Abstract
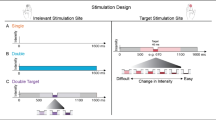
A number of perceptual and neurophysiological studies have investigated the effects of delivering unilateral versus bilateral tactile sensory stimulation. While a number of studies indicate that perceptual discrimination degrades with opposite-hand stimulation, there have been no reports that examined the digit specificity of cross-hemispheric interactions to discriminative capabilities. The purpose of this study was to determine whether unattended hand (UH) stimulation significantly degraded or improved amplitude discriminative capacity on the attended hand (AH) in a digit-specific manner. The methods are based on a sensory perceptual task (vibrotactile amplitude discriminative capacity on the tips of the fingers D2 and D3 of the left hand) in the absence and presence of conditioning stimuli delivered to D2 and D3 of the right hand. Non-specific equal-amplitude stimulation to D2 and D3 of the UH significantly worsened amplitude discrimination (AD) performance, while delivering unequal-amplitude stimuli to D2 and D3 of the UH worsened task performance only under the condition in which the unattended stimuli failed to appropriately match the stimulus parameters on the AH. Additionally, delivering single-site stimuli to D2 or D3 of the UH resulted in degraded performance on the AD task when the stimulus amplitude did not match the amplitude of the stimulus applied to homologous digits of the AH. The findings demonstrate that there is a reduction in performance under conditions where UH stimulation least matched stimulation applied to the AH, while there was little or no change in performance when stimulus conditions on the homologous digit(s) of the contralateral sites were similar. Results suggest that bilateral interactions influence perception in a context-dependent manner that is digit specific.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnea-Goraly N, Kwon H, Menon V, Eliez S, Lotspeich L, Reiss AL (2004) White matter structure in autism: preliminary evidence from diffusion tensor imaging. Biol Psychiatry 55:323–326
Blankenburg F, Ruff CC, Bestmann S, Bjoertomt O, Eshel N, Josephs O, Weiskopf N, Driver J (2008) Interhemispheric effect of parietal TMS on somatosensory response confirmed directly with concurrent TMS-fMRI. J Neurosci 28(49):13202–13208
Braun C, Hess H, Burkhardt M, Wühle A, Preissl H (2005) The right hand knows what the left hand is feeling. Exp Brain Res 162:366–373
Chiu JS, Tommerdahl M, Whitsel BL, Favorov OV (2005) Stimulus-dependent spatial patterns of response in SI cortex. BMC Neurosci 19(6):47
Cornsweet TN (1962) The staircase-method in psychophysics. Am J Psychol 75:485–491
Degreef G, Lantos G, Bogerts B, Ashtari M, Lieberman J (1992) Abnormalities of the septum pellucidum on MR scans in first-episode schizophrenia patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 13:835–840
Eickhoff SB, Grefkes C, Fink GR, Zilles K (2008) Functional lateralization of face, hand, and trunk representation in anatomically defined human somatosensory areas. Cereb Cortex 18(12):2820–2830
Eshel N, Ruff CC, Spitzer B, Blankenburg F, Driver J (2010) Effects of parietal TMS on somatosensory judgments challenge interhemispheric rivalry accounts. Neuropsychologia 48(12):3470–3481
Fabri M, Del Pesce M, Paggi A, Polonara G, Bartolini M, Salvolini U, Manzoni T (2005) Contribution of posterior corpus callosum to the interhemispheric transfer of tactile information. Cogn Brain Res 24:73–80
