Abstract
Rationale
Growing evidence supports a role for the microbiota in regulating gut-brain interactions and, thus, psychiatric disorders. Despite substantial scientific efforts to delineate the mechanism of action of psychotropic medications at a central nervous system (CNS) level, there remains a critical lack of understanding on how these drugs might affect the microbiota and gut physiology.
Objectives
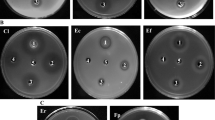
We investigated the antimicrobial activity of psychotropics against two bacterial strain residents in the human gut, Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Escherichia coli. In addition, we examined the impact of chronic treatment with these drugs on microbiota and intestinal parameters in the rat.
Results
In vitro fluoxetine and escitalopram showed differential antimicrobial effects. Lithium, valproate and aripiprazole administration significantly increased microbial species richness and diversity, while the other treatments were not significantly different from controls. At the genus level, several species belonging to Clostridium, Peptoclostridium, Intestinibacter and Christenellaceae were increased following treatment with lithium, valproate and aripiprazole when compared to the control group. Animals treated with escitalopram, venlafaxine, fluoxetine and aripiprazole exhibited an increased permeability in the ileum.
Conclusions
These data show that psychotropic medications differentially influence the composition of gut microbiota in vivo and that fluoxetine and escitalopram have specific antimicrobial activity in vitro. Interestingly, drugs that significantly altered gut microbial composition did not increase intestinal permeability, suggesting that the two factors are not causally linked. Overall, unravelling the impact of psychotropics on gastrointestinal and microbiota measures offers the potential to provide critical insight into the mechanism of action and side effects of these medications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackenheil M, Weber K (2004) Differing response to antipsychotic therapy in schizophrenia: pharmacogenomic aspects. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 6:71–77
Al-Harbi KS (2012) Treatment-resistant depression: therapeutic trends, challenges, and future directions. Patient Preference Adherence 6:369–388
Ariel L, Inbar S, Edut S, Richter-Levin G (2017) Fluoxetine treatment is effective in a rat model of childhood-induced post-traumatic stress disorder. Transl Psychiatry 7:1260
Ayaz M, Subhan F, Ahmed J, Khan A-u, Ullah F, Ullah I, Ali G, Syed N-i-H, Hussain S (2015a) Sertraline enhances the activity of antimicrobial agents against pathogens of clinical relevance. J Biol Res 22:4
Ayaz M, Subhan F, Ahmed J, Khan AU, Ullah F, Ullah I, Ali G, Syed NI, Hussain S (2015b) Sertraline enhances the activity of antimicrobial agents against pathogens of clinical relevance. J Biol Res (Thessalon) 22:4
Bahr SM, Tyler BC, Wooldridge N, Butcher BD, Burns TL, Teesch LM, Oltman CL, Azcarate-Peril MA, Kirby JR, Calarge CA (2015a) Use of the second-generation antipsychotic, risperidone, and secondary weight gain are associated with an altered gut microbiota in children. Transl Psychiatry 5:e652
Bahr SM, Weidemann BJ, Castro AN, Walsh JW, deLeon O, Burnett CML, Pearson NA, Murry DJ, Grobe JL, Kirby JR (2015b) Risperidone-induced weight gain is mediated through shifts in the gut microbiome and suppression of energy expenditure. EBioMedicine 2:1725–1734
Bercik P, Collins SM, Verdu EF (2012) Microbes and the gut-brain axis. Neurogastroenterology Motility 24:405–413
