Abstract
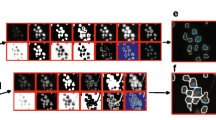
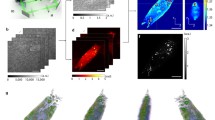
The accumulation of lipids in macrophages is a key factor that promotes the formation of atherosclerotic lesions. Several methods such as biochemical assays and neutral lipid staining have been used for the detection of lipids in cells. However, a method for real-time quantitative assessment of the lipid content in living macrophages has yet to be shown, particularly for its kinetic process with drugs, due to the lack of suitable tools for non-invasive chemical detection. Here we demonstrate label-free real-time monitoring of lipid droplets (LDs) in living macrophages by using coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscopy. In addition, we have established an automated image analysis method based on maximum entropy thresholding (MET) to quantify the cellular lipid content. The result of CARS image analysis shows a good correlation (R 2 > 0.9) with the measurement of biochemical assay. Using this method, we monitored the processes of lipid accumulation and hydrolysis in macrophages. We further characterized the effect of a lipid hydrolysis inhibitor (diethylumbelliferyl phosphate, DEUP) and determined the kinetic parameters such as the inhibition constant, K i. Our work demonstrates that the automated quantitative analysis method is useful for the studies of cellular lipid metabolism and has potential for preclinical high-throughput screening of therapeutic agents related to atherosclerosis and lipid-associated disorders.

Automated quantitative analysis for the label-free detection of lipid content in living cells





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woollard KJ, Geissmann F (2010) Monocytes in atherosclerosis: subsets and functions. Nat Rev Cardiol 7(2):77–86
Glass CK, Witztum JL (2001) Atherosclerosis: the road ahead. Cell 104(4):503–516
Maxfield FR, Tabas I (2005) Role of cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature 438(7068):612–621
Ouimet M, Marcel YL (2012) Regulation of lipid droplet cholesterol efflux from macrophage foam cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32(3):575–581
Cuchel M, Rader DJ (2006) Macrophage reverse cholesterol transport—key to the regression of atherosclerosis? Circulation 113(21):2548–2555
Zhao B, Fisher BJ, St Clair RW, Rudel LL, Ghosh S (2005) Redistribution of macrophage cholesteryl ester hydrolase from cytoplasm to lipid droplets upon lipid loading. J Lipid Res 46(10):2114–2121
Okazaki H, Igarashi M, Nishi M, Sekiya M, Tajima M, Takase S, Takanashi M, Ohta K, Tamura Y, Okazaki S, Yahagi N, Ohashi K, Amemiya-Kudo M, Nakagawa Y, Nagai R, Kadowaki T, Osuga J, Ishibashi S (2008) Identification of neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase, a key enzyme removing cholesterol from macrophages. J Biol Chem 283(48):33357–33364
Sekiya M, Osuga J, Nagashima S, Ohshiro T, Igarashi M, Okazaki H, Takahashi M, Tazoe F, Wada T, Ohta K, Takanashi M, Kumagai M, Nishi M, Takase S, Yahagi N, Yagyu H, Ohashi K, Nagai R, Kadowaki T, Furukawa Y, Ishibashi S (2009) Ablation of neutral cholesterol ester hydrolase 1 accelerates atherosclerosis. Cell Metab 10(3):219–228
Ghosh S, Zhao B, Bie JH, Song JM (2010) Macrophage cholesteryl ester mobilization and atherosclerosis. Vasc Pharmacol 52(1–2):1–10
Ishikawa TT, Macgee J, Morrison JA, Glueck CJ (1974) Quantitative-analysis of cholesterol in 5 to 20 Mu1 of plasma. J Lipid Res 15(3):286–291
Stclair RW, Smith BP, Wood LL (1977) Stimulation of cholesterol esterification in rhesus-monkey arterial smooth-muscle cells. Circ Res 40(2):166–173
