Abstract
Rationale
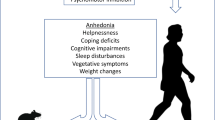
Despite substantial research efforts the aetiology of major depressive disorder (MDD) remains poorly understood, which is due in part to the heterogeneity of the disorder and the complexity of designing appropriate animal models. However, in the last few decades, a focus on the development of novel stress-based paradigms and a focus on using hedonic/anhedonic behaviour have led to renewed optimism in the use of animal models to assess aspects of MDD.
Objectives
Therefore, in this review article, dedicated to Athina Markou, we summarise the use of stress-based animal models for studying MDD in rodents and how reward-related readouts can be used to validate/assess the model and/or treatment.
Results
We reveal the use and limitations of chronic stress paradigms, which we split into non-social (i.e. chronic mild stress), social (i.e. chronic social defeat) and drug-withdrawal paradigms for studying MDD and detail numerous reward-related readouts that are employed in preclinical research. Finally, we finish with a section regarding important factors to consider when using animal models.
Conclusions
One of the most consistent findings following chronic stress exposure in rodents is a disruption of the brain reward system, which can be easily assessed using sucrose, social interaction, food, drug of abuse or intracranial self-stimulation as a readout. Probing the underlying causes of such alterations is providing a greater understanding of the potential systems and processes that are disrupted in MDD.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bale TL, Epperson CN (2016) Sex as a Biological Variable: Who, What, When, Why, and How. Neuropsychopharmacology
Baranyi J, Bakos N, Haller J (2005) Social instability in female rats: the relationship between stress-related and anxiety-like consequences. Physiol Behav 84:511–518
Barnes SA, Der-Avakian A, Markou A (2014) Anhedonia, avolition, and anticipatory deficits: assessments in animals with relevance to the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 24:744–758
Bartlang MS, Neumann ID, Slattery DA, Uschold-Schmidt N, Kraus D, Helfrich-Forster C, Reber SO (2012) Time matters: pathological effects of repeated psychosocial stress during the active, but not inactive, phase of male mice. J Endocrinol 215:425–437
Bateson P, Gluckman P, Hanson M (2014) The biology of developmental plasticity and the predictive adaptive response hypothesis. J Physiol 592:2357–2368
Belujon P, Jakobowski NL, Dollish HK, Grace AA (2016) Withdrawal from acute amphetamine induces an amygdala-driven attenuation of dopamine neuron activity: reversal by ketamine. Neuropsychopharmacology 41:619–627
Belzung C (2014) Innovative drugs to treat depression: did animal models fail to be predictive or did clinical trials fail to detect effects? Neuropsychopharmacology 39:1041–1051
Belzung C, Lemoine M (2011) Criteria of validity for animal models of psychiatric disorders: focus on anxiety disorders and depression. Biol Mood Anxiety Disord 1:9
Berton O, McClung CA, Dileone RJ, Krishnan V, Renthal W, Russo SJ, Graham D, Tsankova NM, Bolanos CA, Rios M, Monteggia LM, Self DW, Nestler EJ (2006) Essential role of BDNF in the mesolimbic dopamine pathway in social defeat stress. Science 311:864–868
Berton O, Hahn CG, Thase ME (2012) Are we getting closer to valid translational models for major depression? Science 338:75–79
Bredt DS, Furey ML, Chen G, Lovenberg T, Drevets WC, Manji HK (2015) Translating depression biomarkers for improved targeted therapies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 59:1–15
Brockhurst J, Cheleuitte-Nieves C, Buckmaster CL, Schatzberg AF, Lyons DM (2015) Stress inoculation modeled in mice. Transl Psychiatry 5:e537
Brown KJ, Grunberg NE (1995) Effects of housing on male and female rats: crowding stresses male but calm females. Physiol Behav 58:1085–1089
Buwalda B, Stubbendorff C, Zickert N, Koolhaas JM (2013) Adolescent social stress does not necessarily lead to a compromised adaptive capacity during adulthood: a study on the consequences of social stress in rats. Neuroscience 249:258–270
Calati R, Salvina Signorelli M, Balestri M, Marsano A, De Ronchi D, Aguglia E, Serretti A (2013) Antidepressants in elderly: metaregression of double-blind, randomized clinical trials. J Affect Disord 147:1–8