Beyazyüz M, Albayrak Y, Eğilmez OB, Albayrak N, Beyazyüz E (2013) Relationship between SSRIs and metabolic syndrome abnormalities in patients with generalized anxiety disorder: a prospective study. Psychiatry Investigation 10:148–154
Bischoff SC, Mailer R, Pabst O, Weier G, Sedlik W, Li Z, Chen JJ, Murphy DL, Gershon MD (2009) Role of serotonin in intestinal inflammation: knockout of serotonin reuptake transporter exacerbates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296:G685–G695
Bohnert JA, Szymaniak-Vits M, Schuster S, Kern WV (2011a) Efflux inhibition by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother 66:2057–2060
Bohnert JA, Szymaniak-Vits M, Schuster S, Kern WV (2011b) Efflux inhibition by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother 66:2057–2060
Cani PD, Lecourt E, Dewulf EM, Sohet FM, Pachikian BD, Naslain D, De Backer F, Neyrinck AM, Delzenne NM (2009) Gut microbiota fermentation of prebiotics increases satietogenic and incretin gut peptide production with consequences for appetite sensation and glucose response after a meal. Am J Clin Nutr 90:1236–1243
Caparrós-Martín JA, Lareu RR, Ramsay JP, Peplies J, Reen FJ, Headlam HA, Ward NC, Croft KD, Newsholme P, Hughes JD, O’Gara F (2017) Statin therapy causes gut dysbiosis in mice through a PXR-dependent mechanism. Microbiome 5:95
Chen JX, Pan H, Rothman TP, Wade PR, Gershon MD (1998) Guinea pig 5-HT transporter: cloning, expression, distribution, and function in intestinal sensory reception. Am J Phys 275:G433–G448
Chen JJ, Li Z, Pan H, Murphy DL, Tamir H, Koepsell H, Gershon MD (2001) Maintenance of serotonin in the intestinal mucosa and ganglia of mice that lack the high-affinity serotonin transporter: abnormal intestinal motility and the expression of cation transporters. J Neurosci 21:6348–6361
Chen L, Wilson JE, Koenigsknecht MJ, Chou WC, Montgomery SA, Truax AD, Brickey WJ, Packey CD, Maharshak N, Matsushima GK, Plevy SE, Young VB, Sartor RB, Ting JP (2017) NLRP12 attenuates colon inflammation by maintaining colonic microbial diversity and promoting protective commensal bacterial growth. Nat Immunol 18:541–551
Coates MD, Mahoney CR, Linden DR, Sampson JE, Chen J, Blaszyk H, Crowell MD, Sharkey KA, Gershon MD, Mawe GM, Moses PL (2004) Molecular defects in mucosal serotonin content and decreased serotonin reuptake transporter in ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 126:1657–1664
Coban AY, Tanriverdi Cayci Y, Keles Uludag S, Durupinar B (2009) Investigation of antibacterial activity of sertralin. Mikrobiyol Bul 43:651–656
Collins SM, Surette M, Bercik P (2012) The interplay between the intestinal microbiota and the brain. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:735–742
Correll CU, Detraux J, De Lepeleire J, De Hert M (2015) Effects of antipsychotics, antidepressants and mood stabilizers on risk for physical diseases in people with schizophrenia, depression and bipolar disorder. World Psychiatry 14:119–136
Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2012a) Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:701–712
Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2012b) Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci 13:701–712
Davey KJ, O’Mahony SM, Schellekens H, O’Sullivan O, Bienenstock J, Cotter PD, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2012) Gender-dependent consequences of chronic olanzapine in the rat: effects on body weight, inflammatory, metabolic and microbiota parameters. Psychopharmacology 221:155–169
Davey KJ, Cotter PD, O'Sullivan O, Crispie F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF, O'Mahony SM (2013) Antipsychotics and the gut microbiome: olanzapine-induced metabolic dysfunction is attenuated by antibiotic administration in the rat. Transl Psychiatry 3:e309
