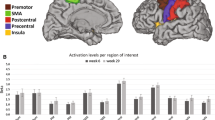
Abstract
Motor imagery (MI - i.e., the mental representation of an action without physically executing it) stimulates brain motor networks and promotes motor learning after spinal cord injury (SCI). An interesting issue is whether the brain networks controlling MI are being reorganized with reference to spared motor functions. In this pilot study, we tested using magnetoencephalography (MEG) whether changes in cortical recruitment during MI were related to the motor changes elicited by rehabilitation. Over a 1-year period of inclusion, C6 SCI participants (n = 4) met stringent criteria for inclusion in a rehabilitation program focused on the tenodesis prehension (i.e., a compensatory prehension enabling seizing of objects in spite of hand and forearm muscles paralysis). After an extended baseline period of 5 weeks including repeated MEG and chronometric assessments of motor performance, MI training was embedded to the classical course of physiotherapy for five additional weeks. Posttest MEG and motor performance data were collected. A group of matched healthy control participants underwent a similar procedure. The MI intervention resulted in changes in the variability of the wrist extensions, i.e., a key movement of the tenodesis grasp (p < .05). Interestingly, the extent of cortical recruitment, quantified by the number of MEG activation sources recorded within Brodmann areas 1–8 during MI of the wrist extension, significantly predicted actual movement variability changes across sessions (p < .001). However, no such relationship was present for movement times. Repeated measurements afforded a reliable statistical power (range .70–.97). This pilot study does not provide straightforward evidence of MI efficacy, which would require a randomized controlled trial. Nonetheless, the data showed that the relationship between action and imagery of spared actions may be preserved after SCI.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For a figure of raw MEG and motor performance data plotted as in Fig. 5, see supplementary material 3.
Hence, including a group healthy participants performing MI represents further development of the present design.
References
Alkadhi H, Brugger P, Boendermaker SH, Crelier G, Curt A, Hepp-Reymond MC, Kollias SS (2005) What disconnection tells about motor imagery: evidence from paraplegic patients. Cereb Cortex 15(2):131–140. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhh116
Baguley T (2012) Serious stats: a guide to advanced statistics for the behavioral sciences. Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2014) lme4: linear mixed-effects models using Eigen and S4. R package version 1.0-6. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lme4
Burianova H, Marstaller L, Sowman P, Tesan G, Rich AN, Williams M, Savage G, Johnson BW (2013) Multimodal functional imaging of motor imagery using a novel paradigm. NeuroImage. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.01.001
Chang Y, Lee JJ, Seo JH, Song HJ, Kim YT, Lee HJ, Kim HJ, Lee J, Kim W, Woo M, Kim JG (2011) Neural correlates of motor imagery for elite archers. NMR Biomed 24(4):366–372. doi:10.1002/nbm.1600
Cox RW (1996) AFNI: software for analysis and visualization of functional magnetic resonance neuroimages. Comput Biomed Res 29(3):162–173
Cramer SC, Orr EL, Cohen MJ, Lacourse MG (2007) Effects of motor imagery training after chronic, complete spinal cord injury. Exp Brain Res 177(2):233–242. doi:10.1007/s00221-006-0662-9
Curt A, Van Hedel HJ, Klaus D, Dietz V (2008) Recovery from a spinal cord injury: significance of compensation, neural plasticity, and repair. J Neurotrauma 25(6):677–685. doi:10.1089/neu.2007.0468
Davids K, Bennett S, Newell KM (2006) Movement system variability. Human Kinetics Publishers, Champaign
Debarnot U, Sperduti M, Di Rienzo F, Guillot A (2014) Experts bodies, experts minds: how physical and mental training shape the brain. Front Hum Neurosci 8:280. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2014.00280
Di Rienzo F, Guillot A, Daligault S, Delpuech C, Rode G, Collet C (2013) Motor inhibition during motor imagery: a MEG study with a quadriplegic patient. Neurocase. doi:10.1080/13554794.2013.826685
Di Rienzo F, Collet C, Hoyek N, Guillot A (2014a) Impact of neurologic deficits on motor imagery: a systematic review of clinical evaluations. Neuropsychol Rev. doi:10.1007/s11065-014-9257-6
Di Rienzo F, Guillot A, Mateo S, Daligault S, Delpuech C, Rode G, Collet C (2014b) Neuroplasticity of prehensile neural networks after quadriplegia. Neuroscience. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.05.021