Casey BJ, Craddock N, Cuthbert BN, Hyman SE, Lee FS, Ressler KJ (2013) DSM-5 and RDoC: progress in psychiatry research? Nat Rev Neurosci 14:810–814
Chadman KK, Yang M, Crawley JN (2009) Criteria for validating mouse models of psychiatric diseases. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 150B:1–11
Chaouloff F (2013) Social stress models in depression research: what do they tell us? Cell Tissue Res 354:179–190
Chen F, Wegener G, Madsen TM, Nyengaard JR (2013) Mitochondrial plasticity of the hippocampus in a genetic rat model of depression after antidepressant treatment. Synapse 67:127–134
Couillard-Despres S, Wuertinger C, Kandasamy M, Caioni M, Stadler K, Aigner R, Bogdahn U, Aigner L (2009) Ageing abolishes the effects of fluoxetine on neurogenesis. Mol Psychiatry 14:856–864
Crabbe JC, Wahlsten D, Dudek BC (1999) Genetics of mouse behavior: interactions with laboratory environment. Science 284:1670–1672
Crofton EJ, Zhang Y, Green TA (2015) Inoculation stress hypothesis of environmental enrichment. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 49:19–31
Crowley JJ, Blendy JA, Lucki I (2005) Strain-dependent antidepressant-like effects of citalopram in the mouse tail suspension test. Psychopharmacology 183:257–264
Cryan JF, Holmes A (2005) The ascent of mouse: advances in modelling human depression and anxiety. Nat Rev 4:775–790
Cryan JF, Slattery DA (2007) Animal models of mood disorders: recent developments. Curr Opin Psychiatry 20:1–7
Cryan JF, Slattery DA (2010) Animal models of depression - where are we going? In: Cryan JF, Leonard BE (eds) Experimental models of depression and the mechanisms of action of antidepressants. S. Karger, A.G, Basal
Cryan JF, Sweeney FF (2011) The age of anxiety: role of animal models of anxiolytic action in drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol 164:1129–1161
Cryan JF, Markou A, Lucki I (2002) Assessing antidepressant activity in rodents: recent developments and future needs. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:238–245
Cryan JF, Hoyer D, Markou A (2003) Withdrawal from chronic amphetamine induces depressive-like behavioral effects in rodents. Biol Psychiatry 54:49–58
Cryan JF, Mombereau C, Vassout A (2005) The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:571–625
Cuthbert BN, Insel TR (2013) Toward the future of psychiatric diagnosis: the seven pillars of RDoC. BMC Med 11:126
Czeh B, Fuchs E, Wiborg O, Simon M (2016) Animal models of major depression and their clinical implications. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 64:293–310
Dalla C, Pitychoutis PM, Kokras N, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z (2010) Sex differences in animal models of depression and antidepressant response. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 106:226–233
Dalla C, Pitychoutis PM, Kokras N, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z (2011) Sex differences in response to stress and expression of depressive-like behaviours in the rat. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 8:97–118
Daskalakis NP, Bagot RC, Parker KJ, Vinkers CH, de Kloet ER (2013) The three-hit concept of vulnerability and resilience: toward understanding adaptation to early-life adversity outcome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38:1858–1873
Der-Avakian A, Markou A (2012) The neurobiology of anhedonia and other reward-related deficits. Trends Neurosci 35:68–77
Der-Avakian A, D’Souza MS, Pizzagalli DA, Markou A (2013) Assessment of reward responsiveness in the response bias probabilistic reward task in rats: implications for cross-species translational research. Transl Psychiatry 3:e297
Der-Avakian A, Mazei-Robison MS, Kesby JP, Nestler EJ, Markou A (2014) Enduring deficits in brain reward function after chronic social defeat in rats: susceptibility, resilience, and antidepressant response. Biol Psychiatry 76:542–549
Drevets WC, Price JL, Furey ML (2008) Brain structural and functional abnormalities in mood disorders: implications for neurocircuitry models of depression. Brain Struct Funct 213:93–118
