Abstract
Rationale
Early life stress is a major risk factor for cocaine addiction; however, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain relatively unexplored. MicroRNA-212 (miR-212) and methyl CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) have recently emerged as key regulators of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling during the acquisition and maintenance of cocaine-seeking behaviors.
Objectives
We therefore investigated the effect of maternal separation (MS) on cocaine-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) during periadolescence and how this influences miR-212, Mecp2, and Bdnf expressions in the prefrontal cortex.
Methods
Male BALB/c mice subjected to MS (3 h/day) from postnatal day 2 to 15 or normal animal facility rearing (AFR) were tested for CPP at postnatal day 45, or not exposed to experimental manipulations (drug-naïve animals). Cultured primary cortical neurons were used to determine miR-212 expression changes following depolarization by KCL treatment.
Results
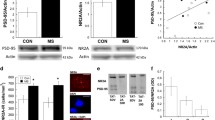
MS increased cocaine-induced CPP and decreased Bdnf exon IV expression, which correlated with higher CPP scores in such animals. An experience-dependent decrease in miR-212 expression was observed following CPP test. This effect was mimicked in primary cortical neurons in vitro, under activity-dependent conditions. In contrast, increased Mecp2 expression was found after CPP test, suggesting an opposing relationship between miR-212 and Mecp2 expression following cocaine place preference acquisition. However, these effects were not present in mice exposed to MS.
Conclusions
Together, our results suggest that early life stress can enhance the motivational salience for cocaine-paired cues during periadolescence, and that altered expression of miR-212, Mecp2, and Bdnf in the prefrontal cortex is involved in this process.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand KJ, Scalzo FM (2000) Can adverse neonatal experiences alter brain development and subsequent behavior? Biol Neonate 77:69–82
Andersen SL, Teicher MH (2004) Delayed effects of early stress on hippocampal development. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1988–1993
Andersen SL, Teicher MH (2009) Desperately driven and no brakes: developmental stress exposure and subsequent risk for substance abuse. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33:516–524
Baker-Andresen D, Flavell CR, Li X, Bredy TW (2013) Activation of BDNF signaling prevents the return of fear in female mice. Learn Mem 20:237–240
Bali P, Kenny PJ (2013) MicroRNAs and drug addiction. Front Genet 4:43
Barik J, Parnaudeau S, Saint Amaux AL, Guiard BP, Golib Dzib JF, Bocquet O, Bailly A, Benecke A, Tronche F (2010) Glucocorticoid receptors in dopaminoceptive neurons, key for cocaine, are dispensable for molecular and behavioral morphine responses. Biol Psychiatry 68:231–239
Baroukh N, Ravier MA, Loder MK, Hill EV, Bounacer A, Scharfmann R, Rutter GA, Van Obberghen E (2007) MicroRNA-124a regulates Foxa2 expression and intracellular signaling in pancreatic beta-cell lines. J Biol Chem 282:19575–19588
Berglind WJ, See RE, Fuchs RA, Ghee SM, Whitfield TW, Miller SW, McGinty JF (2007) A BDNF infusion into the medial prefrontal cortex suppresses cocaine seeking in rats. Eur J Neurosci 26:757–766
Bhansali P, Dunning J, Singer SE, David L, Schmauss C (2007) Early life stress alters adult serotonin 2C receptor pre-mRNA editing and expression of the alpha subunit of the heterotrimeric G-protein G q. J Neurosci 27:1467–1473
Blaze J, Asok A, Roth TL (2015) Long-term effects of early-life caregiving experiences on brain-derived neurotrophic factor histone acetylation in the adult rat mPFC. Stress 18:607–615
