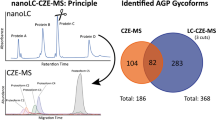
Abstract
Capillary electrophoresis (CE) offers excellent efficiency and orthogonality to liquid chromatographic (LC) separations for oligosaccharide structural analysis. Combination of CE with high resolution mass spectrometry (MS) for glycan analysis remains a challenging task due to the MS incompatibility of background electrolyte buffers and additives commonly used in offline CE separations. Here, a novel method is presented for the analysis of 2-aminobenzoic acid (2-AA) labelled glycans by capillary electrophoresis coupled to mass spectrometry (CE-MS). To ensure maximum resolution and excellent precision without the requirement for excessive analysis times, CE separation conditions including the concentration and pH of the background electrolyte, the effect of applied pressure on the capillary inlet and the capillary length were evaluated. Using readily available 12/13C6 stable isotopologues of 2-AA, the developed method can be applied for quantitative glycan profiling in a twoplex manner based on the generation of extracted ion electropherograms (EIE) for 12C6 ‘light’ and 13C6 ‘heavy’ 2-AA labelled glycan isotope clusters. The twoplex quantitative CE-MS glycan analysis platform is ideally suited for comparability assessment of biopharmaceuticals, such as monoclonal antibodies, for differential glycomic analysis of clinical material for potential biomarker discovery or for quantitative microheterogeneity analysis of different glycosylation sites within a glycoprotein. Additionally, due to the low injection volume requirements of CE, subsequent LC-MS analysis of the same sample can be performed facilitating the use of orthogonal separation techniques for structural elucidation or verification of quantitative performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold JN, Wormald MR, Sim RB, Rudd PM, Dwek RA. The impact of glycosylation on the biological function and structure of human immunoglobulins. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:21–50. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141702.
Bard F, Chia J. Cracking the glycome encoder: signaling, trafficking, and glycosylation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2015.12.004.
Clerc F, Reiding KR, Jansen BC, Kammeijer GS, Bondt A, Wuhrer M. Human plasma protein N-glycosylation. Glycoconj J. 2015. doi:10.1007/s10719-015-9626-2.
Moremen KW, Tiemeyer M, Nairn AV. Vertebrate protein glycosylation: diversity, synthesis and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(7):448–62. doi:10.1038/nrm3383.
Marino K, Bones J, Kattla JJ, Rudd PM. A systematic approach to protein glycosylation analysis: a path through the maze. Nat Chem Biol. 2010;6(10):713–23. doi:10.1038/nchembio.437.
Suzuki S. Recent developments in liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis for the analysis of glycoprotein glycans. Anal Sci. 2013;29(12):1117–28.
Mittermayr S, Bones J, Doherty M, Guttman A, Rudd PM. Multiplexed analytical glycomics: rapid and confident IgG N-glycan structural elucidation. J Proteome Res. 2011;10(8):3820–9. doi:10.1021/pr200371s.
Mittermayr S, Bones J, Guttman A. Unraveling the glyco-puzzle: glycan structure identification by capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chem. 2013;85(9):4228–38. doi:10.1021/ac4006099.
Zaia J. Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry of carbohydrates. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;984:13–25. doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-296-4_2.
Kamoda S, Ishikawa R, Kakehi K. Capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection for detailed studies on N-linked oligosaccharide profile of therapeutic recombinant monoclonal antibodies. J Chromatogr A. 2006;1133(1–2):332–9. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2006.08.028.
Sato K, Sato K, Okubo A, Yamazaki S. Separation of 2-aminobenzoic acid-derivatized glycosaminoglycans and asparagine-linked glycans by capillary electrophoresis. Anal Sci. 2005;21(1):21–4.
Millan Martin S, Delporte C, Farrell A, Navas Iglesias N, McLoughlin N, Bones J. Comparative analysis of monoclonal antibody N-glycosylation using stable isotope labelling and UPLC-fluorescence-MS. Analyst. 2015;140(5):1442–7.
Prien JM, Prater BD, Qin Q, Cockrill SL. Mass spectrometric-based stable isotopic 2-aminobenzoic acid glycan mapping for rapid glycan screening of biotherapeutics. Anal Chem. 2010;82(4):1498–508. doi:10.1021/ac902617t.
Mechref Y, Hu Y, Desantos-Garcia JL, Hussein A, Tang H. Quantitative glycomics strategies. Mol Cell Proteomics MCP. 2013;12(4):874–84. doi:10.1074/mcp.R112.026310.
Zaia J. Mass spectrometry and the emerging field of glycomics. Chem Biol. 2008;15(9):881–92. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.07.016.
Zhou S, Tello N, Harvey A, Boyes B, Orlando R, Mechref Y. Reliable LC-MS quantitative glycomics using iGlycoMab stable isotope labeled glycans as internal standards. Electrophoresis. 2016;37(11):1489–97. doi:10.1002/elps.201600013.
Lu H, Zhang Y, Yang P. Advancements in mass-spectrometry-based glycoproteomics and glycomics. Natl Sci Rev. 2016. doi:10.1093/nsr/nww019.
Atwood 3rd JA, Cheng L, Alvarez-Manilla G, Warren NL, York WS, Orlando R. Quantitation by isobaric labeling: applications to glycomics. J Proteome Res. 2008;7(1):367–74. doi:10.1021/pr070476i.
Gimenez E, Sanz-Nebot V, Rizzi A. Relative quantitation of glycosylation variants by stable isotope labeling of enzymatically released N-glycans using [12C]/[13C] aniline and ZIC-HILIC-ESI-TOF-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013;405(23):7307–19. doi:10.1007/s00216-013-7178-5.
