Abstract
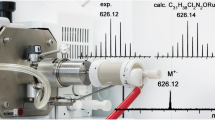
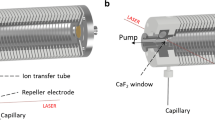
Liquid injection field desorption/ionization (LIFDI) has been applied to identify transition metal complexes that are highly reactive to air and moisture by mass spectrometry. The complexes of nickel and rhodium were supplied as dilute solutions (∼0.2 mg ml−1) in toluene, tetrahydrofuran or acetonitrile, and were applied onto the field desorption emitter inside the vacuum of the ion source under inert conditions by means of the injection capillary unique to the LIFDI set-up. LIFDI mass spectrometry on a double-focusing magnetic sector instrument provided spectra exhibiting intense molecular ion peaks for the species investigated or signals that could easily be related to the target compound by assuming neutral loss of the weakest-bound ligand. Eventually, byproducts of the synthesis or other components resulting from incomplete reactions or some degree of decomposition were also detected.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beckey HD (1969) Int J Mass Spectrom Ion Phys 2:500–503
Beckey HD, Schulten H-R (1975) Angew Chem 87:425–438
Beckey HD (1977) Principles of field desorption and field ionization mass spectrometry. Pergamon, Oxford
Schulten H-R (1978) Adv Mass Spectrom 7A:83–97
Prókai L (1990) Field desorption mass spectrometry. Marcel Dekker, New York
Inghram MG, Gomer R (1955) Z Naturforsch 10A:863–872
Heinen HJ, Giessmann U, Röllgen FW (1977) Org Mass Spectrom 12:710–715
Giessmann U, Heinen HJ, Röllgen FW (1979) Org Mass Spectrom 14:177–179
Beckey HD, Hilt E, Schulten H-R (1973) J Phys E Sci Instrum 6:1043–1044
Linden HB, Hilt E, Beckey HD (1978) J Phys E Sci Instrum 11:1033–1036
Rabrenovic M, Ast T, Kramer V (1981) Int J Mass Spectrom Ion Phys 37:297–307
Linden HB (2004) Eur J Mass Spectrom 10:459–468
Linden HB (2001) In: Proc 49th ASMS Annual Conf Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, MPA 024, 27–31 May 2001, Chicago, IL
Linden HB (2002) In: Proc 50th ASMS Annual Conf Mass Spectrometry and Allied Topics, MPL 373, 2–6 June 2002, Orlando, IL
Schaub TM, Hendrickson CL, Qian K, Quinn JP, Marshall AG (2003) Anal Chem 75:2172–2176
Schaub TM, Hendrickson CL, Quinn JP, Rodgers RP, Marshall AG (2005) Anal Chem 77:1317–1324
Dole RB (ed) (1997) Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry—fundamentals, instrumentation and applications. Wiley, Chichester, UK
Pramanik BN, Ganguly AK, Gross ML (eds) (2002) Applied electrospray mass spectrometry. Marcel Dekker, New York
Gross JH (1998) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 12:1833–1838
Hofmann P, Volland MAO, Hansen SM, Eisenträger F, Gross JH, Stengel K (2000) J Organomet Chem 606:88–92
Arduengo AJ III, Harlow RL, Kline M (1991) J Am Chem Soc 113:361–363
Scott NM, Nolan SP (2005) Eur J Inorg Chem 1:1815–1828
Crudden CM, Allen DP (2004) Coord Chem Rev 248:2247–2273
Acknowledgements
Generous support of this work by the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie, by BASF AG and by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 623) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dedicated to Prof. J. J. Veith on the occasion of his 65th birthday.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gross, J.H., Nieth, N., Linden, H.B. et al. Liquid injection field desorption/ionization of reactive transition metal complexes. Anal Bioanal Chem 386, 52–58 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0524-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0524-0