Drysdale AT, Grosenick L, Downar J, Dunlop K, Mansouri F, Meng Y, Fetcho RN, Zebley B, Oathes DJ, Etkin A, Schatzberg AF, Sudheimer K, Keller J, Mayberg HS, Gunning FM, Alexopoulos GS, Fox MD, Pascual-Leone A, Voss HU, Casey BJ, Dubin MJ, Liston C (2017) Resting-state connectivity biomarkers define neurophysiological subtypes of depression. Nat Med 23:28–38
Dulawa SC, Hen R (2005) Recent advances in animal models of chronic antidepressant effects: the novelty-induced hypophagia test. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:771–783
El Yacoubi M, Rappeneau V, Champion E, Malleret G, Vaugeois JM (2013) The H/Rouen mouse model displays depression-like and anxiety-like behaviors. Behav Brain Res 256:43–50
Figlewicz DP, Bennett J, Evans SB, Kaiyala K, Sipols AJ, Benoit SC (2004) Intraventricular insulin and leptin reverse place preference conditioned with high-fat diet in rats. Behav Neurosci 118:479–487
Frazer A, Morilak DA (2005) What should animal models of depression model? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:515–523
Friedman AK, Walsh JJ, Juarez B, Ku SM, Chaudhury D, Wang J, Li X, Dietz DM, Pan N, Vialou VF, Neve RL, Yue Z, Han MH (2014) Enhancing depression mechanisms in midbrain dopamine neurons achieves homeostatic resilience. Science 344:313–319
Friedman AK, Juarez B, Ku SM, Zhang H, Calizo RC, Walsh JJ, Chaudhury D, Zhang S, Hawkins A, Dietz DM, Murrough JW, Ribadeneira M, Wong EH, Neve RL, Han MH (2016) KCNQ channel openers reverse depressive symptoms via an active resilience mechanism. Nat Commun 7:11671
Fuchs E (2005) Social stress in tree shrews as an animal model of depression: an example of a behavioral model of a CNS disorder. CNS Spectr 10:182–190
Fuertig R, Azzinnari D, Bergamini G, Cathomas F, Sigrist H, Seifritz E, Vavassori S, Luippold A, Hengerer B, Ceci A, Pryce CR (2016) Mouse chronic social stress increases blood and brain kynurenine pathway activity and fear behaviour: both effects are reversed by inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Brain Behav Immun 54:59–72
Galea LA, Frick KM, Hampson E, Sohrabji F, Choleris E (2016) Why estrogens matter for behavior and brain health. Neurosci Biobehav Rev
Geyer MA, Markou A (1995a) Animal models of psychiatric disorders. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation of progress. Raven Press, New York, pp 787–798
Geyer MA, Markou A (1995b) Animal models of psychiatric disorders. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology - the 4th generation of progress. Raven, New York, pp 787–798
Gobinath AR, Mahmoud R, Galea LA (2014) Influence of sex and stress exposure across the lifespan on endophenotypes of depression: focus on behavior, glucocorticoids, and hippocampus. Front Neurosci 8:420
Gosselin RD, Gibney S, O’Malley D, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2009) Region specific decrease in glial fibrillary acidic protein immunoreactivity in the brain of a rat model of depression. Neuroscience 159:915–925
Gottesman II, Gould TD (2003) The endophenotype concept in psychiatry: etymology and strategic intentions. Am J Psychiatry 160:636–645
Gould TD, Einat H (2007) Animal models of bipolar disorder and mood stabilizer efficacy: a critical need for improvement. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 31:825–831
Gould TD, Gottesman II (2006) Psychiatric endophenotypes and the development of valid animal models. Genes Brain Behav 5:113–119
Hasler G, Northoff G (2011) Discovering imaging endophenotypes for major depression. Mol Psychiatry 16:604–619
Hasler G, Drevets WC, Manji HK, Charney DS (2004) Discovering endophenotypes for major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1765–1781
Hasler G, Neumeister A, van der Veen JW, Tumonis T, Bain EE, Shen J, Drevets WC, Charney DS (2005) Normal Prefrontal Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Levels in Remitted Depressed Subjects Determined by Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Biol Psychiatry
Henn FA, Vollmayr B (2005) Stress models of depression: forming genetically vulnerable strains. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:799–804
Hill MN, Hellemans KG, Verma P, Gorzalka BB, Weinberg J (2012) Neurobiology of chronic mild stress: parallels to major depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:2085–2117
Hillerer KM, Neumann ID, Slattery DA (2012) From stress to postpartum mood and anxiety disorders: how chronic peripartum stress can impair maternal adaptations. Neuroendocrinology 95:22–38