De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Goncalves D, Vinera J, Zitoun C, Duchampt A, Backhed F, Mithieux G (2014) Microbiota-generated metabolites promote metabolic benefits via gut-brain neural circuits. Cell 156:84–96
van de Wouw M, Schellekens H, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2017) Microbiota-gut-brain axis: modulator of host metabolism and appetite. J Nutr 147:727–745
Dinan TG, Stanton C, Cryan JF (2013) Psychobiotics: a novel class of psychotropic. Biol Psychiatry 74:720–726
Dinan TG, Borre YE, Cryan JF (2014) Genomics of schizophrenia: time to consider the gut microbiome? Mol Psychiatry 19:1252–1257
Erny D, Hrabe de Angelis AL, Jaitin D, Wieghofer P, Staszewski O, David E, Keren-Shaul H, Mahlakoiv T, Jakobshagen K, Buch T, Schwierzeck V, Utermohlen O, Chun E, Garrett WS, McCoy KD, Diefenbach A, Staeheli P, Stecher B, Amit I, Prinz M (2015) Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat Neurosci 18:965–977
Evans SJ, Bassis CM, Hein R, Assari S, Flowers SA, Kelly MB, Young VB, Ellingrod VE, McInnis MG (2017) The gut microbiome composition associates with bipolar disorder and illness severity. J Psychiatr Res 87:23–29
Falony G, Joossens M, Vieira-Silva S, Wang J, Darzi Y, Faust K, Kurilshikov A, Bonder MJ, Valles-Colomer M, Vandeputte D, Tito RY, Chaffron S, Rymenans L, Verspecht C, De Sutter L, Lima-Mendez G, D'Hoe K, Jonckheere K, Homola D, Garcia R, Tigchelaar EF, Eeckhaudt L, Fu J, Henckaerts L, Zhernakova A, Wijmenga C, Raes J (2016) Population-level analysis of gut microbiome variation. Science 352:560–564
Flowers SA, Evans SJ, Ward KM, McInnis MG, Ellingrod VL (2017a) Interaction between atypical antipsychotics and the gut microbiome in a bipolar disease cohort. Pharmacotherapy 37:261–267
Flowers SA, Evans SJ, Ward KM, McInnis MG, Ellingrod VL (2017b) Interaction between atypical antipsychotics and the gut microbiome in a bipolar disease cohort. Pharmacotherapy: J Human Pharmacology Drug Therapy 37:261–267
Forslund K, Hildebrand F, Nielsen T, Falony G, Le Chatelier E, Sunagawa S, Prifti E, Vieira-Silva S, Gudmundsdottir V, Krogh Pedersen H, Arumugam M, Kristiansen K, Yvonne Voigt A, Vestergaard H, Hercog R, Igor Costea P, Roat Kultima J, Li J, Jørgensen T, Levenez F, Dore J, Meta HIT c, Bjørn Nielsen H, Brunak S, Raes J, Hansen T, Wang J, Dusko Ehrlich S, Bork P, Pedersen O (2015) Disentangling type 2 diabetes and metformin treatment signatures in the human gut microbiota. Nature 528:262–266
Foster JA, McVey Neufeld K-A (2013) Gut–brain axis: how the microbiome influences anxiety and depression. Trends Neurosci 36:305–312
Freier TA, Beitz DC, Li L, Hartman PA (1994) Characterization of Eubacterium coprostanoligenes sp. nov., a cholesterol-reducing anaerobe. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:137–142
Gafoor R, Booth HP, Gulliford MC (2018) Antidepressant utilisation and incidence of weight gain during 10 years’ follow-up: population based cohort study. BMJ 361:k1951
Golubeva AV, Joyce SA, Moloney G, Burokas A, Sherwin E, Arboleya S, Flynn I, Khochanskiy D, Moya-Pérez A, Peterson V, Rea K, Murphy K, Makarova O, Buravkov S, Hyland NP, Stanton C, Clarke G, Gahan CGM, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2017) Microbiota-related changes in bile acid and tryptophan metabolism are associated with gastrointestinal dysfunction in a mouse model of autism. EBioMedicine 24:166–178
Goodrich JK, Davenport ER, Waters JL, Clark AG, Ley RE (2016) Cross-species comparisons of host genetic associations with the microbiome. Science 352:532–535
Grubbs FE (1950) Sample criteria for testing outlying observations. Ann Math Stat 21:27–58
