Abstract.
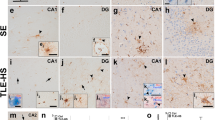
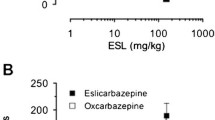
Kainic acid (KA) induces seizures and degeneration in CA1 of the ventral hippocampus, though its mechanism of action is unknown. We used KA to induce seizures in freely moving rats prepared for in vivo microdialysis with probe placement, and then measured extracellular glutamate with an online fluorometric detector. Generation of free radicals was monitored by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy coupled with perfusion of the spin-trapping agent, α-(4-pyridyl-N-oxide)-N-tert-butylnitrone (POBN). Regional antioxidant efficacy was measured by observing the eliminating ratio of nitroxide radicals, using 3-carbamoyl-2, 2, 5, 5-tetramethylpyrrolidine-1-oxyl (carbamoyl-PROXYL) applied exogenously from the probe. Increased levels of extracellular glutamate observed at the initiation of KA-induced seizures appear to be associated with generation of lipid free radicals and with a decrease in residual antioxidant effects. These data suggest that collapse of the redox state in the hippocampus, the region most vulnerable to injury from seizure activity, may be critical in the regional injury induced by seizures. Further, we propose that the functional failure of glutamate transporters due to oxidative stress results in high levels of extracellular glutamate during sustained generalized seizures induced with KA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueda, Y., Yokoyama, H., Nakajima, A. et al. Glutamate excess and free radical formation during and following kainic acid-induced status epilepticus. Exp Brain Res 147, 219–226 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-002-1224-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-002-1224-4