Abstract
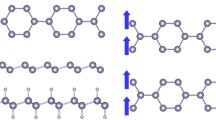
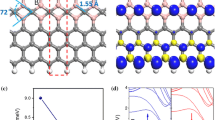
First-principles computations revealed that iodine (I) is an ideal terminal group for zigzag graphene nanoribbons (zGNRs) in terms of stabilizing the pure sp 2 coordinated edges and preserving the edge magnetism. Due to the strong steric effect of I atoms, the unfavorable sp 3 coordination can be efficiently suppressed and the pure sp 2 coordinated edges can be stabilized at rather feasible experimental conditions. Interestingly, the electronic structures of I-terminated zGNRs (I-zGNRs) with different edge configurations can be well rationalized by employing the Clar’s model. I-zGNRs can well reproduce the electronic and magnetic properties of those hydrogen-terminated zGNRs. Remarkably, I termination can significantly lower the critical electric field required to induce the half-metallic behavior. These results open new opportunities in fabricating spintronics devices based on zGNRs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Gregorieva IV, Firsov AA (2004) Science 306:666
Novoselov KS, Jiang D, Schedin F, Booth TJ, Khotkevich VV, Morozov SV, Geim AK (2005) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10451
Novoselov KS, Falko VI, Colombo L, Gellert PR, Schwab MG, Kim PA (2012) Nature 490:192
Tang Q, Zhou Z, Chen ZF (2013) Nanoscale 5:4541
Son Y-W, Cohen ML, Louie SG (2006) Phys Rev Lett 97:216803
Han MY, Özyilmaz B, Zhang Y, Kim P (2007) Phys Rev Lett 98:206805
Fujita M, Wakabayashi K, Nakada K, Kusakabe K (1996) J Phys Soc Jpn 65:1920
Wakabayashi K, Sigrist M, Fujita M (1998) J Phys Soc Jpn 67:2089
Son Y-W, Cohen ML, Louie SG (2006) Nature 444:347
Hod O, Barone V, Peralta JE, Scuseria GE (2007) Nano Lett 7:2295
Kan EJ, Li ZY, Yang JL, Hou JG (2008) J Am Chem Soc 130:4224
Dutta S, Pati SK (2008) J Phys Chem B 112:1333
Joseph Joly VL, Kiguchi M, Hao S-J, Takai K, Enoki T, Sumii R, Amemiya K, Muramatsu H, Hayashi T, Kim YA, Endo M, Campos-Delgado J, López-Urías F, Botello-Méndez A, Terrones H, Terrones M, Dresselhaus MS (2010) Phys Rev B 81:245428
Konishi A, Hirao Y, Matsumoto K, Kurata H, Kishi R, Shigeta Y, Nakano M, Tokunaga K, Kamada K, Kubo T (2013) J Am Chem Soc 135:1430
Tao C, Jiao L, Yazyev OV, Chen Y-C, Feng J, Zhang X, Capaz RB, Tour JM, Zettl A, Louie SG, Dai H, Crommie MF (2011) Nat Phys 7:616
Zhang X, Yazyev OV, Feng J, Xie L, Tao C, Jiao L, Pedramrazi Z, Zettl A, Louie SG, Dai H, Crommie AF (2013) ACS Nano 7:198
Wassmann T, Seitsonen AP, Saitta AM, Lazzeri M, Mauri F (2008) Phys Rev Lett 101:096402
Seitsonen AP, Saitta AM, Wassmann T, Lazzeri M, Mauri F (2010) Phys Rev B 82:115425
Jiang DE, Sumpter BG, Dai S (2007) J Chem Phys 126:134701
Plasser F, Pašalić H, Gerzabek MH, Libisch F, Reiter R, Burgdörfer J, Müller T, Shepard R, Lischka H (2013) Angew Chem Int Ed 52:2581
Chia C-I, Crespi VH (2012) Phys Rev Lett 109:076802
Li YF, Zhou Z, Carlos CR, Chen ZF (2013) Sci Rep 3:2030
Kresse G, Hafner J (1993) Phys Rev B 47:558
Blöchl PE (1994) Phys Rev B 50:17953
Kresse G, Joubert D (1999) Phys Rev B 59:1758
Perdew JP, Burke L, Ernzerhof M (1996) Phys Rev Lett 77:3865
Koskinen P, Malola S, Häkkinen H (2009) Phys Rev B 80:073401
Clar E (1964) Polycyclic hydrocarbons. Academic Press, New York
Clar E (1972) The aromatic sextet. Wiley, London
Watson MD, Fechtenkötter A, Müllen K (2001) Chem Rev 101:1267
Randic M (2003) Chem Rev 103:3449
Wassmann T, Seitsonen AP, Saitta AM, Lazzeri M, Mauri F (2010) J Am Chem Soc 132:3440
Liu X, Zhang Z, Guo W (2013) Small 9:1405
Lide DR (2008) CRC textbook of chemistry and physics. CRC press, Boca Raton
Kalita G, Wakita K, Takahashi M, Umeno M (2011) J Mater Chem 21:15209
Poh HL, Simek P, Sofer Z, Pumera M (2013) Chem Eur J 19:2655
Zhang ZH, Chen CF, Guo WL (2009) Phys Rev Lett 103:187204
Zhang ZH, Chen CF, Zeng XC, Guo WL (2010) Phys Rev Lett 81:155428
Acknowledgments
Support in China by startup funds of Nanjing Normal University (184080H20145) and Jiangsu Specially Appointed Professor Plan are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
214_2014_1548_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Clar’s representations of z 11 and z 21111 in the nonmagnetic state and z 2111 in the magnetic state, phonon spectrum of 8-I-zGNR with z 11 edge configuration, DOS of 8-H-zGNR, and band gap of I-zGNRs as a function of ribbon width. Supplementary material 1 (DOC 539 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Li, Y. Preserving the edge magnetism of graphene nanoribbons by iodine termination: a computational study. Theor Chem Acc 133, 1548 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-014-1548-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-014-1548-8