Dobkin BH (1993) Neuroplasticity. Key to recovery after central nervous system injury. West J Med 159(1):56–60
Eckert HM (1974) Variability in skill acquisition. Child Dev 45(2):487–489
Grangeon M, Guillot A, Sancho PO, Picot M, Revol P, Rode G, Collet C (2010) Rehabilitation of the elbow extension with motor imagery in a patient with quadriplegia after tendon transfer. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 91(7):1143–1146. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2010.04.011
Grangeon M, Revol P, Guillot A, Rode G, Collet C (2012) Could motor imagery be effective in upper limb rehabilitation of individuals with spinal cord injury? A case study. Spinal Cord 50(10):766–771. doi:10.1038/sc.2012.41
Green JB, Sora E, Bialy Y, Ricamato A, Thatcher RW (1998) Cortical sensorimotor reorganization after spinal cord injury: an electroencephalographic study. Neurology 50(4):1115–1121. doi:10.1212/WNL.50.4.1115
Green JB, Sora E, Bialy Y, Ricamato A, Thatcher RW (1999) Cortical motor reorganization after paraplegia: an EEG study. Neurology 53(4):736–743. doi:10.1212/WNL.53.4.736
Guillot A, Collet C, Nguyen VA, Malouin F, Richards C, Doyon J (2008) Functional neuroanatomical networks associated with expertise in motor imagery. NeuroImage 41(4):1471–1483. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.042
Guillot A, Di Rienzo F, Macintyre T, Moran A, Collet C (2012) Imagining is not doing but involves specific motor commands: a review of experimental data related to motor inhibition. Front Hum Neurosci 6:1–22. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2012.00247
Hoffmann G, Laffont I, Roby-Brami A (2002) Coordination of reaching movements in patients with a cervical spinal cord injury. Cahiers de psychologie cognitive 21:305–340
Hoffmann G, Laffont I, Hanneton S, Roby-Brami A (2006) How to extend the elbow with a weak or paralyzed triceps: control of arm kinematics for aiming in C6–C7 quadriplegic patients. Neuroscience 139(2):749–765. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.12.018
Holm S (1979) A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure. Scand J Stat 6:65–70. doi:10.2307/4615733
Hotz-Boendermaker S, Funk M, Summers P, Brugger P, Hepp-Reymond MC, Curt A, Kollias SS (2008) Preservation of motor programs in paraplegics as demonstrated by attempted and imagined foot movements. NeuroImage 39(1):383–394. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.07.065
Jackson PL, Lafleur MF, Malouin F, Richards CL, Doyon J (2003) Functional cerebral reorganization following motor sequence learning through mental practice with motor imagery. NeuroImage 20(2):1171–1180. doi:10.1016/s1053-8119(03)00369-0
Jeannerod M (1994) The representing brain: neural correlates of motor intention and imagery. Behav Brain Sci 17(02):187–202. doi:10.1017/S0140525X00034026
Jeannerod M (2001) Neural simulation of action: a unifying mechanism for motor cognition. NeuroImage 14(1 Pt 2):S103–S109. doi:10.1006/nimg.2001.0832
Jeannerod M, Frak V (1999) Mental imaging of motor activity in humans. Curr Opin Neurobiol 9(6):735–739
Jurkiewicz MT, Mikulis DJ, McIlroy WE, Fehlings MG, Verrier MC (2007) Sensorimotor cortical plasticity during recovery following spinal cord injury: a longitudinal fMRI study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 21(6):527–538. doi:10.1177/1545968307301872
Kakulas BA (2004) Neuropathology: the foundation for new treatments in spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 42(10):549–563. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3101670
Kokotilo KJ, Eng JJ, Curt A (2009) Reorganization and preservation of motor control of the brain in spinal cord injury: a systematic review. J Neurotrauma 26(11):2113–2126. doi:10.1089/neu.2008.0688
Lacourse MG, Turner JA, Randolph-Orr E, Schandler SL, Cohen MJ (2004) Cerebral and cerebellar sensorimotor plasticity following motor imagery-based mental practice of a sequential movement. J Rehabil Res Dev 41(4):505–524
Laffont I, Briand E, Dizien O, Combeaud M, Bussel B, Revol M, Roby-Brami A (2000) Kinematics of prehension and pointing movements in C6 quadriplegic patients. Spinal Cord 38(6):354–362
Levy WJ Jr, Amassian VE, Traad M, Cadwell J (1990) Focal magnetic coil stimulation reveals motor cortical system reorganized in humans after traumatic quadriplegia. Brain Res 510(1):130–134. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(90)90738-w