Boku S, Toda H, Nakagawa S, Kato A, Inoue T, Koyama T, Hiroi N, Kusumi I (2015) Neonatal maternal separation alters the capacity of adult neural precursor cells to differentiate into neurons via methylation of retinoic acid receptor gene promoter. Biol Psychiatry 77:335–344
Bredy TW, Lin Q, Wei W, Baker-Andresen D, Mattick JS (2011) MicroRNA regulation of neural plasticity and memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 96:89–94
Bredy TW, Wu H, Crego C, Zellhoefer J, Sun YE, Barad M (2007) Histone modifications around individual BDNF gene promoters in prefrontal cortex are associated with extinction of conditioned fear. Learn Mem 14:268–276
Calfa G, Li W, Rutherford JM, Pozzo-Miller L (2015) Excitation/inhibition imbalance and impaired synaptic inhibition in hippocampal area CA3 of Mecp2 knockout mice. Hippocampus 25:159–168
Chahrour M, Jung SY, Shaw C, Zhou X, Wong ST, Qin J, Zoghbi HY (2008) MeCP2, a key contributor to neurological disease, activates and represses transcription. Science 320:1224–1229
Chen WG, Chang Q, Lin Y, Meissner A, West AE, Griffith EC, Jaenisch R, Greenberg ME (2003) Derepression of BDNF transcription involves calcium-dependent phosphorylation of MeCP2. Science 302:885–889
Choi DC, Gourley SL, Ressler KJ (2012) Prelimbic BDNF and TrkB signaling regulates consolidation of both appetitive and aversive emotional learning. Transl Psychiatry 2:e205
Ciccocioppo R, Sanna PP, Weiss F (2001) Cocaine-predictive stimulus induces drug-seeking behavior and neural activation in limbic brain regions after multiple months of abstinence: reversal by D(1) antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:1976–1981
Crombag HS, Gorny G, Li Y, Kolb B, Robinson TE (2005) Opposite effects of amphetamine self-administration experience on dendritic spines in the medial and orbital prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 15:341–348
Cunningham CL, Gremel CM, Groblewski PA (2006) Drug-induced conditioned place preference and aversion in mice. Nat Protoc 1:1662–1670
de Lima MN, Presti-Torres J, Vedana G, Alcalde LA, Stertz L, Fries GR, Roesler R, Andersen ML, Quevedo J, Kapczinski F, Schroder N (2011) Early life stress decreases hippocampal BDNF content and exacerbates recognition memory deficits induced by repeated D-amphetamine exposure. Behav Brain Res 224:100–106
Dong E, Dzitoyeva SG, Matrisciano F, Tueting P, Grayson DR, Guidotti A (2015) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor epigenetic modifications associated with schizophrenia-like phenotype induced by prenatal stress in mice. Biol Psychiatry 77:589–596
Dube SR, Felitti VJ, Dong M, Chapman DP, Giles WH, Anda RF (2003) Childhood abuse, neglect, and household dysfunction and the risk of illicit drug use: the adverse childhood experiences study. Pediatrics 111:564–572
Eisener-Dorman AF, Grabowski-Boase L, Tarantino LM (2011) Cocaine locomotor activation, sensitization and place preference in six inbred strains of mice. Behav Brain Funct 7:29
Elton A, Smitherman S, Young J, Kilts CD (2015) Effects of childhood maltreatment on the neural correlates of stress- and drug cue-induced cocaine craving. Addict Biol 20:820–831
Francke ID, Viola TW, Tractenberg SG, Grassi-Oliveira R (2013) Childhood neglect and increased withdrawal and depressive severity in crack cocaine users during early abstinence. Child Abuse Negl 37:883–889
Fumagalli F, Caffino L, Racagni G, Riva MA (2009) Repeated stress prevents cocaine-induced activation of BDNF signaling in rat prefrontal cortex. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 19: 402–408.