Matthaus C, Krafft C, Dietzek B, Brehm BR, Lorkowski S, Popp J (2012) Noninvasive imaging of intracellular lipid metabolism in macrophages by Raman microscopy in combination with stable isotopic labeling. Anal Chem 84(20):8549–8556
Lu KY, Ching LC, Su KH, Yu YB, Kou YR, Hsiao SH, Huang YC, Chen CY, Cheng LC, Pan CC, Lee TS (2010) Erythropoietin suppresses the formation of macrophage foam cells role of liver X receptor alpha. Circulation 121(16):1828–1837
Koren E, Franzen J, Fugate RD, Alaupovic P (1990) Analysis of cholesterol ester accumulation in macrophages by the use of digital imaging fluorescence microscopy. Atherosclerosis 85(2–3):175–184
Etzion Y, Hackett A, Proctor BM, Ren J, Nolan B, Ellenberger T, Muslin AJ (2009) An unbiased chemical biology screen identifies agents that modulate uptake of oxidized LDL by macrophages. Circ Res 105(2):148–157
van de Poll SWE, Bakker Schut TC, van der Laarse A, Puppels GJ (2002) In situ investigation of the chemical composition of ceroid in human atherosclerosis by Raman spectroscopy. J Raman Spectrosc 33(7):544–551
Zumbusch A, Holtom GR, Xie XS (1999) Three-dimensional vibrational imaging by coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering. Phys Rev Lett 82(20):4142–4145
Duncan MD, Reintjes J, Manuccia TJ (1982) Scanning coherent anti-Stokes Raman microscope. Opt Lett 7(8):350–352
Freudiger CW, Min W, Saar BG, Lu S, Holtom GR, He CW, Tsai JC, Kang JX, Xie XS (2008) Label-free biomedical imaging with high sensitivity by stimulated Raman scattering microscopy. Science 322(5909):1857–1861
Nan XL, Cheng JX, Xie XS (2003) Vibrational imaging of lipid droplets in live fibroblast cells with coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy. J Lipid Res 44(11):2202–2208
Konorov SO, Glover CH, Piret JM, Bryan J, Schulze HG, Blades MW, Turner RFB (2007) In situ analysis of living embryonic stem cells by coherent anti-stokes Raman microscopy. Anal Chem 79(18):7221–7225
Paar M, Jungst C, Steiner NA, Magnes C, Sinner F, Kolb D, Lass A, Zimmermann R, Zumbusch A, Kohlwein SD, Wolinski H (2012) Remodeling of lipid droplets during lipolysis and growth in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 287(14):11164–11173
Kong LJ, Ji MB, Holtom GR, Fu D, Freudiger CW, Xie XS (2013) Multicolor stimulated Raman scattering microscopy with a rapidly tunable optical parametric oscillator. Opt Lett 38(2):145–147
Henry FP, Cote D, Randolph MA, Rust EAZ, Redmond RW, Kochevar IE, Lin CP, Winograd JM (2009) Real-time in vivo assessment of the nerve microenvironment with coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy. Plast Reconstr Surg 123(2):123s–130s
Yen K, Le TT, Bansal A, Narasimhan D, Cheng JX, Tissenbaum HA (2010) A comparative study of fat storage quantitation in nematode Caenorhabditis elegans using label and label-free methods. PLoS One 5(9):e12810
Chien CH, Chen WW, Wu JT, Chang TC (2011) Label-free imaging of Drosophila in vivo by coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering and two-photon excitation autofluorescence microscopy. J Biomed Opt 16(1):016012
Urasaki Y, Johlfs MG, Fiscus RR, Le TT (2012) Imaging immune and metabolic cells of visceral adipose tissues with multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy. PLoS One 7(6):e38418
Hellerer T, Axang C, Brackmann C, Hillertz P, Pilon M, Enejder A (2007) Monitoring of lipid storage in Caenorhabditis elegans using coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscopy. P Natl Acad Sci USA 104(37):14658–14663