Folger SE, Tannan V, Zhang Z, Holden JK, Tommerdahl M (2008) Effects of the N-methyl-D-Aspartate receptor antagonist dextromethorphan on vibrotactile adaptation. BMC Neurosci 9:87
Francisco E, Tannan V, Zhang Z, Holden J, Tommerdahl M (2008) Vibrotactile amplitude discrimination capacity parallels magnitude changes in somatosensory cortex follows Weber’s Law. Exp Brain Res 191:49–56
Francisco E, Holden J, Zhang Z, Favorov O, Tommerdahl M (2011) Rate dependency of vibrotactile stimulus modulation. Brain Res 1415:76–83
Gröschel S, Sohns JM, Schmidt-Samoa C, Baudewig J, Becker L, Dechent P, Kastrup A (2013) Effects of age on negative BOLD signal changes in the primary somatosensory cortex. NeuroImage 71:10–18
Hardan AY, Pabalan M, Gupta N, Bansal R, Melhem NM, Fedorov S, Keshavan MS, Minshew NJ (2009) Corpus callosum volume in children with autism. Psychiatry Res 174:57–61
Heiss JE, Katz Y, Ganmor E, Lampl I (2008) Shift in balance between excitation and inhibition during sensory adaptation of S1 neurons. J Neurosci 28:13320–13330
Hlushchuk Y, Hari R (2006) Transient suppression of ipsilateral primary somatosensory cortex during tactile finger stimulation. J Neurosci 26:5819–5824
Holden JK, Nguyen RH, Francisco EM, Zhang Z, Dennis RG, Tommerdahl M (2011) A novel device for the study of somatosensory information processing. J Neurosci Methods 204:215–220
Hull C, Isaacson JS, Scanziani M (2009) Postsynaptic mechanisms govern the differential excitation of cortical neurons by thalamic inputs. J Neurosci 29:9127–9136
Hynd GW, Semrud-Clikeman M, Lorys AR, Novey ES, Eliopulos D, Lyytinen H (1991) Corpus callosum morphology in attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder: morphometric analysis of MRI. J Learn Disabil 24:141–146
Iwamura Y, Taoka M, Iriki A (2001) Bilateral activity and callosal connections in the somatosensory cortex. Neuroscientist 7:419–429
Jung P, Klein JC, Wibral M, Hoechstetter K, Bliem B, Lu M, Wahl M, Ziemann U (2012) Spatiotemporal dynamics of bimanual integration in human somatosensory cortex and their relevance to bimanual object manipulation. J Neurosci 32(16):5667–5677
Klingner CM, Hasler C, Brodoehl S, Witte OW (2012) Excitatory and inhibitory mechanisms underlying somatosensory habituation. Hum Brain Mapp 35(1):152–160
Levin HS, Benton AL (1973) A comparison of ipsilateral and contralateral effects of tactile masking. Am J Psychol 86:435–444
Lewis SW, Reveley MA, David AS, Ron MA (1988) Agenesis of the corpus callosum and schizophrenia: a case report. Psychol Med 18:341–347
Lipton ML, Fu KM, Branch CA, Schroeder CE (2006) Ipsilateral hand input to area 3b revealed by converging hemodynamic and electrophysiological analyses in macaque monkeys. J Neurosci 26:180–185
Nelson AJ, Premji A, Rai N, Hogue T, Tommerdahl M, Chen R (2012) Dopamine alters tactile perception in Parkinson’s disease. Can J Neurol Sci 39:52–57
Nguyen RH, Ford S, Calhoun AH, Holden JK, Gracely RH, Tommerdahl M (2013a) Neurosensory assessments of migraine. Brain Res 1498:50–58
Nguyen RH, Gillen C, Garbutt JC, Kampov-Polevoi A, Holden JK, Francisco EM, Tommerdahl M (2013b) Centrally-mediated sensory information processing is impacted with increased alcohol consumption in college-aged individuals. Brain Res 1492:53–62
Nihashi T, Naganawa S, Sato C, Kawai H, Nakamura T, Fukatsu H, Ishigaki T, Aoki I (2005) Contralateral and ipsilateral responses in primary somatosensory cortex following electrical median nerve stimulation—an fMRI study. Clin Neurophysiol 116:842–848