Fumagalli F, Di Pasquale L, Caffino L, Racagni G, Riva MA (2007) Repeated exposure to cocaine differently modulates BDNF mRNA and protein levels in rat striatum and prefrontal cortex. Eur J Neurosci 26:2756–2763
Hays SL, McPherson RJ, Juul SE, Wallace G, Schindler AG, Chavkin C, Gleason CA (2012) Long-term effects of neonatal stress on adult conditioned place preference (CPP) and hippocampal neurogenesis. Behav Brain Res 227:7–11
Hollander JA, Im HI, Amelio AL, Kocerha J, Bali P, Lu Q, Willoughby D, Wahlestedt C, Conkright MD, Kenny PJ (2010) Striatal microRNA controls cocaine intake through CREB signalling. Nature 466:197–202
Im HI, Hollander JA, Bali P, Kenny PJ (2010) MeCP2 controls BDNF expression and cocaine intake through homeostatic interactions with microRNA-212. Nat Neurosci 13:1120–1127
Kikusui T, Faccidomo S, Miczek KA (2005) Repeated maternal separation: differences in cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in adult male and female mice. Psychopharmacology 178:202–210
Kundakovic M, Lim S, Gudsnuk K, Champagne FA (2013) Sex-specific and strain-dependent effects of early life adversity on behavioral and epigenetic outcomes. Front Psychiatry 4:78
Laviola G, Adriani W, Terranova ML, Gerra G (1999) Psychobiological risk factors for vulnerability to psychostimulants in human adolescents and animal models. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:993–1010
Leussis MP, Andersen SL (2008) Is adolescence a sensitive period for depression? Behavioral and neuroanatomical findings from a social stress model. Synapse 62:22–30
Lewis CR, Staudinger K, Scheck L, Olive MF (2013) The effects of maternal separation on adult methamphetamine self-administration, extinction, reinstatement, and MeCP2 immunoreactivity in the nucleus accumbens. Front Psychiatry 4:55
Li X, Wei W, Zhao QY, Widagdo J, Baker-Andresen D, Flavell CR, D’Alessio A, Zhang Y, Bredy TW (2014) Neocortical Tet3-mediated accumulation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine promotes rapid behavioral adaptation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:7120–7125
Li X, Wolf ME (2015) Multiple faces of BDNF in cocaine addiction. Behav Brain Res 279:240–254
Liu QR, Lu L, Zhu XG, Gong JP, Shaham Y, Uhl GR (2006) Rodent BDNF genes, novel promoters, novel splice variants, and regulation by cocaine. Brain Res 1067:1–12
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Lonetti G, Angelucci A, Morando L, Boggio EM, Giustetto M, Pizzorusso T (2010) Early environmental enrichment moderates the behavioral and synaptic phenotype of MeCP2 null mice. Biol Psychiatry 67:657–665
Lu H, Cheng PL, Lim BK, Khoshnevisrad N, Poo MM (2010) Elevated BDNF after cocaine withdrawal facilitates LTP in medial prefrontal cortex by suppressing GABA inhibition. Neuron 67:821–833
Martini M, Valverde O (2012) A single episode of maternal deprivation impairs the motivation for cocaine in adolescent mice. Psychopharmacology 219:149–158
McEwen BS, Gray JD, Nasca C (2015) 60 Years of neuroendocrinology: redefining neuroendocrinology: stress, sex and cognitive and emotional regulation. J Endocrinol 226:T67–T83
McGinty JF, Whitfield TW, Berglind WJ (2010) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cocaine addiction. Brain Res 1314:183–193
Moffett MC, Vicentic A, Kozel M, Plotsky P, Francis DD, Kuhar MJ (2007) Maternal separation alters drug intake patterns in adulthood in rats. Biochem Pharmacol 73:321–330
Munoz-Cuevas FJ, Athilingam J, Piscopo D, Wilbrecht L (2013) Cocaine-induced structural plasticity in frontal cortex correlates with conditioned place preference. Nat Neurosci 16:1367–1369
Plotsky PM, Meaney MJ (1993) Early, postnatal experience alters hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) mRNA, median eminence CRF content and stress-induced release in adult rats. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 18:195–200
Quinn RK, Brown AL, Goldie BJ, Levi EM, Dickson PW, Smith DW, Cairns MJ, Dayas CV (2015) Distinct miRNA expression in dorsal striatal subregions is associated with risk for addiction in rats. Transl Psychiatry 5:e503