Lopes da Silva FH (2010) Electrophysiological basis of MEG signals. In: Hansen PC, Kringelbach ML, Salmelin R (eds) MEG. An introduction to methods. Oxford university press, New York, pp 1–23
Lotze M, Halsband U (2006) Motor imagery. J Physiol Paris 99(4–6):386–395. doi:10.1016/j.jphysparis.2006.03.012
Lotze M, Montoya P, Erb M, Hulsmann E, Flor H, Klose U, Birbaumer N, Grodd W (1999) Activation of cortical and cerebellar motor areas during executed and imagined hand movements: an fMRI study. J Cogn Neurosci 11(5):491–501. doi:10.1162/089892999563553
Louis M, Guillot A, Maton S, Doyon J, Collet C (2008) Effect of imagined movement speed on subsequent motor performance. J Mot Behav 40(2):117–132. doi:10.3200/JMBR.40.2.117-132
Malouin F, Richards CL (2010) Mental practice for relearning locomotor skills. Phys Ther 90(2):240–251. doi:10.2522/ptj.20090029
Malouin F, Richards CL, Jackson PL, Lafleur MF, Durand A, Doyon J (2007) The Kinesthetic and Visual Imagery Questionnaire (KVIQ) for assessing motor imagery in persons with physical disabilities: a reliability and construct validity study. J Neurol Phys Ther 31(1):20–29. doi:10.1097/01.NPT.0000260567.24122.64
Malouin F, Jackson PL, Richards CL (2013) Towards the integration of mental practice in rehabilitation programs. A critical review. Front Hum Neurosci. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2013.00576
Mateo S, Revol P, Fourtassi M, Rossetti Y, Collet C, Rode G (2013) Kinematic characteristics of tenodesis grasp in C6 quadriplegia. Spinal Cord 51(2):144–149. doi:10.1038/sc.2012.101
Maynard FM Jr, Bracken MB, Creasey G, Ditunno JF Jr, Donovan WH, Ducker TB, Garber SL, Marino RJ, Stover SL, Tator CH, Waters RL, Wilberger JE, Young W (1997) International standards for neurological and functional classification of spinal cord injury. American Spinal Injury Association. Spinal Cord 35(5):266–274. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3100432
Milton J, Solodkin A, Hlustik P, Small SL (2007) The mind of expert motor performance is cool and focused. NeuroImage 35(2):804–813. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.01.003
Müller H, Sternad D (2004) Decomposition of variability in the execution of goal-oriented tasks: three components of skill improvement. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 30(1):212–233. doi:10.1037/0096-1523.30.1.212
Munzert J, Lorey B, Zentgraf K (2009) Cognitive motor processes: the role of motor imagery in the study of motor representations. Brain Res Rev 60(2):306–326. doi:10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.12.024
Nardone R, Holler Y, Brigo F, Seidl M, Christova M, Bergmann J, Golaszewski S, Trinka E (2013) Functional brain reorganization after spinal cord injury: systematic review of animal and human studies. Brain Res 1504:58–73. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2012.12.034
Neuper C, Pfurtscheller G (2010) Electroencephalographic characteristics during motor imagery. In: Guillot A, Collet C (eds) The neurophysiological foundations of mental and motor imagery. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 65–81
Page SJ, Szaflarski JP, Eliassen JC, Pan H, Cramer SC (2009) Cortical plasticity following motor skill learning during mental practice in stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 23(4):382–388. doi:10.1177/1545968308326427
Pascual-Leone A, Nguyet D, Cohen LG, Brasil-Neto JP, Cammarota A, Hallett M (1995) Modulation of muscle responses evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation during the acquisition of new fine motor skills. J Neurophysiol 74(3):1037–1045
Pfurtscheller G (2000) Spatiotemporal ERD/ERS patterns during voluntary movement and motor imagery. Suppl Clin Neurophysiol 53:196–198
Pfurtscheller G (2001) Functional brain imaging based on ERD/ERS. Vision Res 41(10–11):1257–1260. doi:10.1016/S0042-6989(00)00235-2
Pfurtscheller G, Lopes da Silva FH (1999) Event-related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization: basic principles. Clin Neurophysiol 110(11):1842–1857. doi:10.1016/s1388-2457(99)00141-8
Pfurtscheller G, Neuper C, Brunner C, da Silva FL (2005) Beta rebound after different types of motor imagery in man. Neurosci Lett 378(3):156–159. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2004.12.034
Porro CA, Francescato MP, Cettolo V, Diamond ME, Baraldi P, Zuiani C, Bazzocchi M, di Prampero PE (1996) Primary motor and sensory cortex activation during motor performance and motor imagery: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurosci 16(23):7688–7698