Hillerer KM, Neumann ID, Couillard-Despres S, Aigner L, Slattery DA (2013) Sex-dependent regulation of hippocampal neurogenesis under basal and chronic stress conditions in rats. Hippocampus 23:476–487
Ineichen C, Sigrist H, Spinelli S, Lesch KP, Sautter E, Seifritz E, Pryce CR (2012) Establishing a probabilistic reversal learning test in mice: evidence for the processes mediating reward-stay and punishment-shift behaviour and for their modulation by serotonin. Neuropharmacology 63:1012–1021
Jacobson LH, Cryan JF (2005) Differential sensitivity to the motor and hypothermic effects of the GABA B receptor agonist baclofen in various mouse strains. Psychopharmacology 179:688–699
Jacobson LH, Cryan JF (2007) Feeling strained? Influence of genetic background on depression-related behavior in mice: a review. Behav Genet 37:171–213
Jonkman S, Kenny PJ (2013) Molecular, cellular, and structural mechanisms of cocaine addiction: a key role for microRNAs. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:198–211
Katz RJ (1981) Animal model of depression: effects of electroconvulsive shock therapy. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 5:273–277
Kelly JP, Wrynn AS, Leonard BE (1997) The olfactory bulbectomized rat as a model of depression: an update. Pharmacol Ther 74:299–316
Kendler KS, Gardner CO, Prescott CA (1999) Clinical characteristics of major depression that predict risk of depression in relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56:322–327
Kenny PJ (2011) Common cellular and molecular mechanisms in obesity and drug addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:638–651
Kenny PJ, Markou A (2004) The ups and downs of addiction: role of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:265–272
Kessler RC (2003) Epidemiology of women and depression. J Affect Disord 74:5–13
Kokras N, Dalla C (2014) Sex Differences in Animal Models of Psychiatric Disorders. British journal of pharmacology
Kokras N, Dalla C, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z (2011) Sex differences in pharmacokinetics of antidepressants. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 7:213–226
Koob GF, Volkow ND (2016) Neurobiology of addiction: a neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 3:760–773
Krishnan V, Han MH, Graham DL, Berton O, Renthal W, Russo SJ, Laplant Q, Graham A, Lutter M, Lagace DC, Ghose S, Reister R, Tannous P, Green TA, Neve RL, Chakravarty S, Kumar A, Eisch AJ, Self DW, Lee FS, Tamminga CA, Cooper DC, Gershenfeld HK, Nestler EJ (2007) Molecular adaptations underlying susceptibility and resistance to social defeat in brain reward regions. Cell 131:391–404
Landgraf R, Kessler MS, Bunck M, Murgatroyd C, Spengler D, Zimbelmann M, Nussbaumer M, Czibere L, Turck CW, Singewald N, Rujescu D, Frank E (2007) Candidate genes of anxiety-related behavior in HAB/LAB rats and mice: focus on vasopressin and glyoxalase-I. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 31:89–102
Langgartner D, Fuchsl AM, Uschold-Schmidt N, Slattery DA, Reber SO (2015) Chronic subordinate colony housing paradigm: a mouse model to characterize the consequences of insufficient glucocorticoid signaling. Front Psychiatry 6:18
Langgartner D, Foertsch S, Fuchsl AM, Reber SO (2016a) Light and water are not simple conditions: Fine tuning of animal housing in male C57BL/6 mice. Stress: 1–23
Langgartner D, Peterlik D, Foertsch S, Füchsl AM, Brokmann P, Flor PJ, Shen Z, Fox JG, Uschold-Schmidt N, Lowry CA, Reber SO (2016b) Individual differences in stress vulnerability: the role of gut pathobionts in stress-induced colitis. Brain Behav Immun. doi.10.1016/j.bbi.2016.12.019
Lhuillier L, Mombereau C, Cryan JF, Kaupmann K (2007) GABA(B) receptor-positive modulation decreases selective molecular and behavioral effects of cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:388–398
Lucassen PJ, Bosch OJ, Jousma E, Kromer SA, Andrew R, Seckl JR, Neumann ID (2009) Prenatal stress reduces postnatal neurogenesis in rats selectively bred for high, but not low, anxiety: possible key role of placental 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2. Eur J Neurosci 29:97–103
Lucki I (1997) The forced swimming test as a model for core and component behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs. Behav Pharmacol 8:523–532
