald DG (1984) Acid–base balance in the sea mussel, Mytilus edulis. III. Effects of environmental hypercapnia on intra- and extracellular acid–base balance. Mar Biol Lett 5:371–381
Lorenti M, Scipione MB (1990) Relationships between trophic structure and diel migrations of Isopods and Amphipods in a Posidonia oceanica bed of the island of Ischia (Gulf of Naples, Italy). Rapp Comm int Expl Mer Médit 32(1):17
Martin S, Rodolfo-Metalpa R, Ransome E, Rowley S, Buia MC, Gattuso JP, Hall-Spencer JM (2008) Effects of naturally acidified seawater on seagrass calcareous epibionts. Biol Lett 4(6):689–692
Menge BA (1992) Community regulation: under what conditions are bottom-up factors important on rocky shores? Ecology 73:755–765
Michaelidis B, Ouzounis C, Paleras A, Portner HO (2005) Effects of long-term moderate hypercapnia on acid–base balance and growth rate in marine mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 293:109–118
Porri F, McQuaid CD, Radloff S (2006) Spatio-temporal variability of larval abundances and settlement of Perna perna: differential delivery of mussels. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 315:141–150
Porzio L, Hall-Spencer J, Buia MC (2008) Macroalgal community response to increasing CO2. II International Symposium on the ocean in a high-CO2 world. Monaco, p 75 (abstract)
Pulitzer Finali G (1970) Report on a collection of sponges from the Bay of Naples. I. Sclerospongiae, Lithistida, Tetractinellida, Epipolasida. Pubbl St Zool Napoli 38:328–354
Pulitzer Finali G, Pronzato R (1976) Report on a collection of sponges from the Bay of Naples. II. Keratosa. Pubbl St Zool Napoli 40:83–104
Raven J, Caldeira K, Elderfield H, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Liss P, Riebesell U, Shepherd J, Turley C, Watson A (2005) Ocean acidification due to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide. The Royal Society policy document 12/05. The Clyvedon Press Ltd, Cardiff
Riebesell U (2008) Acid test for marine biodiversity. Nature 454:46–47
Riebesell U, Wolf-Gladrow DA, Smetacek V (1993) Carbon dioxide limitation of marine phytoplankton growth rates. Nature 361:249–251
Riebesell U, Zondervan I, Rost B, Tortell PD, Richard EZ, Morel FMM (2000) Reduced calcification of marine plankton in response to increased atmospheric CO2. Nature 407:364–367
Riebesell U, Schulz KG, Bellerby RGJ, Botros M, Fritsche P, Meyerhöfer M, Neill C, Nondal G, Oschlies A, Wohlers J, Zöllner E (2007) Enhanced biological carbon consumption in a high CO2 ocean. Nature 450:545–554
Ries JB, Cohen AL, McCorkle DC (2009) Marine calcifiers exhibit mixed responses to CO2-induced ocean acidification. Geology 37:1131–1134
Rittmann A, Gottini V (1981) L’Isola d’Ischia. Geologia. Boll Servizio Geol It 101:131–274
Rodolfo-Metalpa R, Martin S, Ferrier-Pages C, Gattuso JP (2010a) Response of Mediterranean corals to ocean acidification. Biogeosci Discuss 6:7103–7131
Rodolfo-Metalpa R, Lombardi C, Cocito S, Hall-Spencer JM, Gambi MC (2010b) Effects of ocean acidification and high temperatures on the bryozoan Myriapora truncata at natural CO2 vents. Mar Ecol Evol Persp 31(3). doi:10.1111/j.1439-0485.2009.00354.x
Rouse GW, Gambi MC (1997) Cladistic relationships within Amphiglena Claparède (Polychaeta: Sabellidae) with a new species and a redescription of A. mediterranea (Leydig). J Nat Hist 31:999–1018
Russo GF, Fresi E, Vinci D, Chessa LA (1984a) Malacofauna di strato foliare delle praterie di Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile intorno all’isola d’Ischia (Golfo di Napoli): analisi strutturale del popolamento estivo in rapporto alla profondità ed alla esposizione. Nova Thalassia 6:655–661
Russo GF, Fresi E, Vinci D, Chessa LA (1984b) Mollusk syntaxon of foliar stratum along a depth gradient in a Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile meadow: diel variability. In: Boudouresque C-F, Jeudy de Grissac A, Olivier J (Eds) GIS Posidonie publ Fr 1:303–310
Sarà M (1959) Poriferi del litorale dell’isola d’Ischia e loro ripartizione per ambienti. Pubbl St Zool Napoli 31:421–472
Scipione MB (1999) Amphipod biodiversity in the foliar stratum of shallow-water Posidonia oceanica beds in the Mediterranean Sea. In: Schram FR, van Vaupel Kelin JC (eds) Crustacean and the Biodiversity Crisis. Brill, Leiden, pp 649–662
Seibel BA, Fabry VJ (2003) Marine biotic response to elevated carbon dioxide. Adv Appl Biodiv Sci 4:59–67
Tedesco D (1996) Chemical and isotopic investigation of fumarolic gases from Ischia Island (Southern Italy): evidence of magmatic and crustal contribution. J Vulcanol Geother Res 74:233–242
Thornton H, Shirayama Y (2001) III-1 Effects on benthic organisms. In: CO2 ocean sequestration and its biological impacts. Bull Jpn Soc Sci Fish 67(4):756–757
Vezina AF, Hoegh-Guldberg O (Coordinators) (2008) Effects of ocean acidification on marine ecosystems. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 373:199–309
Widdicombe S, Needham HR (2007) Impact of CO2-induced seawater acidification on the burrowing activity of Nereis virens and sediment nutrient flux. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 341:111–122
Wood HL, Spicer JI, Widdicombe S (2008) Ocean acidification may increase calcification rates, but at a cost. Proc R Soc Lond 275B:1767–1773
Zeebe RE, Wolf-Gladrow D (2001) CO2 in seawater: equilibrium, kinetics, isotopes. In: Halpern D (ed) Elsevier oceanography series, Series 65. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to MC Buia and the staff of the benthic ecology group of the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn, located at Villa Dohrn (Ischia), for support in the laboratory and at sea. We are also indebted to E Vecchi (foraminiferans), MB Scipione (amphipods) and M Lorenti (isopods and tanaids) for the identification of some of the benthic taxa. C Vasapollo helped with the statistical analyses. The captain V Rando and B Iacono supported the work at sea. We also thank two anonymous reviewers whose comments improved the Ms. This work is a contribution to the European Project on Ocean Acidification (EPOCA FP7/2007-2013 grant agreement no 211384) and was partly funded by the Save Our Seas Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Bulleri.
M. Cigliano and M. C. Gambi contributed equally.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cigliano, M., Gambi, M.C., Rodolfo-Metalpa, R. et al. Effects of ocean acidification on invertebrate settlement at volcanic CO2 vents. Mar Biol 157, 2489–2502 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-010-1513-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-010-1513-6