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Ranganathan VK, Siemionow V, Liu JZ, Sahgal V, Yue GH (2004) From mental power to muscle power–gaining strength by using the mind. Neuropsychologia 42(7):944–956. doi:10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2003.11.018
Rickham PP (1964) Human experimentation. Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki. Br Med J 2(5402):177
Robinson SE (2004) Localization of event-related activity by SAM(erf). Neurol Clin Neurophysiol 2004:109
Ross JS, Tkach J, Ruggieri PM, Lieber M, Lapresto E (2003) The mind’s eye: functional MR imaging evaluation of golf motor imagery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24(6):1036–1044
Sabbah P, de Schonen S, Leveque C, Gay S, Pfefer F, Nioche C, Sarrazin JL, Barouti H, Tadie M, Cordoliani YS (2002) Sensorimotor cortical activity in patients with complete spinal cord injury: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurotrauma 19(1):53–60. doi:10.1089/089771502753460231
Schlesinger I, Benyakov O, Erikh I, Suraiya S, Schiller Y (2009) Parkinson’s disease tremor is diminished with relaxation guided imagery. Mov Disord 24(14):2059–2062. doi:10.1002/mds.22671
Schmidt RA, Lee T (1988) Motor control and learning, 5th edn. Human Kinetics. Champaign, IL. ISBN:1450412297
Schmidt RA, Wrisberg CA (2004) Motor learning and performance, 3rd edn. Human Kinetics. Champaign, IL. ISBN:0-7360-6964-X
Schuster C, Hilfiker R, Amft O, Scheidhauer A, Andrews B, Butler J, Kischka U, Ettlin T (2011) Best practice for motor imagery: a systematic literature review on motor imagery training elements in five different disciplines. BMC Med 9:75. doi:10.1186/1741-7015-9-75
Snoek GJ, IJzerman MJ, Hermens HJ, Maxwell D, Biering-Sorensen F (2004) Survey of the needs of patients with spinal cord injury: impact and priority for improvement in hand function in tetraplegics. Spinal Cord 42(9):526–532. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3101638
Subramanian L, Hindle JV, Johnston S, Roberts MV, Husain M, Goebel R, Linden D (2011) Real-time functional magnetic resonance imaging neurofeedback for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 31(45):16309–16317. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.3498-11.2011
Sun L, Yin D, Zhu Y, Fan M, Zang L, Wu Y, Jia J, Bai Y, Zhu B, Hu Y (2013) Cortical reorganization after motor imagery training in chronic stroke patients with severe motor impairment: a longitudinal fMRI study. Neuroradiology. doi:10.1007/s00234-013-1188-z
Tadel F, Baillet S, Mosher JC, Pantazis D, Leahy RM (2011) Brainstorm: a user-friendly application for MEG/EEG analysis. Comput Intell Neurosci 2011:879716. doi:10.1155/2011/879716
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988) Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain: 3-dimensional proportional System—an approach to cerebral imaging. Thieme Medical Publishers, New York
Tamir R, Dickstein R, Huberman M (2007) Integration of motor imagery and physical practice in group treatment applied to subjects with Parkinson’s disease. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 21(1):68–75. doi:10.1177/1545968306292608
Topka H, Cohen LG, Cole RA, Hallett M (1991) Reorganization of corticospinal pathways following spinal cord injury. Neurology 41(8):1276–1283. doi:10.1212/WNL.41.8.1276
Waters RL, Adkins RH, Yakura JS, Sie I (1993) Motor and sensory recovery following complete tetraplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 74(3):242–247
Winter B (2013) Linear models and linear mixed effects models in R with linguistic applications. arXiv:1308.5499
Wirth B, Van Hedel HJ, Curt A (2008) Changes in corticospinal function and ankle motor control during recovery from incomplete spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 25(5):467–478. doi:10.1089/neu.2007.0472
Yakura JS (1996) Recovery following spinal cord injury. American Rehabilitation. http://www.thefreelibrary.com/Recovery+following+spinal+cord+injury.-a019662789
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Grant from Hospital Clinical Research Program (PHRC) 2010-541/142. We gratefully acknowledge CC-IN2P3 through TIDRA (http://www.tidra.org) for providing a significant amount of computing resources and services needed for this work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Rienzo, F., Guillot, A., Mateo, S. et al. Neuroplasticity of imagined wrist actions after spinal cord injury: a pilot study. Exp Brain Res 233, 291–302 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-014-4114-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-014-4114-7