Abstract
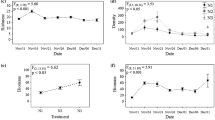
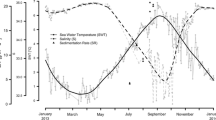
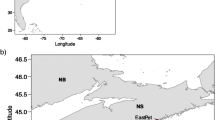
Secondary production of a macrobenthic community at an intertidal mudflat was estimated for 33 successive months. Sampling was carried out along a eutrophication gradient, including non-eutrophied Zostera meadows, an intermediate muddy area, and a strongly eutrophied sand-muddy flat, where macroalgal blooms of Enteromorpha spp. usually occur. The Zostera meadows were always the most productive habitat (145–225 g ash-free dry weight m−2 year−1). In the short term, the macroalgal bloom benefited the total estuarine production by enhancing the annual production in the eutrophied area. Nevertheless, our results show that this increase was short lived and in no way sufficient to match the production in the Zostera meadows. In the long term, the present study provides evidence that the disappearance of macrophyte beds, as a result of ongoing eutrophication, constitutes a major threat to the sustainability of the estuarine ecosystem.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarnio K, Matilla J (2000) Predation by juvenile Platichthys flesus (L.) on shelled prey species in a bare sand and a drift algae habitat. Hydrobiologia 440:347–355
Aníbal JMC (1998) Impacte da macroepifauna sobre as macroalgas Ulvales (Chlorophyta) na ria Formosa. MSc thesis, University of Coimbra, Portugal
Arias AM, Drake P (1994) Structure and production of the benthic macroinvertebrate community in a shallow lagoon in the Bay of Cádiz. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 115:151–167
Asmus H, Asmus R (1985) The importance of grazing food chain for energy flow and production in three intertidal sand bottom communities of the northern Wadden Sea Field. Helgol Meeresunters 39:273–301
Asmus H, Asmus R (2000) Material exchange and food web of seagrass beds in the Sylt-Romo Bight: how significant are community changes at the ecosystem level? Helgol Mar Res 54(2–3):137–150
Bachelet G (1982) Quelques problèmes liés à l'estimation de la production secondaire. Cas des bivalves Macoma balthica et Scrobicularia plana. Oceanol Acta 4(5):421–431
Bachelet G, De Montaudouin X, Auby I, Labourg PJ (2000) Seasonal changes in macrophyte and macrobethos assemblages in three coastal lagoons under varying degrees of eutrophication. J Mar Sci 57:1495–1506
Beukema JJ, Cadée GC, Dekker R (2002) Zoobenthic biomass limited by phytoplankton abundance: evidence from parallel changes in two long-term data series in the Wadden Sea. J Sea Res 48:111–125
Boaventura D, Fonseca LC da, Teles-Ferreira CM (1999) Trophic structure of macrobenthic communities on the Portuguese coast. A review of lagoonal, estuarine and rocky littoral habitats. Acta Oecol 20(4):407–415
Cabral JA, Pardal MA, Lopes RJ, Múrias T, Marques JC (1999) The impact of macroalgal blooms on the use of the intertidal area and feeding behaviour of waders (Charadrii) in the Mondego estuary (west Portugal). Acta Oecol 20(4):417–427
Cardoso PG, Lillebø AI, Pardal MA, Ferreira SM, Marques JC (2002) The effects of different primary producers on Hydrobia ulvae population dynamics: a case study in a temperate intertidal estuary. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 277(2):173–195
Cloern JE (2001) Our evolving conceptual model of coastal eutrophication problem. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 210:223–253
Edgar GJ (1990) The use of size structure of benthic macrofaunal communities to estimate faunal biomass and secondary production. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 137:195–214
Edgar GJ, Shaw C, Watson GF, Hammond LS (1994) Comparisons of species richness, size-structure and production of benthos in vegetated and unvegetated habitats in Western Port, Victoria. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 176:201–226
Ferreira SMFF (2001) Impacto da eutrofização em Cyathura carinata (Isopoda), no estuário do Mondego. MSc thesis, University of Coimbra, Portugal
Flindt MR, Pardal MA, Lillebø AI, Martins I, Marques JC (1999) Nutrient cycling and plant dynamics in estuaries: a brief review. Acta Oecol 20(4):237–248
Heck KL, Able KW, Roman CT, Fahay MP (1995) Composition, abundance, biomass, and production of macrofauna in a New England estuary—comparisons among eelgrass meadows and other nursery habitats. Estuaries 18(2):379–389
Jorge I, Monteiro CC, Lasserre G (2002) Fish community of Mondego estuary: space-temporal organisation. In: Pardal MA, Marques JM, Graça M (eds) Aquatic ecology of the Mondego river basin. Global importance of local experience. Imprensa da Universidade, Coimbra, Portugal, pp 199–217
Jørgensen BB, Richardson K (1996) Eutrophication in coastal marine ecosystems. American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C.
