Abstract
Rationale
Traditionally, the non-selective muscarinic antagonist scopolamine has been used to induce episodic memory impairments as found in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, it also impairs attention and induces drowsiness. Muscarinic antagonists more selective for the M1 receptor might, therefore, be preferred.
Objectives
We examined the effects of the M1 antagonist biperiden on cognitive functions in order to test the specificity of this drug on memory performance. Additionally, we assessed whether the selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitor citalopram can reverse a possible biperiden-induced impairment.
Methods
The study was conducted according to a double-blind, placebo-controlled, four-way cross-over design. Sixteen volunteers received biperiden (2 mg), citalopram (20 mg), a combination of the two, or a placebo in counterbalanced order with a washout of at least 4 days. Cognitive tests (verbal memory, continuous recognition memory, spatial memory, choice reaction) were performed 4 and 1 h after treatment with citalopram and biperiden, respectively.
Results
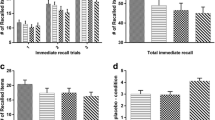
Biperiden impaired memory performance in the verbal learning task, the continuous recognition memory test, and the spatial memory task. Effects on attention and side effects, as measured using the choice reaction time test and questionnaires respectively, could be neglected. Citalopram did not affect any of the memory or attention measures taken. Most importantly, citalopram was also unable to reverse the biperiden-induced memory impairments.
Conclusions
Our results, thus, show that the M1 antagonist biperiden may serve as a translational model to induce episodic memory deficits as seen in AD. However, the interactive influence of acetylcholine and serotonin on memory could not be confirmed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atri A, Sherman S, Norman KA, Kirchhoff BA, Nicolas MM, Greicius MD, Cramer SC, Breiter HC, Hasselmo ME, Stern CE (2004) Blockade of central cholinergic receptors impairs new learning and increases proactive interference in a word paired-associate memory task. Behav Neurosci 118:223–236
Bishop KI, Curran HV, Lader M (1996) Do scopolamine and lorazepam have dissociable effects on human memory systems? A dose–response study with normal volunteers. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 4:292–299
Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E (1992) Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 260:576–580
Broks P, Preston GC, Traub M, Poppleton P, Ward C, Stahl SM (1988) Modelling dementia: effects of scopolamine on memory and attention. Neuropsychologia 26:685–700
Brooks A, Little JT, Martin A, Minichiello MD, Dubbert B, Mack C, Tune L, Murphy DL, Sunderland T (1998) The influence of ondansetron and m-chlorophenylpiperazine on scopolamine-induced cognitive, behavioral, and physiological responses in young healthy controls. Biol Psychiatry 43:408–416
Cassel JC, Jeltsch H (1995) Serotonergic modulation of cholinergic function in the central nervous system: cognitive implications. Neuroscience 69:1–41
Crow TJ, Grove-White I, Ross DG (1975) The specificity of the action of hyoscine on human learning. P Brit Pharmacol Soc 368P:24–25
Curran HV, Pooviboonsuk P, Dalton JA, Lader MH (1998) Differentiating the effects of centrally acting drugs on arousal and memory: an event-related potential study of scopolamine, lorazepam and diphenhydramine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 135:27–36
Decker MW, McGaugh JL (1991) The role of interactions between the cholinergic system and other neuromodulatory systems in learning and memory. Synapse 7:151–168
Drachman DA, Leavitt J (1974) Human memory and the cholinergic system. A relationship to aging? Arch Neurol 30:113–121
Egashira N, Matsumoto Y, Mishima K, Iwasaki K, Fujioka M, Matsushita M, Shoyama Y, Nishimura R, Fujiwara M (2006) Low dose citalopram reverses memory impairment and electroconvulsive shock-induced immobilization. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 83:161–167
Evers EAT, van der Veen FM, Jolles J, Deutz NEP, Schmitt JAJ (2009) The effect of acute tryptophan depletion on performance and the BOLD response during a Stroop task in healthy first-degree relatives of patients with unipolar depression. Psychiatr Res 173:52–58
Frith CD, Richardson JTE, Samuel M, Crow TJ, McKenna PJ (1984) The effects of intravenous diazepam and hyoscine upon human memory. Q J Exp Psychol A 36:133–144
Garcia-Alloza M, Gil-Bea FJ, Diez-Ariza M, Chen CP, Francis PT, Lasheras B, Ramirez MJ (2005) Cholinergic-serotonergic imbalance contributes to cognitive and behavioral symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychologia 43:442–449
Green A, Ellis KA, Ellis J, Bartholomeusz CF, Ilic S, Croft RJ, Phan KL, Nathan PJ (2005) Muscarinic and nicotinic receptor modulation of object and spatial n-back working memory in humans. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:575–584
Harmer CJ, Bhagwagar Z, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2002) Acute administration of citalopram facilitates memory consolidation in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 163:106–110
Hollman M, Brode E, Greger G, Müller-Peltzer H, Wetzelsberger N (1984) Biperiden effects and plasma levels in volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 27:619–621