Suhalim JL, Chung CY, Lilledahl MB, Lim RS, Levi M, Tromberg BJ, Potma EO (2012) Characterization of cholesterol crystals in atherosclerotic plaques using stimulated Raman scattering and second-harmonic generation microscopy. Biophys J 102(8):1988–1995
Freudiger CW, Min W, Holtom GR, Xu BW, Dantus M, Xie XS (2011) Highly specific label-free molecular imaging with spectrally tailored excitation-stimulated Raman scattering (STE-SRS) microscopy. Nat Photonics 5(2):103–109
Klapper M, Ehmke M, Palgunow D, Bohme M, Matthaus C, Bergner G, Dietzek B, Popp J, Doring F (2011) Fluorescence-based fixative and vital staining of lipid droplets in Caenorhabditis elegans reveal fat stores using microscopy and flow cytometry approaches. J Lipid Res 52(6):1281–1293
Burkacky O, Zumbusch A, Brackmann C, Enejder A (2006) Dual-pump coherent anti-Stokes-Raman scattering microscopy. Opt Lett 31(24):3656–3658
Le TT, Langohr IM, Locker MJ, Sturek M, Cheng JX (2007) Label-free molecular imaging of atherosclerotic lesions using multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy. J Biomed Opt 12(5):054007
Kim SH, Lee ES, Lee JY, Lee BS, Park JE, Moon DW (2010) Multiplex coherent anti-Stokes Raman spectroscopy images intact atheromatous lesions and concomitantly identifies distinct chemical profiles of atherosclerotic lipids. Circ Res 106(8):1332–1341
Chen S, Zhao M, Wu G, Yao C, Zhang J (2012) Recent advances in morphological cell image analysis. Comput Math Methods Med 2012:101536
Hagmar J, Brackmann C, Gustavsson T, Enejder A (2008) Image analysis in nonlinear microscopy. J Opt Soc Am A 25(9):2195–2206
Vogler N, Bocklitz T, Mariani M, Deckert V, Markova A, Schelkens P, Rosch P, Akimov D, Dietzek B, Popp J (2010) Separation of CARS image contributions with a Gaussian mixture model. J Opt Soc Am A 27(6):1361–1371
Gao L, Zhou HJ, Thrall MJ, Li F, Yang YL, Wang ZY, Luo PF, Wong KK, Palapattu GS, Wong STC (2011) Label-free high-resolution imaging of prostate glands and cavernous nerves using coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy. Biomed Opt Express 2(4):915–926
Medyukhina A, Meyer T, Schmitt M, Romeike BFM, Dietzek B, Popp J (2012) Towards automated segmentation of cells and cell nuclei in nonlinear optical microscopy. J Biophotonics 5(11–12):878–888
Sezgin M, Sankur B (2004) Survey over image thresholding techniques and quantitative performance evaluation. J Electron Imaging 13(1):146–168
Otsu N (1979) Threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9(1):62–66
Kapur JN, Sahoo PK, Wong AKC (1985) A new method for gray-level picture thresholding using the entropy of the histogram. Comput Vis Graph 29(3):273–285
Schulze K, Lopez DA, Tillich UM, Frohme M (2011) A simple viability analysis for unicellular cyanobacteria using a new autofluorescence assay, automated microscopy, and image. J BMC Biotechnol 11:118
Harrison EH, Bernard DW, Scholm P, Quinn DM, Rothblat GH, Glick JM (1990) Inhibitors of neutral cholesteryl ester hydrolase. J Lipid Res 31(12):2187–2193
Chien CH, Chen WW, Wu JT, Chang TC (2012) Investigation of lipid homeostasis in living Drosophila by coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy. J Biomed Opt 17(12):126001
Abramoff MDM, Paulo J, Ram SJ (2004) Image processing with image. J Biophotonics Int 11(7):36–42
van Manen HJ, Otto C (2009) Cholesterol esters are detected by Raman microspectroscopy in HeLa cells. J Raman Spectrosc 40(2):117–118
Hawi SR, Nithipatikom K, Wohlfeil ER, Adar F, Campbell WB (1997) Raman microspectroscopy of intracellular cholesterol crystals in cultured bovine coronary artery endothelial cells. J Lipid Res 38(8):1591–1597