Remenyi J, Hunter CJ, Cole C, Ando H, Impey S, Monk CE, Martin KJ, Barton GJ, Hutvagner G, Arthur JS (2010) Regulation of the miR-212/132 locus by MSK1 and CREB in response to neurotrophins. Biochem J 428:281–291
Roma PG, Huntsberry ME, Riley AL (2007) Separation stress, litter size, and the rewarding effects of low-dose morphine in the dams of maternally separated rats. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:429–433
Roth TL, Lubin FD, Funk AJ, Sweatt JD (2009) Lasting epigenetic influence of early-life adversity on the BDNF gene. Biol Psychiatry 65:760–769
Rousseaud A, Delepine C, Nectoux J, Billuart P, Bienvenu T (2015) Differential expression and regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA isoforms in brain cells from Mecp2(308/y) mouse model. J Mol Neurosci 56:758–767
Sadri-Vakili G, Kumaresan V, Schmidt HD, Famous KR, Chawla P, Vassoler FM, Overland RP, Xia E, Bass CE, Terwilliger EF, Pierce RC, Cha JH (2010) Cocaine-induced chromatin remodeling increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcription in the rat medial prefrontal cortex, which alters the reinforcing efficacy of cocaine. J Neurosci 30:11735–11744
Schechter MD, Calcagnetti DJ (1993) Trends in place preference conditioning with a cross-indexed bibliography; 1957-1991. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 17:21–41
Schechter MD, Calcagnetti DJ (1998) Continued trends in the conditioned place preference literature from 1992 to 1996, inclusive, with a cross-indexed bibliography. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 22:827–846
Sun H, Cocker PJ, Zeeb FD, Winstanley CA (2012) Chronic atomoxetine treatment during adolescence decreases impulsive choice, but not impulsive action, in adult rats and alters markers of synaptic plasticity in the orbitofrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 219:285–301
Sun WL, Eisenstein SA, Zelek-Molik A, McGinty JF (2015) A single brain-derived neurotrophic factor infusion into the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex attenuates cocaine self-administration-induced phosphorylation of synapsin in the nucleus accumbens during early withdrawal. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18.
Wanet A, Tacheny A, Arnould T, Renard P (2012) miR-212/132 expression and functions: within and beyond the neuronal compartment. Nucleic Acids Res 40:4742–4753
Wang L, Jiao J, Dulawa SC (2011) Infant maternal separation impairs adult cognitive performance in BALB/cJ mice. Psychopharmacology 216:207–218
Whitfield TW, Shi X, Sun WL, McGinty JF (2011) The suppressive effect of an intra-prefrontal cortical infusion of BDNF on cocaine-seeking is Trk receptor and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase dependent. J Neurosci 31:834–842
Xiao L, Kish VL, Benders KM, Wu ZX (2015) Prenatal and early postnatal exposure to cigarette smoke decreases BDNF/TrkB signaling and increases abnormal behaviors later in life. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol
Yap JJ, Miczek KA (2008) Stress and rodent models of drug addiction: role of VTA-accumbens-PFC-amygdala circuit. Drug Discov Today Dis Models 5:259–270
Zhou Z, Hong EJ, Cohen S, Zhao WN, Ho HY, Schmidt L, Chen WG, Lin Y, Savner E, Griffith EC, Hu L, Steen JA, Weitz CJ, Greenberg ME (2006) Brain-specific phosphorylation of MeCP2 regulates activity-dependent Bdnf transcription, dendritic growth, and spine maturation. Neuron 52:255–269
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experiments were conducted in accordance with the NIH laboratory animal care guidelines and approved by the Ethical Committee on the Use of Animals of the Pontifical Catholic University of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viola, T.W., Wearick-Silva, L.E., De Azeredo, L.A. et al. Increased cocaine-induced conditioned place preference during periadolescence in maternally separated male BALB/c mice: the role of cortical BDNF, microRNA-212, and MeCP2. Psychopharmacology 233, 3279–3288 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4373-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4373-z