Levin LA, Boesch DF, Covich A, Dahm C, Erséus C, Ewel KC, Kneib RT, Moldenke A, Palmer MA, Snelgrove P, Strayer D, Weslawski JM (2001) The function of marine critical transition zones and the importance of sediment biodiversity. Ecosystems 4:430–451
Lillebø AI, Pardal MA, Marques JC (1999) Population structure, dynamics and production of Hydrobia ulvae (Pennant) (Mollusca: Prosobranchia) along an eutrophication gradient in the Mondego estuary (Portugal). Acta Oecol 20(4):289–304
Lopes RJ, Pardal MA, Marques JC (2000) Impact of macroalgal blooms and wader predation on intertidal macroinvertebrates: experimental evidence from the Mondego estuary (Portugal). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 249:165–179
Marques JC, Martins I, Teles-Ferreira C, Cruz S (1994) Population dynamics, life history, and production of Cyathura carinata (Krøyer) (Isopoda: Anthuridae) in the Mondego estuary, Portugal. J Crustac Biol 14(2):259–272
Marques JC, Pardal MA, Nielsen SN, Jørgensen SE (1997) Analysis of the properties of exergy and biodiversity along an estuarine gradient of eutrophication. Ecol Model 102:155–167
Martins I, Pardal MA, Lillebø AI, Flindt MR, Marques JC (2001) Hydrodynamics as a major factor controlling the occurrence of green macroalgal blooms in a eutrophic estuary: a case study on the influence of precipitation and river management. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 52:165–177
Martins I, Pardal MA, Metelo I, Neto JM, Oliveira JM, Marques JC (2002) Enteromorpha spp. (Ulvales: Chlorophyta) growth in the south arm of the Mondego estuary: field growth rates with and without macrofaunal grazer effects. In: Pardal MA, Marques JM, Graça M (eds) Aquatic ecology of the Mondego river basin. Global importance of local experience. Imprensa da Universidade, Coimbra, Portugal, pp 301–312
Mistri M, Rossi R, Fano EA (2001) Structure and secondary production of a soft bottom macrobenthic community in a brackish lagoon (Sacca di Goro, north-eastern Italy). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 52:605–616
Múrias T, Cabral JA, Lopes I, Marques JC (2002) Effects of eutrophication on waders (Aves: Charadrii) in the Mondego estuary: a multi-level approach. In: Pardal MA, Marques JM, Graça M (eds) Aquatic ecology of the Mondego river basin. Global importance of local experience. Imprensa da Universidade, Coimbra, Portugal, pp 527–540
Norkko A, Bonsdorff E (1996) Rapid zoobenthic community responses to accumulations of drifting algae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 131:143–157
Norkko J, Bonsdorff E, Norkko A (2000) Drifting algal mats as an alternative habitat for benthic invertebrates: species responses to a transient resource. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 248:79–104
Pardal MA (1998) Impacto da eutrofização nas comunidades macrobentónicas do braço sul do estuário do Mondego (Portugal). PhD thesis, University of Coimbra, Portugal
Pardal MA, Marques JC, Metelo I, Lillebø AI, Flindt MR (2000) Impact of eutrophication on the life cycle, population dynamics and production of Amphitoe valida (Amphipoda) along an estuarine spatial gradient (Mondego estuary, Portugal). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 196:207–219
Pardal MA, Marques JC, Metelo I, Lillebø AI, Flindt MR (2002) Impact of eutrophication on amphipods Melita palmata and Ampithoe valida in the Mondego estuary. In: Pardal MA, Marques JM, Graça M (eds) Aquatic ecology of the Mondego river basin. Global importance of local experience. Imprensa da Universidade, Coimbra, Portugal, pp 457–472
Raffaelli D (1999) Nutrient enrichment and trophic organisation in an estuarine food web. Acta Oecol 20(4):449–461
Raffaelli D, Milne H (1987) An experimental investigation of the effects of shorebirds and flatfish predation on estuarine invertebrates. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 24:1–13
Raffaelli DG, Raven JA, Poole LJ (1998) Ecological impact of green macroalgal blooms. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 36:97–125
Robertson AI (1979) The relationship between annual production, biomass ratios and lifespans for marine macrobenthos. Oecologia 38:193–202
Sardá R, Foreman K, Valiela I (1995) Macroinfauna of a Southern New England salt marsh: seasonal dynamics and production. Mar Biol 121:431–445
Sprung M (1993) Estimating macrobenthinc secondary production from body weight and biomass: a field test in a non-boreal intertidal habitat. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 100:103–109
Sprung M (1994) Macrobenthic secondary production in the intertidal zone of Ria Formosa—a lagoon in southern Portugal. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 38:539–558
Tumbiolo ML, Downing J (1994) An empirical model for the prediction of secondary production in marine benthic invertebrate populations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 114:165–174
Winberg GG (1971) Methods for the estimating of production of aquatic animals. Academic Press, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S.A. Poulet, Roscoff
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dolbeth, M., Pardal, M.A., Lillebø, A.I. et al. Short- and long-term effects of eutrophication on the secondary production of an intertidal macrobenthic community. Marine Biology 143, 1229–1238 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-003-1133-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-003-1133-5