Hatta K, Ito H (2014) Strategies for early non-response to antipsychotic drugs in the treatment of acute-phase schizophrenia. Clinical Psychopharmacology Neuroscience 12:1–7
Haub S, Ritze Y, Bergheim I, Pabst O, Gershon MD, Bischoff SC (2010) Enhancement of intestinal inflammation in mice lacking interleukin 10 by deletion of the serotonin reuptake transporter. Neurogastroenterol Motil 22(826–834):e229
Huuskonen J, Suuronen T, Nuutinen T, Kyrylenko S, Salminen A (2004) Regulation of microglial inflammatory response by sodium butyrate and short-chain fatty acids. Br J Pharmacol 141:874–880
Jiang H, Ling Z, Zhang Y, Mao H, Ma Z, Yin Y, Wang W, Tang W, Tan Z, Shi J, Li L, Ruan B (2015) Altered fecal microbiota composition in patients with major depressive disorder. Brain Behav Immun 48:186–194
Kaminska K, Rogoz Z (2016) The antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects following co-treatment with escitalopram and risperidone in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 67:471–480
Kao AC-C, Spitzer S, Anthony DC, Lennox B, Burnet PWJ (2018) Prebiotic attenuation of olanzapine-induced weight gain in rats: analysis of central and peripheral biomarkers and gut microbiota. Transl Psychiatry 8:66
Karl JP, Margolis LM, Madslien EH, Murphy NE, Castellani JW, Gundersen Y, Hoke AV, Levangie MW, Kumar R, Chakraborty N, Gautam A, Hammamieh R, Martini S, Montain SJ, Pasiakos SM (2017) Changes in intestinal microbiota composition and metabolism coincide with increased intestinal permeability in young adults under prolonged physiological stress. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 312:G559–g571
Kelly JR, Borre Y, O’ Brien C, Patterson E, El Aidy S, Deane J, Kennedy PJ, Beers S, Scott K, Moloney G, Hoban AE, Scott L, Fitzgerald P, Ross P, Stanton C, Clarke G, Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2016) Transferring the blues: depression-associated gut microbiota induces neurobehavioural changes in the rat. J Psychiatr Res 82:109–118
Kim KA, Gu W, Lee IA, Joh EH, Kim DH (2012) High fat diet-induced gut microbiota exacerbates inflammation and obesity in mice via the TLR4 signaling pathway. PLoS One 7:e47713
Kiraly DD, Walker DM, Calipari ES, Labonte B, Issler O, Pena CJ, Ribeiro EA, Russo SJ, Nestler EJ (2016) Alterations of the host microbiome affect behavioral responses to cocaine. Sci Rep 6:35455
Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Bäckhed F (2016) From dietary Fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 165:1332–1345
Kong F, Hua Y, Zeng B, Ning R, Li Y, Zhao J (2016) Gut microbiota signatures of longevity. Curr Biol 26:R832–R833
Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Nilsson A, Akrami R, Lee YS, De Vadder F, Arora T, Hallen A, Martens E, Björck I, Bäckhed F (2015) Dietary fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of Prevotella. Cell Metab 22:971–982
Li L, Buhman KK, Hartman PA, Beitz DC (1995) Hypocholesterolemic effect of Eubacterium coprostanoligenes ATCC 51222 in rabbits. Lett Appl Microbiol 20:137–140
Li L, Batt SM, Wannemuehler M, Dispirito A, Beitz DC (1998) Effect of feeding of a cholesterol-reducing bacterium, Eubacterium coprostanoligenes, to germ-free mice. Lab Anim Sci 48:253–255
Li M, Wang B, Sun X, Tang Y, Wei X, Ge B, Tang Y, Deng Y, He C, Yuan J, Li X (2017) Upregulation of intestinal barrier function in mice with DSS-induced colitis by a defined bacterial consortium is associated with expansion of IL-17A producing gamma delta T cells. Front Immunol 8:824
Ling Z, Li Z, Liu X, Cheng Y, Luo Y, Tong X, Yuan L, Wang Y, Sun J, Li L, Xiang C (2014) Altered fecal microbiota composition associated with food allergy in infants. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:2546–2554