Baraga JJ, Feld MS, Rava RP (1992) Insitu optical histochemistry of human artery using near-infrared Fourier-transform Raman-spectroscopy. P Natl Acad Sci USA 89(8):3473–3477
Lotem H, Lynch RT, Bloembergen N (1976) Interference between Raman resonances in 4-wave difference mixing. Phys Rev A 14(5):1748–1755
Greenspan P, Mayer EP, Fowler SD (1985) Nile Red—a selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets. J Cell Biol 100(3):965–973
Glasbey CA (1993) An analysis of histogram-based thresholding algorithms. Cvgip-Graph Model Im 55(6):532–537
Zack GW, Rogers WE, Latt SA (1977) Automatic-measurement of sister chromatid exchange frequency. J Histochem Cytochem 25(7):741–753
Shanbhag AG (1994) Utilization of information measure as a means of image thresholding. Cvgip-Graph Model Im 56(5):414–419
Doyle W (1962) Operations useful for similarity-invariant pattern recognition. J ACM 9(3):259–267
Tsai WH (1985) Moment-preserving thresholding—a new approach. Comput Vis Graph 29(3):377–393
Li CH, Lee CK (1993) Minimum cross entropy thresholding. Pattern Recognit 26(4):617–625
Ridler TW, Calvard S (1978) Picture thresholding using an iterative selection method. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 8(8):630–632
Huang LK, Wang MJJ (1995) Image thresholding by minimizing the measures of fuzziness. Pattern Recogn 28(1):41–51
Kittler J, Illingworth J (1986) Minimum error thresholding. Pattern Recogn 19(1):41–47
Yasnoff WA, Mui JK, Bacus JW (1977) Error measures for scene segmentation. Pattern Recogn 9(4):217–231
Gachet D, Billard F, Sandeau N, Rigneault H (2007) Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) microscopy imaging at interfaces: evidence of interference effects. Opt Express 15(16):10408–10420
Adiga U, Taylor D, Bell B, Ponomareva L, Kanzlemar S, Kramer R, Saldanha R, Nelson S, Lamkin TJ (2012) Automated analysis and classification of infected macrophages using bright-field amplitude contrast data. J Biomol Screen 17(3):401–408
Brown AJ, Mander EL, Gelissen IC, Kritharides L, Dean RT, Jessup W (2000) Cholesterol and oxysterol metabolism and subcellular distribution in macrophage foam cells: accumulation of oxidized esters in lysosomes. J Lipid Res 41(2):226–236
Weibel GL, Joshi MR, Jerome WG, Bates SR, Yu KJ, Phillips MC, Rothblat GH (2012) Cytoskeleton disruption in J774 macrophages: consequences for lipid droplet formation and cholesterol flux. BBA-Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1821(3):464–472
Avart SJ, Bernard DW, Jerome WG, Glick JM (1999) Cholesteryl ester hydrolysis in J774 macrophages occurs in the cytoplasm and lysosomes. J Lipid Res 40(3):405–414
Rodrigues AD, Lin JH (2001) Screening of drug candidates for their drug-drug interaction potential. Curr Opin Chem Biol 5(4):396–401
Dixon M (1953) The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J 55(1):170–171
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Academia Sinica and the National Science Council of the Republic of China (Grant No. NSC-101-2113-M-001-022-MY2). We are grateful to Dr. Margaret Hsin-Jui Kuo (Academia Sinica) for her valuable discussion and careful reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wei-Wen Chen and Chen-Hao Chien contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 3043 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, WW., Chien, CH., Wang, CL. et al. Automated quantitative analysis of lipid accumulation and hydrolysis in living macrophages with label-free imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 8549–8559 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7251-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7251-0