Walker SH, Taylor AD, Muddiman DC. Individuality normalization when labeling with isotopic glycan hydrazide tags (INLIGHT): a novel glycan-relative quantification strategy. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2013;24(9):1376–84. doi:10.1007/s13361-013-0681-2.
Xia B, Feasley CL, Sachdev GP, Smith DF, Cummings RD. Glycan reductive isotope labeling for quantitative glycomics. Anal Biochem. 2009;387(2):162–70. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2009.01.028.
Alley Jr WR, Novotny MV. Structural glycomic analyses at high sensitivity: a decade of progress. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto, Calif). 2013;6:237–65. doi:10.1146/annurev-anchem-062012-092609.
Suzuki H, Muller O, Guttman A, Karger BL. Analysis of 1-aminopyrene-3,6,8-trisulfonate-derivatized oligosaccharides by capillary electrophoresis with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 1997;69(22):4554–9.
Gennaro LA, Salas-Solano O. On-line CE-LIF-MS technology for the direct characterization of N-linked glycans from therapeutic antibodies. Anal Chem. 2008;80(10):3838–45. doi:10.1021/ac800152h.
Zhong X, Chen Z, Snovida S, Liu Y, Rogers JC, Li L. Capillary electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry for quantitative analysis of glycans labeled with multiplex carbonyl-reactive tandem mass tags. Anal Chem. 2015;87(13):6527–34. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01835.
Zhou S, Hu Y, Veillon L, Snovida SI, Rogers JC, Saba J, et al. Quantitative LC–MS/MS glycomic analysis of biological samples using AminoxyTMT. Anal Chem. 2016;88(15):7515–22. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.6b00465.
Harvey DJ, Mattu TS, Wormald MR, Royle L, Dwek RA, Rudd PM. “Internal residue loss”: rearrangements occurring during the fragmentation of carbohydrates derivatized at the reducing terminus. Anal Chem. 2002;74(4):734–40.
Wuhrer M, Deelder AM, van der Burgt YE. Mass spectrometric glycan rearrangements. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2011;30(4):664–80. doi:10.1002/mas.20337.
Ceroni A, Maass K, Geyer H, Geyer R, Dell A, Haslam SM. GlycoWorkbench: a tool for the computer-assisted annotation of mass spectra of glycans. J Proteome Res. 2008;7(4):1650–9. doi:10.1021/pr7008252.
Harvey DJ, Merry AH, Royle L, Campbell MP, Dwek RA, Rudd PM. Proposal for a standard system for drawing structural diagrams of N- and O-linked carbohydrates and related compounds. Proteomics. 2009;9(15):3796–801. doi:10.1002/pmic.200900096.
Jayo RG, Thaysen-Andersen M, Lindenburg PW, Haselberg R, Hankemeier T, Ramautar R, et al. Simple capillary electrophoresis–mass spectrometry method for complex glycan analysis using a flow-through microvial interface. Anal Chem. 2014;86(13):6479–86. doi:10.1021/ac5010212.
Bunz SC, Rapp E, Neususs C. Capillary electrophoresis/mass spectrometry of APTS-labeled glycans for the identification of unknown glycan species in capillary electrophoresis/laser-induced fluorescence systems. Anal Chem. 2013;85(21):10218–24. doi:10.1021/ac401930j.
Zapala L, Kalembkiewicz J, Sitarz-Palczak E. Studies on equilibrium of anthranilic acid in aqueous solutions and in two-phase systems: aromatic solvent-water. Biophys Chem. 2009;140(1–3):91–8. doi:10.1016/j.bpc.2008.11.012.
Zapała L, Woźnicka E, Kalembkiewicz J. Tautomeric and microscopic protonation equilibria of anthranilic acid and its derivatives. J Solut Chem. 2014;43(6):1167–83. doi:10.1007/s10953-014-0190-3.
Harvey DJ. Collision-induced fragmentation of negative ions from N-linked glycans derivatized with 2-aminobenzoic acid. J Mass Spectrom. 2005;40(5):642–53. doi:10.1002/jms.836.
Lammerts van Bueren JJ, Rispens T, Verploegen S, van der Palen-Merkus T, Stapel S, Workman LJ, et al. Anti-galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose IgE from allergic patients does not bind alpha-galactosylated glycans on intact therapeutic antibody Fc domains. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(7):574–6. doi:10.1038/nbt.1912.
Domon B, Costello CE. A systematic nomenclature for carbohydrate fragmentations in FAB-MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconj J. 1988;5(4):397–409. doi:10.1007/bf01049915.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge funding from EU Framework Programme 7 under Marie Curie Actions, grants reference: FP7-PEOPLE-2013-ITN-608381 and FP7-PEOPLE-2012-ITN-316929, and Science Foundation Ireland, grant reference 11/SIRG/B107. Prof. Natalia Navas Iglesias from the Department of Analytical Chemistry at the University of Granada, Spain, is kindly acknowledged for the provision of the Cetuximab samples analysed in this study. Agilent Technologies are also kindly acknowledged for the generous provision of the 6520 QToF-MS and PVA capillaries used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Fundamental Aspects of Electromigrative Separation Techniques with guest editors Carolin Huhn and Pablo A. Kler.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 578 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Váradi, C., Mittermayr, S., Millán-Martín, S. et al. Quantitative twoplex glycan analysis using 12C6 and 13C6 stable isotope 2-aminobenzoic acid labelling and capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 8691–8700 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9935-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9935-8