López-Contreras BE, Morán-Ramos S, Villarruel-Vázquez R, Macías-Kauffer L, Villamil-Ramírez H, León-Mimila P, Vega-Badillo J, Sánchez-Muñoz F, Llanos-Moreno LE, Canizalez-Román A, Río-Navarro B, Ibarra-González I, Vela-Amieva M, Villarreal-Molina T, Ochoa-Leyva A, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Canizales-Quinteros S (2018) Composition of gut microbiota in obese and normal-weight Mexican school-age children and its association with metabolic traits. Pediatric Obesity 13:381–388
Luna RA, Foster JA (2015) Gut brain axis: diet microbiota interactions and implications for modulation of anxiety and depression. Curr Opin Biotechnol 32:35–41
Lyons L, ElBeltagy M, Bennett G, Wigmore P (2012) Fluoxetine counteracts the cognitive and cellular effects of 5-fluorouracil in the rat hippocampus by a mechanism of prevention rather than recovery. PLoS One 7:e30010
Maier L, Pruteanu M, Kuhn M, Zeller G, Telzerow A, Anderson EE, Brochado AR, Fernandez KC, Dose H, Mori H, Patil KR, Bork P, Typas A (2018) Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria. Nature 555:623–628
Mayer EA, Knight R, Mazmanian SK, Cryan JF, Tillisch K (2014) Gut microbes and the brain: paradigm shift in neuroscience. J Neurosci 34:15490–15496
Mayer EA, Tillisch K, Gupta A (2015) Gut/brain axis and the microbiota. J Clin Invest 125:926–938
Monti B, Gatta V, Piretti F, Raffaelli SS, Virgili M, Contestabile A (2010) Valproic acid is neuroprotective in the rotenone rat model of Parkinson’s disease: involvement of alpha-synuclein. Neurotox Res 17:130–141
Morgan AP, Crowley JJ, Nonneman RJ, Quackenbush CR, Miller CN, Ryan AK, Bogue MA, Paredes SH, Yourstone S, Carroll IM, Kawula TH, Bower MA, Sartor RB, Sullivan PF (2014) The antipsychotic olanzapine interacts with the gut microbiome to cause weight gain in mouse. PLoS One 9:e115225
Morrison DJ, Preston T (2016) Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 7:189–200
Munoz-Bellido JL, Munoz-Criado S, Garcia-Rodriguez JA (1996) In-vitro activity of psychiatric drugs against Corynebacterium urealyticum (Corynebacterium group D2). J Antimicrob Chemother 37:1005–1009
Munoz-Bellido JL, Munoz-Criado S, Garcia-Rodriguez JA (2000) Antimicrobial activity of psychotropic drugs: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Int J Antimicrob Agents 14:177–180
den Besten G, van Eunen K, Groen AK, Venema K, Reijngoud DJ, Bakker BM (2013) The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J Lipid Res 54:2325–2340
Naseribafrouei A, Hestad K, Avershina E, Sekelja M, Linløkken A, Wilson R, Rudi K (2014) Correlation between the human fecal microbiota and depression. Neurogastroenterology Motility 26:1155–1162
Nelson JC (1998) Treatment of antidepressant nonresponders: augmentation or switch? J Clin Psychiatry 59(Suppl 15):35–41
O’Leary OF, O’Connor RM, Cryan JF (2012) Lithium-induced effects on adult hippocampal neurogenesis are topographically segregated along the dorso-ventral axis of stressed mice. Neuropharmacology 62:247–255
O’Mahony SM, Felice VD, Nally K, Savignac HM, Claesson MJ, Scully P, Woznicki J, Hyland NP, Shanahan F, Quigley EM, Marchesi JR, O’Toole PW, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2014) Disturbance of the gut microbiota in early-life selectively affects visceral pain in adulthood without impacting cognitive or anxiety-related behaviors in male rats. Neuroscience 277:885–901
Olguner Eker Ö, ÖZsoy S, Eker B, DoĞAn H (2017) Metabolic effects of antidepressant treatment. Archives Neuropsychiatry 54:49–56
Olivares, M., Neef, A., Castillejo, G., Palma, G. D., Varea, V., Capilla, A., Palau, F., Nova, E., Marcos, A., Polanco, I., Ribes-Koninckx, C., Ortigosa, L., Izquierdo, L., Sanz, Y., 2014. The HLA-DQ2 genotype selects for early intestinal microbiota composition in infants at high risk of developing coeliac disease. Gut