Lucki I, Dalvi A, Mayorga AJ (2001) Sensitivity to the effects of pharmacologically selective antidepressants in different strains of mice. Psychopharmacology 155:315–322
Malkesman O, Weller A (2009) Two different putative genetic animal models of childhood depression--a review. Prog Neurobiol 88:153–169
Malkesman O, Scattoni ML, Paredes D, Tragon T, Pearson B, Shaltiel G, Chen G, Crawley JN, Manji HK (2010) The female urine sniffing test: a novel approach for assessing reward-seeking behavior in rodents. Biol Psychiatry 67:864–871
Markou A, Kosten TR, Koob GF (1998) Neurobiological similarities in depression and drug dependence: a self-medication hypothesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 18:135–174
Markou A, Chiamulera C, Geyer MA, Tricklebank M, Steckler T (2009) Removing obstacles in neuroscience drug discovery: the future path for animal models. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:74–89
Markou A, Salamone JD, Bussey TJ, Mar AC, Brunner D, Gilmour G, Balsam P (2013) Measuring reinforcement learning and motivation constructs in experimental animals: relevance to the negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:2149–2165
McArthur R, Borsini F (2006) Animal models of depression in drug discovery: a historical perspective. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 84:436–452
McGrath JJ, Saha S, Al-Hamzawi A, Andrade L, Benjet C, Bromet EJ, Browne MO, Caldas de Almeida JM, Chiu WT, Demyttenaere K, Fayyad J, Florescu S, de Girolamo G, Gureje O, Haro JM, Ten Have M, Hu C, Kovess-Masfety V, Lim CC, Navarro-Mateu F, Sampson N, Posada-Villa J, Kendler KS, Kessler RC (2016) The bidirectional associations between psychotic experiences and DSM-IV mental disorders. Am J Psychiatry 173:997–1006
McKinney WT Jr, Bunney WE Jr (1969) Animal model of depression. I. Review of evidence: implications for research. Arch Gen Psychiatry 21:240–248
Mombereau C, Lhuillier L, Kaupmann K, Cryan JF (2007) GABA(B) receptor-positive modulation-induced blockade of the rewarding properties of nicotine is associated with a reduction in nucleus accumbens Delta FosB accumulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:172–177
Moreau JL, Scherschlicht R, Jenck F, Martin JR (1995) Chronic mild stress-induced anhedonia model of depression; sleep abnormalities and curative effects of electroshock treatment. Behav Pharmacol 6:682–687
Nederhof E, Schmidt MV (2012) Mismatch or cumulative stress: toward an integrated hypothesis of programming effects. Physiol Behav 106:691–700
Nestler EJ, Hyman SE (2010) Animal models of neuropsychiatric disorders. Nat Neurosci 13:1161–1169
Neumann ID, Wegener G, Homberg JR, Cohen H, Slattery DA, Zohar J, Olivier JD, Mathe AA (2011) Animal models of depression and anxiety: what do they tell us about human condition? Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:1357–1375
O’Leary OF, Cryan JF (2013) Towards translational rodent models of depression. Cell Tissue Res 354:141–153
O’Connor RM, Pusceddu MM, O’Leary OF, Savignac HM, Bravo JA, El Yacoubi M, Vaugeois JM, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2013) Hippocampal group III mGlu receptor mRNA levels are not altered in specific mouse models of stress, depression and antidepressant action. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103:561–567
Olds J, Milner P (1954) Positive reinforcement produced by electrical stimulation of septal area and other regions of rat brain. J Comp Physiol Psychol 47:419–427
O’Mahony SM, Marchesi JR, Scully P, Codling C, Ceolho AM, Quigley EM, Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2009) Early life stress alters behavior, immunity, and microbiota in rats: implications for irritable bowel syndrome and psychiatric illnesses. Biol Psychiatry 65:263–267
Perani CV, Slattery DA (2014) Using Animal Models to study Postpartum Psychiatric Disorders. British journal of pharmacology
Phillips AG, Blaha CD, Fibiger HC (1989) Neurochemical correlates of brain-stimulation reward measured by ex vivo and in vivo analyses. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 13:99–104
Picciotto MR, Kenny PJ (2013) Molecular mechanisms underlying behaviors related to nicotine addiction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 3:a012112
