Abstract
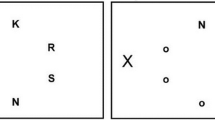
Previous studies have used analogy completion tasks (e.g., abe is to abf as ijk is to what?) to examine the event-related potential (ERP) parameters of analogical reasoning. In the present study, ERP responses to analogies were investigated using an analogy comparison task (e.g., is abe to abf as ijk is to ijl?), with a focus on structural evaluation. The results showed that the identical match task elicited an N2 component with smaller amplitude than that of the N2 component in the zero- and one-step consistent analogies, reflecting automatic match detection. The data also showed that there were significant differences in the N400 during the consistent and inconsistent analogies, which may reflect a delayed perceptual mismatch with semantic strategies. Moreover, one-step consistent analogies evoked smaller late positive component (LPC) amplitudes than that evoked by identical match or zero-step consistent analogies in the 500- to 800-ms time interval, and one-step inconsistent analogies elicited smaller amplitude LPCs than that elicited by zero-step inconsistent analogies in the 500- to 750-ms time interval, which suggested that LPCs reflected structure evaluation in analogy comparison tasks.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett MA, Duke PA, Fuggetta G (2014) Event-related potential N270 delayed and enhanced by the conjunction of relevant and inrelevant perceptual match. Psychophysiology 51:456–463
Bigman Z, Pratt H (2004) Time course and nature of stimulus evaluation in category induction as revealed by visual event-related potentials. Biol Psychol 66:99–127
Bonnefond M, Van der Henst J (2009) What’s behind an inference? An EEG study with conditional arguments. Neuropsychologia 47:3125–3133
Bonnefond M, Van der Henst J (2013) Deduction electrified: eRPs elicited by the processing of words in conditional arguments. Brain Lang 124:244–256
Bonnefond M, Kaliuzhna M, Van der Henst J (2014) Disabling conditional inferences: an EEG study. Neuropsychologia 56:255–262
Bunge SA, Wendelken C, Badre D, Wagner AD (2005) Analogical reasoning and prefrontal cortex: evidence for separable retrieval and integration mechanisms. Cereb Cortex 15:239–249
Chen A, Luo Y, Wang Q, Yuan J, Yao D, Li H (2007) Electrophysiological correlates of category induction: PSW amplitude as an index of identifying shared attributes. Biol Psychol 76:230–238
Donchin E (1981) Surprise!. Surprise? Psychophysiology 18:493–513
Dunbar K, Blachette I (2001) The in vivo/in vitro approach to cognition: the case of analogy. Trends Cognit Sci 5:334–339
Folstein JR, Petten CV (2008) Influence of cognitive control and mismatch on the N2 component of the ERP: a review. Psychophysiology 45:152–170
Friederici AD (2011) The brain basis of language processing: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 91(4):1357–1392
Geake JG, Hansen PC (2005) Neural correlates of intelligence as revealed by fMRI of fluid analogies. Neuroimage 26:555–564
Gentner D (1983) Structure-mapping: a theoretical framework for analogy. Cognit Sci 7:155–170
Gentner D, Forbus K (2011) Computational models of analogy. WIREs Cognit Sci 2:266–276
Gentner D, Smith L (2012) Analogical reasoning. In: Ramachandran VS (ed) Encyclopedia of Human Behavior 2nd edn. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 130–136
Green AE, Fugelsang JA, Kraemer DJ, Shamosh NA, Dunbar KN (2006) Frontopolar cortex mediates abstract integration in analogy. Brain Res 1096:125–137
Green AE, Kraeme DJM, Fugelsang JA, Gray JR, Dunbar KN (2010) Connecting long distance: semantic distance in analogical reasoning modulates frontopolar cortex activity. Cereb Cortex 20:70–76
Hillyard SA, Kutas M (1983) Electrophysiology of cognitive processing. Annu Rev Psychol 34:33–61
Holcomb PJ (1993) Semantic priming and stimulus degradation: implications for the role of the N400 in language processing. Psychophysiology 30:47–61
Holyoak KJ (2012) Analogy and relational reasoning. In: Holyoak KJ, Morrison RG (eds) The Oxford handbook of thinking and reasoning. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 234–259
Holyoak KJ, Thagard P (1997) The analogical mind. Am Psychol 52:35–44
Jani NG, Levine DS (2000) A neural network theory of proportional analogy-making. Neural Netw 13:149–183
Kok A (2001) On the utility of P3 amplitude as a measure of processing capacity. Psychophysiology 38:557–577
