Abstract
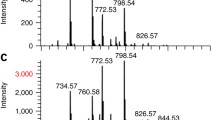
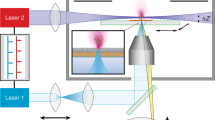
A commercial hybrid quadrupole time–of–flight mass spectrometer has been modified for high-speed matrix-assisted laser desorption ionisation (MALDI) imaging using a short-pulse optical technology Nd:YVO4 laser. The laser operating in frequency-tripled mode (λ = 355 nm) is capable of delivering 1.5-ns pulses of energy at up to 8 μJ at 5–10 kHz and 3 μJ at 20 kHz. Experiments to improve beam homogeneity and reduce laser speckle by mechanical vibration of the fibre-optic laser delivery system are reported along with data from trial and tissue imaging experiments using the modified instrument. The laser appeared to yield best results for MALDI-MS imaging experiments when operating at repetition rates 5–10 kHz. Combining this with raster imaging allowed images of rat brain sections to be recorded in 37 min. Similarly, images of the distribution of peptides in “on-tissue” digest experiments from tumour tissues were recorded in 1 h and 30 min rather than the 8-h acquisition time previously used. A brief investigation of targeted protein analysis/imaging by multiple reaction monitoring experiments “on-tissue” is reported. A total of 26 transitions were recorded over a 3-s cycle time and images of abundant proteins were successfully recorded.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caprioli RM, Farmer TB, Gile J (1997) Molecular imaging of biological samples: localization of peptides and proteins using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal Chem 69:4751–4760
Holle A, Haase A, Kayser M, Höhndorf J (2006) Optimizing UV laser focus profiles for improved MALDI performance. J Mass Spectrom 41:705–716
McLean JA, Russell WK, Russell DH (2003) A high repetition rate (1 kHz) microcrystal laser for high throughput atmospheric pressure MALDI-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 75:648–654
Moskovets E, Preisler J, Chen HS, Rejtar T, Andreev V, Karger BL (2006) High-throughput axial MALDI-TOF MS using a 2-kHz repetition rate laser. Anal Chem 78:921–919
Simmons DA (2008) ABI Technical note, improved MALDI-MS imaging performance using continuous laser rastering
Loboda AV, Krutchinsky AN, Bromirski M, Ens W, Standing KG (2000) A tandem quadrupole/time-of-flight mass spectrometer with a matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization source: design and performance. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 14:1047–1057
Qiao H, Spicer V, Ens W (2008) The effect of laser profile, fluence, and spot size on sensitivity in orthogonal-injection matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22:2779–2790
Trim PJ, Atkinson SJ, Princivalle AP, Marshall PS, West A, Clench MR (2008) MALDI-MS imaging of lipids in rat brain tissue with integrated unsupervised and supervised multivariant statistical analysis. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22:1503–1509
Takai N, Asakura T (1988) Laser speckles produced by a diffuse object under illumination from a multimode optical fiber: an experimental study. Appl Opt 27:557–562
Jurchen JC, Rubakhin SS, Sweedler JV (2005) MALDI-MS imaging of features smaller than the size of the laser beam. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 16:1654–1659
Djidja M-C, Claude E, Snel M, Scriven P, Francese S, Carolan VA, Clench MR (2009) MALDI-ion mobility separation–mass spectrometry imaging of glucose-regulated protein 78 kDa (Grp78) in human formalin fixed paraffin embedded pancreatic adenocarcinoma tissue sections. J Proteome Res 8:4876–4884
Acknowledgements
The acquisition of the SPOT laser by Sheffield Hallam University was supported by a grant from CR-UK/EPSRC/MRC/NIHR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Oscillation of the fibre optic in a MALDI system to improve sensitivity is protected by UK Patent GB2460478A; international patents are pending.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trim, P.J., Djidja, MC., Atkinson, S.J. et al. Introduction of a 20 kHz Nd:YVO4 laser into a hybrid quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer for MALDI-MS imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem 397, 3409–3419 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3874-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3874-6