Pizzagalli DA, Jahn AL, O’Shea JP (2005) Toward an objective characterization of an anhedonic phenotype: a signal-detection approach. Biol Psychiatry 57:319–327
Pizzagalli DA, Evins AE, Schetter EC, Frank MJ, Pajtas PE, Santesso DL, Culhane M (2008) Single dose of a dopamine agonist impairs reinforcement learning in humans: behavioral evidence from a laboratory-based measure of reward responsiveness. Psychopharmacology 196:221–232
Pryce CR, Fuchs E (2017) Chronic psychosocial stressors in adulthood: studies in mice, rats and tree shrews. Neurobiology of Stress (in press)
Pryce CR, Seifritz E (2011) A translational research framework for enhanced validity of mouse models of psychopathological states in depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36:308–329
Pryce CR, Ruedi-Bettschen D, Dettling AC, Weston A, Russig H, Ferger B, Feldon J (2005) Long-term effects of early-life environmental manipulations in rodents and primates: potential animal models in depression research. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:649–674
Pryce CR, Azzinnari D, Spinelli S, Seifritz E, Tegethoff M, Meinlschmidt G (2011) Helplessness: a systematic translational review of theory and evidence for its relevance to understanding and treating depression. Pharmacol Ther 132:242–267
Razzoli M, Carboni L, Andreoli M, Ballottari A, Arban R (2011) Different susceptibility to social defeat stress of BalbC and C57BL6/J mice. Behav Brain Res 216:100–108
Reber SO (2012) Stress and animal models of inflammatory bowel disease--an update on the role of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 37:1–19
Reber SO, Siebler PH, Donner NC, Morton JT, Smith DG, Kopelman JM, Lowe KR, Wheeler KJ, Fox JH, Hassell JE, Jr, Greenwood BN, Jansch C, Lechner A, Schmidt D, Uschold-Schmidt N, Fuchsl AM, Langgartner D, Walker FR, Hale MW, Lopez Perez G, Van Treuren W, Gonzalez A, Halweg-Edwards AL, Fleshner M, Raison CL, Rook GA, Peddada SD, Knight R, Lowry CA (2016) Immunization with a heat-killed preparation of the environmental bacterium Mycobacterium vaccae promotes stress resilience in mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 113: E3130–9
Rizvi SJ, Pizzagalli DA, Sproule BA, Kennedy SH (2016) Assessing anhedonia in depression: potentials and pitfalls. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 65:21–35
Robinson ES, Roiser JP (2016) Affective biases in humans and animals. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 28:263–286
Russo SJ, Murrough JW, Han MH, Charney DS, Nestler EJ (2012) Neurobiology of resilience. Nat Neurosci 15:1475–1484
Sah A, Schmuckermair C, Sartori SB, Gaburro S, Kandasamy M, Irschick R, Klimaschewski L, Landgraf R, Aigner L, Singewald N (2012) Anxiety- rather than depression-like behavior is associated with adult neurogenesis in a female mouse model of higher trait anxiety- and comorbid depression-like behavior. Transl Psychiatry 2:e171
Santarelli S, Lesuis SL, Wang XD, Wagner KV, Hartmann J, Labermaier C, Scharf SH, Muller MB, Holsboer F, Schmidt MV (2014) Evidence supporting the match/mismatch hypothesis of psychiatric disorders. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 24:907–918
Savignac HM, Finger BC, Pizzo RC, O’Leary OF, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2011) Increased sensitivity to the effects of chronic social defeat stress in an innately anxious mouse strain. Neuroscience 192:524–536
Savitz JB, Drevets WC (2013) Neuroreceptor imaging in depression. Neurobiol Dis 52:49–65
Schmidt MV (2011) Animal models for depression and the mismatch hypothesis of disease. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36:330–338
Schmidt MV, Sterlemann V, Muller MB (2008) Chronic stress and individual vulnerability. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1148:174–183
Schmidt MV, Scharf SH, Liebl C, Harbich D, Mayer B, Holsboer F, Muller MB (2010) A novel chronic social stress paradigm in female mice. Horm Behav 57:415–420
Schultz W (2016) Dopamine reward prediction-error signalling: a two-component response. Nat Rev Neurosci 17:183–195
Seese RR, Chen LY, Cox CD, Schulz D, Babayan AH, Bunney WE, Henn FA, Gall CM, Lynch G (2013) Synaptic abnormalities in the infralimbic cortex of a model of congenital depression. J Neurosci 33:13441–13448