Krawczyk DC (2012) The cognition and neuroscience of relational reasoning. Brain Res 1428:13–23
Kutas M, Federmeier KD (2000) Electrophysiology reveals semantic memory use in language comprehension. Trends Cognit Sci 4:463–470
Kutas M, Federmeier KD (2011) Thirty years and counting: finding meaning in the N400 component of the event-related brain potential (ERP). Annu Rev Psychol 62:621–647
Kutas M, McCarthy G, Donchin E (1977) Augmenting mental chronometry: the P300 as a measure of stimulus evaluation time. Science 197:792–795
Lelekov T, Dominey PF, García-Larrea L (2000) Dissociable ERP profiles for processing rules vs instance in a cognitive sequence task. NeuroReport 11:1129–1132
Lelekov-Boissard T, Dominey PF (2002) Human brain potentials reveal similar processing of non-linguistic abstract structure and linguistic syntactic structure. Clin Neurophysiol 32:72–84
Luck SJ (ed) (2005) An introduction to event-related potentials and their neural origins. In: An Introduction to the Event-Related Potential Technique. MIT Press, Cambridge, p 107
Luck SJ, Hillyard SA (1995) The role of attention in feature detection and conjunction discrimination: an electrophysiological analysis. Int J Neurosci 80:281–297
Maguire MJ, McClelland MM, Donovan CM, Tillman GD, Krawczyk DC (2012) Tracking cognitive phases in analogical reasoning with event-related potentials. J Exp Psychol : Learn Mem Cognit 38:273–281
Mangun GR (1995) Neural mechanisms of visual selective attention. Psychophysiology 32:4–18
Markman AB, Gentner D (2000) Structure mapping in the comparison process. Am J Psychol 113:501–538
McCarthy G, Donchin E (1981) A metric for thought: a comparison of P300 latency and reaction time. Science 211:77–80
Núñez-Peña MI, Honrubia-Serrano ML (2004) P600 related to rule violation in an arithmetic task. Cognit Brain Res 18:130–141
Pardo J, Kaliuzhna M, Cheylus A, Noveck IA (2008) Overcoming perceptual features in logical reasoning: an event-related potentials study. Neuropsychologia 46:2629–2637
Petit J-P, Midgley KJ, Holcomb PJ, Grainger J (2006) On the time course of letter perception: a masked priming ERP investigation. Psychon Bull Rev 13:674–681
Polich J (2007) Updating P300: an integrative theory of P3a and P3b. Clin Neurophysiol 118:2128–2148
Qiu J, Li H, Chen AT, Zhang QL (2008) The neural basis of analogical reasoning: an event-related potential study. Neuropsychologia 46:3006–3013
Szucs D, Soltesz F, Czigler I, Csepe V (2007) Electroencephalography effects to semantic and non-semantic mismatch in properties of visually presented single-characters: the N2b and the N400. Neurosci Lett 412:18–23
Wang Y, Tian S, Wang H, Cui L, Zhang Y, Zhang X (2003) Event-related potentials evoked by multi-feature conflict under different attentive conditions. Exp Brain Res 148:451–457
Wang Y, Cui L, Wang H, Tian S, Zhang X (2004) The sequential processing of visual feature conjunction mismatches in the human brain. Psychophysiology 41:21–29
Wendelken C, Nakhabenko D, Donohue SE, Carter CS, Bunge SA (2008) “Brain is to thought as stomach is to??”: investigating the role of rostrolateral prefrontal cortex in relational reasoning. J Cognit Neurosci 20(4):682–693
Wharton CM, Grafman J, Flitman SS, Hansen EK, Brauner J, Marks A, Honda M (2000) Toward neuroanatomical models of analogy: a positron emission tomography study of analogical mapping. Cognit Psychol 40:173–197
Zhang X, Wang Y, Li S, Wang L (2003) Event-related potential N270, a negative component to identification of conflicting information following memory retrieval. Clin Neurophysiol 114:2461–2468
Zhao M, Meng HS, Xu ZY, Du FL, Liu T, Li YX, Chen FY (2011) The neuromechanism underlying verbal analogical reasoning of metaphorical relations: an event-related potentials study. Brain Res 1425:62–74
Zhao M, Xu ZY, Liu T, Du FL, Li YX, Chen FY (2012) The Neuromechanism underlying language analogical reasoning: evidence from an ERP study. Acta Psychol Sinica 44:711–719
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31200780 and 31300866) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SWU1309002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Long, C., Li, J., Chen, A. et al. Event-related potential responses to letter-string comparison analogies. Exp Brain Res 233, 1563–1573 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4230-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-015-4230-z