Palmer LM, Schulz JM, Murphy SC, Ledergerber D, Murayama M, Larkum ME (2012) The cellular basis of GABAB-mediated interhemispheric inhibition. Science 335:989–993
Pienkowski M, Hagerman B (2009) Auditory intensity discrimination as a function of level-rove and tone duration in normal-hearing and impaired subjects: the “mid-level hump” revisited. Hear Res 253:107–115
Premji A, Zapallow C, Tsang P, Tang R, Jacobs M, Nelson AJ (2011) Influence of area 5 on interhemispheric inhibition. Neuroreport 22(18):974–978
Puts NA, Edden RA, Wodka EL, Mostofsky SH, Tommerdahl M (2013) A vibrotactile behavioral battery for investigating somatosensory processing in children and adults. J Neurosci Methods 218(1):39–47
Ragert P, Nierhaus T, Cohen LG, Villringer A (2011) Interhemispheric interactions between the primary somatosensory cortices. PLoS One 6(2):e16150
Rai N, Premji A, Tommerdahl M, Nelson AJ (2012) Continuous theta-burst rTMS over primary somatosensory cortex modulates tactile perception on the hand. Clin Neurophysiol 123:1226–1233
Reed JL, Qi H, Kaas JH (2012) Spatiotemporal properties of neuron response suppression in owl monkey primary somatosensory cortex when stimuli are presented to both hands. J Neurosci 31:3589–3601
Schäfer K, Blankenburg F, Kupers R, Grüner JM, Law I, Lauritzen M, Larsson HBW (2012) Negative BOLD signal changes in ipsilateral primary somatosensory cortex are associated with perfusion decreases and behavioral evidence for functional inhibition. NeuroImage 59:3119–3127
Schweizer R, Maier M, Braun C, Birbaumer N (2000) Distributions of mislocalizations of tactile stimuli on the fingers of the human hand. Somatosens Mot Res 17:309–316
Schweizer R, Braun C, Fromm C, Wilms A, Birbaumer N (2001) The distribution of mislocalizations across fingers demonstrates training-induced neuroplastic changes in the somatosensory cortex. Exp Brain Res 139:435–442
Simons SB, Chiu J, Favorov OV, Whitsel BL, Tommerdahl M (2007) Duration-dependent response of SI to vibrotactile stimulation in squirrel monkey. J Neurophys 97:2121–2129
Swayze VW II, Andreasen NC, Ehrhardt JC, Yuh WT, Alliger RJ, Cohen GA (1990) Developmental abnormalities of the corpus callosum in schizhophrenia. Arch Neurol 47:805–808
Tannan V, Dennis R, Tommerdahl M (2005) Stimulus-dependent effects on tactile spatial acuity. Behav Brain Funct 1:18
Tannan V, Simons S, Dennis RG, Tommerdahl M (2007a) Effects of adaptation on the capacity to differentiate simultaneously delivered dual-site vibrotactile stimuli. Brain Res 1186:164–170
Tannan V, Dennis RG, Zhang Z, Tommerdahl M (2007b) A portable tactile sensory diagnostic device. J Neurosci Methods 164:131–138
Tannan V, Holden JK, Zhang Z, Baranek GT, Tommerdahl MA (2008) Perceptual metrics of individuals with autism provide evidence for disinhibition. Autism Res 1:223–230
Tibbo P, Nopoulos P, Arndt S, Andreasen NC (1998) Corpus callosum shape and size in male patients with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 44:405–412
Tommerdahl M, Favorov OV, Whitsel BL (2005a) Effects of high-frequency skin stimulation on SI cortex: mechanisms and functional implications. Somatosens Mot Res 22:151–169
Tommerdahl M, Simons SB, Chiu JS, Favorov OV, Whitsel BL (2005b) Response of SI cortex to ipsilateral, contralateral and bilateral flutter stimulation in the cat. BMC Neurosci 6:29
Tommerdahl M, Simons SB, Chiu JS, Tannan V, Favorov OV, Whitsel BL (2005c) Response of SII cortex to ipsilateral, contralateral and bilateral flutter stimulation in the cat. BMC Neurosci 6:11