Ott B, Skurk T, Hastreiter L, Lagkouvardos I, Fischer S, Büttner J, Kellerer T, Clavel T, Rychlik M, Haller D, Hauner H (2017) Effect of caloric restriction on gut permeability, inflammation markers, and fecal microbiota in obese women. Sci Rep 7:11955
Paquin-Proulx D, Ching C, Vujkovic-Cvijin I, Fadrosh D, Loh L, Huang Y, Somsouk M, Lynch SV, Hunt PW, Nixon DF, SenGupta D (2016) Bacteroides are associated with GALT iNKT cell function and reduction of microbial translocation in HIV-1 infection. Mucosal Immunol 10:69
Raman M, Ahmed I, Gillevet PM, Probert CS, Ratcliffe NM, Smith S, Greenwood R, Sikaroodi M, Lam V, Crotty P, Bailey J, Myers RP, Rioux KP (2013) Fecal microbiome and volatile organic compound metabolome in obese humans with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clinical Gastroenterology Hepatology 11 e863:868–875
Rath HC, Herfarth HH, Ikeda JS, Grenther WB, Hamm TE Jr, Balish E, Taurog JD, Hammer RE, Wilson KH, Sartor RB (1996) Normal luminal bacteria, especially Bacteroides species, mediate chronic colitis, gastritis, and arthritis in HLA-B27/human beta2 microglobulin transgenic rats. J Clin Invest 98:945–953
Ren D, Li L, Schwabacher AW, Young JW, Beitz DC (1996) Mechanism of cholesterol reduction to coprostanol by Eubacterium coprostanoligenes ATCC 51222. Steroids 61:33–40
Reynolds GP, Kirk SL (2010) Metabolic side effects of antipsychotic drug treatment – pharmacological mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther 125:169–179
Schroeder FA, Lin CL, Crusio WE, Akbarian S (2007) Antidepressant-like effects of the histone deacetylase inhibitor, sodium butyrate, in the mouse. Biol Psychiatry 62:55–64
Schubert AM, Rogers MA, Ring C, Mogle J, Petrosino JP, Young VB, Aronoff DM, Schloss PD (2014) Microbiome data distinguish patients with Clostridium difficile infection and non-C. difficile-associated diarrhea from healthy controls. MBio 5:e01021–e01014
Schwarz E, Maukonen J, Hyytiäinen T, Kieseppä T, Orešič M, Sabunciyan S, Mantere O, Saarela M, Yolken R, Suvisaari J (2017) Analysis of microbiota in first episode psychosis identifies preliminary associations with symptom severity and treatment response. Schizophr Res 192:398–403
Scott KA, Ida M, Peterson VL, Prenderville JA, Moloney GM, Izumo T, Murphy K, Murphy A, Ross RP, Stanton C, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2017) Revisiting Metchnikoff: age-related alterations in microbiota-gut-brain axis in the mouse. Brain Behav Immun 65:20–32
Segnitz N, Schmitt A, Gebicke-Harter PJ, Zink M (2009) Differential expression of glutamate transporter genes after chronic oral treatment with aripiprazole in rats. Neurochem Int 55:619–628
Sogaard B, Mengel H, Rao N, Larsen F (2005) The pharmacokinetics of escitalopram after oral and intravenous administration of single and multiple doses to healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 45:1400–1406
Thursby E, Juge N (2017) Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem J 474:1823–1836
Torres-Fuentes C, Schellekens H, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2017) The microbiota–gut–brain axis in obesity. Lancet Gastroenterology Hepatology 2:747–756
Tschoner A, Engl J, Laimer M, Kaser S, Rettenbacher M, Fleischhacker WW, Patsch JR, Ebenbichler CF (2007) Metabolic side effects of antipsychotic medication. Int J Clin Pract 61:1356–1370
Ulluwishewa D, Anderson RC, McNabb WC, Moughan PJ, Wells JM, Roy NC (2011) Regulation of tight junction permeability by intestinal bacteria and dietary components. J Nutr 141:769–776