Sherwin E, Rea K, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2016a) A gut (microbiome) feeling about the brain. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 32:96–102
Sherwin E, Sandhu KV, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2016b) May the Force Be With You: The Light and Dark Sides of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Neuropsychiatry. CNS Drugs
Slattery DA, Cryan JF (2011) Animal models of depression – where are We going? In: Cryan JF, Leonard BE (eds) Depression: from psychopathology to pharmacotherapy. S. Karger AG, Basel
Slattery DA, Cryan JF (2014) The ups and downs of modelling mood disorders in rodents. ILAR J 55:297–309
Slattery DA, Hillerer KM (2016) The maternal brain under stress: consequences for adaptive peripartum plasticity and its potential functional implications. Front Neuroendocrinol 41:114–128
Slattery DA, Markou A, Cryan JF (2007) Evaluation of reward processes in an animal model of depression. Psychopharmacology 190:555–568
Song C, Leonard BE (2005) The olfactory bulbectomised rat as a model of depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:627–647
Sorge RE, Martin LJ, Isbester KA, Sotocinal SG, Rosen S, Tuttle AH, Wieskopf JS, Acland EL, Dokova A, Kadoura B, Leger P, Mapplebeck JC, McPhail M, Delaney A, Wigerblad G, Schumann AP, Quinn T, Frasnelli J, Svensson CI, Sternberg WF, Mogil JS (2014) Olfactory exposure to males, including men, causes stress and related analgesia in rodents. Nat Methods 11:629–632
Stuart SA, Butler P, Munafo MR, Nutt DJ, Robinson ES (2013) A translational rodent assay of affective biases in depression and antidepressant therapy. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1625–1635
Tanti A, Belzung C (2010) Open questions in current models of antidepressant action. Br J Pharmacol 159:1187–1200
Vialou V, Robison AJ, Laplant QC, Covington HE 3rd, Dietz DM, Ohnishi YN, Mouzon E, Rush AJ 3rd, Watts EL, Wallace DL, Iniguez SD, Ohnishi YH, Steiner MA, Warren BL, Krishnan V, Bolanos CA, Neve RL, Ghose S, Berton O, Tamminga CA, Nestler EJ (2010) DeltaFosB in brain reward circuits mediates resilience to stress and antidepressant responses. Nat Neurosci 13:745–752
Volkow ND, Morales M (2015) The brain on drugs: from reward to addiction. Cell 162:712–725
Volkow ND, Koob GF, McLellan AT (2016) Neurobiologic advances from the brain disease model of addiction. N Engl J Med 374:363–371
Willner P (1984) The validity of animal models of depression. Psychopharmacology 83:1–16
Willner P (2005) Chronic mild stress (CMS) revisited: consistency and behavioural-neurobiological concordance in the effects of CMS. Neuropsychobiology 52:90–110
Willner P, Belzung C (2015) Treatment-resistant depression: are animal models of depression fit for purpose? Psychopharmacology 232:3473–3495
Willner P, Towell A, Sampson D, Sophokleous S, Muscat R (1987) Reduction of sucrose preference by chronic unpredictable mild stress, and its restoration by a tricyclic antidepressant. Psychopharmacology 93:358–364
Wise RA (2002) Brain reward circuitry: insights from unsensed incentives. Neuron 36:229–240
Wittchen HU, Jacobi F, Rehm J, Gustavsson A, Svensson M, Jonsson B, Olesen J, Allgulander C, Alonso J, Faravelli C, Fratiglioni L, Jennum P, Lieb R, Maercker A, van Os J, Preisig M, Salvador-Carulla L, Simon R, Steinhausen HC (2011) The size and burden of mental disorders and other disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21:655–679
Young JW, Markou A (2015) Translational rodent paradigms to investigate Neuromechanisms underlying behaviors relevant to Amotivation and altered reward processing in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 41:1024–1034
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Funding
JFC is funded by Science Foundation Ireland (SFI), through the Irish Government’s National Development Plan in the form of a centre grant (Alimentary Pharmabiotic Centre Grant Number SFI/12/RC/2273).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slattery, D.A., Cryan, J.F. Modelling depression in animals: at the interface of reward and stress pathways. Psychopharmacology 234, 1451–1465 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4552-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-017-4552-6