Tommerdahl M, Simons SB, Chiu J, Favorov OV, Whitsel BL (2006) Ipsilateral input modifies the SI response to contralateral skin flutter. J Neurosci 26:5970–5977
Tommerdahl M, Tannan V, Cascio CJ, Baranek GT, Whitsel BL (2007a) Vibrotactile adaptation fails to enhance spatial localization in adults with autism. Brain Res 1154:116–123
Tommerdahl M, Tannan V, Zachek M, Holden JK, Favorov OV (2007b) Effects of stimulus-driven synchronization on sensory perception. Behav Brain Funct 3:61
Tommerdahl M, Tannan V, Holden J, Baranek G (2008) Absense of stimulus-driven synchronization effects on sensory perception in autism: evidence for local underconnectivity? Behav and Brain Funct 4:19
Tommerdahl M, Favorov OV, Whitsel BL (2010) Dynamic Representations of the Somatosensory Cortex. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34:160–170
Van der Knaap LJ, Van der Ham IJ (2011) How does the corpus callosum mediate interhemispheric transfer? A review. Behav Brain Res 223:211–221
Voineskos AN, Rajji TK, Lobaugh NJ, Miranda D, Shenton ME (2010) Age-related decline in white matter tract integrity and cognitive performance: a DTI tractography study and structural equation modeling studying. Neurobiol Aging 33:21–34
Wahl M, Lauterbach-Soon B, Hattingen E, Jung P, Singer O, Volz S, Klein JC, Steinmetz H, Ziemann U (2007) Human motor corpus callosum: topography, somatotopy, and link between microstructure and function. J Neurosci 27(45):12132–12138
Wolf RC, Höse A, Frasch K, Walter H, Vasic N (2008) Volumetric abnormalities associated with cognitive deficits in patients with schizophrenia. Eur Psychiatry 23:541–548
Zahr NM, Rohlfing T, Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV (2009) Problem solving, working memory and motor correlates of association and commissural fiber bundles in normal aging: a quantitative fiber tracking study. Neuroimage 44:1050–1062
Zapallow CM, Jacobs M, Lee KGH, Asmussen MJ, Tsang P, Nelson AJ (2013) Continuous theta-burst stimulation over the primary somatosensory cortex modulates interhemispheric inhibition. Neuroreport 24(7):394–398
Zhang Z, Sun QQ (2011) The balance between excitation and inhibition and functional sensory processing in the somatosensory cortex. Int Rev Neurobiol 97:302–333
Zhang Z, Tannan V, Holden JK, Dennis RG, Tommerdahl M (2008) A quantitative method for determining spatial discriminative capacity. Biomed Eng Online 10:12
Zhang Z, Francisco EM, Holden JK, Dennis RG, Tommerdahl M (2009) The impact of non-noxious heat on tactile information processing. Brain Res 1302:97–105
Zhang Z, Zolnoun DA, Francisco EM, Holden JK, Dennis RG, Tommerdahl M (2011a) Altered central sensitization in subgroups of women with vulvodynia. Clin J Pain 27:755–763
Zhang Z, Francisco E, Holden JK, Dennis RG, Tommerdahl M (2011b) Somatosensory information processing in the aging population. Front Aging Neurosci 3:18
Zhu Z, Disbrow EA, Zumer JM, McGonigle DJ, Nagarajan SS (2007) Spatiotemporal integration of tactile information in human somatosensory cortex. BMC Neurosci 8:21
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by NIH R01 HD072983.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, R.H., Forshey, T.M., Holden, J.K. et al. Vibrotactile discriminative capacity is impacted in a digit-specific manner with concurrent unattended hand stimulation. Exp Brain Res 232, 3601–3612 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-014-4045-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-014-4045-3