Vidal R, Valdizan E, Vilaró M, Pazos A, Castro E (2010) Reduced signal transduction by 5-HT4 receptors after long-term venlafaxine treatment in rats. Br J Pharmacol 161:695–706
Wade PR, Chen J, Jaffe B, Kassem IS, Blakely RD, Gershon MD (1996) Localization and function of a 5-HT transporter in crypt epithelia of the gastrointestinal tract. J Neurosci 16:2352–2364
Walter J (2008) Ecological role of lactobacilli in the gastrointestinal tract: implications for fundamental and biomedical research. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:4985–4996
Watase K, Gatchel JR, Sun Y, Emamian E, Atkinson R, Richman R, Mizusawa H, Orr HT, Shaw C, Zoghbi HY (2007) Lithium therapy improves neurological function and hippocampal dendritic arborization in a spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 mouse model. PLoS Med 4:e182
World Health Organization, 2017. Depression and other common mental disorders: global health estimates. Geneva
Wu H, Esteve E, Tremaroli V, Khan MT, Caesar R, Mannerås-Holm L, Ståhlman M, Olsson LM, Serino M, Planas-Fèlix M, Xifra G, Mercader JM, Torrents D, Burcelin R, Ricart W, Perkins R, Fernàndez-Real JM, Bäckhed F (2017) Metformin alters the gut microbiome of individuals with treatment-naive type 2 diabetes, contributing to the therapeutic effects of the drug. Nat Med 23:850–858
Xie, Y., Zhou, G., Wang, C., Xu, X., Li, C., 2018. Temporal changes in gut microbiota and signaling molecules of the gut-brain axis in mice fed meat protein diets. bioRxiv
Yamada T, Inui A, Hayashi N, Fujimura M, Fujimiya M (2003) Serotonin stimulates endotoxin translocation via 5-HT3 receptors in the rat ileum. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284:G782–G788
Zhan G, Yang N, Li S, Huang N, Fang X, Zhang J, Zhu B, Yang L, Yang C, Luo A (2018) Abnormal gut microbiota composition contributes to cognitive dysfunction in SAMP8 mice. Aging (Albany NY) 10:1257–1267
Zheng P, Zeng B, Zhou C, Liu M, Fang Z, Xu X, Zeng L, Chen J, Fan S, Du X, Zhang X, Yang D, Yang Y, Meng H, Li W, Melgiri ND, Licinio J, Wei H, Xie P (2016) Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host's metabolism. Mol Psychiatry 21:786–796
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Pat Fitzgerald, Gonzalo Rabasa, Karen Scott, Gilliard Lach, Gerry Moloney, Anna Golubeva and Kieran Rea for their invaluable support. We would also like to acknowledge Wiley Barton for his assistance in R scripts and the Teagasc Sequencing Facility, Dr. Paul Cotter, Dr. Fiona Crispie and Ms. Laura Finnegan.
Funding
APC Microbiome Ireland is a research centre funded by Science Foundation Ireland (SFI), through the Irish Government’s National Development Plan (grant no. 12/RC/2273). JFC, TGD and CS have research funding from Dupont Nutrition Biosciences APS, Cremo SA, Alkermes Inc., 4D Pharma PLC, Mead Johnson Nutrition, Nutricia Danone, Suntory Wellness. JFC, TGD, CS and GC have spoken at meetings sponsored by food and pharmaceutical companies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Experiments were conducted in accordance with the European Directive 2010/63/EU. Approval by the Animal Experimentation Ethics Committee of University College Cork was obtained before commencement of all animal-related experiments.
Conflict of interest
All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article belongs to a Special Issue on Microbiome in Psychiatry & Psychopharmacology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cussotto, S., Strain, C.R., Fouhy, F. et al. Differential effects of psychotropic drugs on microbiome composition and gastrointestinal function. Psychopharmacology 236, 1671–1685 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5006-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-5006-5