Hollman M, Müller-Peltzer H, Greger G, Brode E, Peruca E, Grimaldi R, Crema A (1987) Pharmacokinetic-dynamic study on different oral biperiden formulations in volunteers. Pharmacopsychiatry 20:72–77
Jeltsch-David H, Koenig J, Cassel JC (2008) Modulation of cholinergic functions by serotonin and possible implications in memory: general data and focus on 5-HT(1A) receptors of the medial septum. Behav Brain Res 195:86–97
Kamboj SK, Curran HV (2006) Neutral and emotional episodic memory: global impairment after lorazepam or scopolamine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 188:482–488
Katayama S, Ishizaki F, Yamamura Y, Khoriyama T, Kito S (1990) Effects of anticholinergic antiparkinsonian drugs on binding of muscarinic receptor subtypes in rat brain. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 69:261–270
Kessels RP, Postma A, de Haan EH (1999) Object Relocation: a program for setting up, running, and analyzing experiments on memory for object locations. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput 31:423–428
Klaassen T, Riedel WJ, Deutz NE, Van Praag HM (2002) Mood congruent memory bias induced by tryptophan. Psychol Med 32:167–172
Klinkenberg I, Blokland A (2010) The validity of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment: a review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34:1307–1350
Klinkenberg I, Blokland A (2011) A comparison of scopolamine and biperiden as a rodent model for cholinergic cognitive impairment. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 215:549–566
Klinkenberg I, Blokland A, Riedel WJ, Sambeth A (2012) Human electrophysiological correlates of learned irrelevance: effects of the muscarinic M1 antagonist biperiden. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:1375–1385
Kopelman MD, Corn TH (1988) Cholinergic ‘blockade’ as a model for cholinergic depletion. A comparison of the memory deficit with those of Alzheimer-type dementia and the alcoholic Korsakoff syndrome. Brain 111:1079–1110
Kragh Sorensen P, Overo KF, Petersen OL, Jensen K, Parnas W (1981) The kinetics of citalopram: single and multiple dose studies in man. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 48:53–60
Kuypers KP, Ramaekers JG (2005) Transient memory impairment after acute dose of 75 mg 3.4-methylene-dixymethamphetamine. J Psychopharmacol 19:633–639
Langmead CJ, Watson J, Reavill C (2008) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and CNS drug targets. Pharmacol Ther 117:232–243
Lee J, Monette J, Sourial N, Monette M, Bergman H (2007) The use of a cholinesterase inhibitor review committee in long-term care. J Am Med Dir Assoc 8:243–247
Lenz RA, Baker FD, Locke C, Rueter LE, Mohler EG, Wesnes K, Abi-Saab W, Saltarelli MD (2012) The scopolamine model as a pharmacological marker in early drug development. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 220:97–107
Lezak M (1995) Neuropsychological assessment, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Lieben CK, Blokland A, Sik A, Sung E, Van Nieuwenhuizen P, Schreiber R (2005) The selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist Ro4368554 restores memory performance in cholinergic and serotonergic models of memory deficiency in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:2169–2179
Little JT, Brooks A, Martin A, Hill JL, Tune LE, Mack C, Cantillon M, Molchan S, Murphy DL, Sunderland T (1995) Serotonergic modulation of anticholinergic effects on cognition and behavior in elderly humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 120:280–288
Lleo A, Greenberg SM, Growdon JH (2006) Current pharmacotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Rev Med 57:513–533
McNair DM, Lorr M, Droppleman LF (1971) Manual for the profile of mood states. San Diego, CA: Educational and Industrial Testing Service
Milne RJ, Goa KL (1991) Citalopram. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in depressive illness. Drugs 41:450–477
Mintzer J, Burns A (2000) Anticholinergic side-effects of drugs in elderly people. J Roy Soc Med 93:457–462
Mintzer MZ, Griffiths RR (2003) Lorazepam and scopolamine: a single-dose comparison of effects on human memory and attentional processes. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 11:56–72
Mintzer MZ, Griffiths RR (2005) Drugs, memory, and metamemory: a dose-effect study with lorazepam and scopolamine. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 13:336–347
Mintzer MZ, Griffiths RR (2007) Differential effects of scopolamine and lorazepam on working memory maintenance versus manipulation processes. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 7:120–129
Nakra BR, Margolis RB, Gfeller JD, Grossberg GT, Sata LS (1992) The effect of a single low dose of trihexyphenidyl on memory functioning in the healthy elderly. Int Psychogeriatr 4:207–214
Ogino S, Miyamoto S, Tenjin T, Kitajima R, Ojima K, Miyake N, Funamoto Y, Arai J, Tsukahara S, Ito Y, Tadokoro M, Anai K, Tatsunami S, Kubota H, Kaneda Y, Yamaguchi N (2011) Effects of discontinuation of long-term biperiden use on cognitive function and quality of life in schizophrenia. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 35:78–83
Peters NL (1989) Snipping the thread of life. Antimuscarinic side-effects of medications in the elderly. Arch Intern Med 149:2414–2420
Pomara N, Willoughby LM, Wesnes K, Sidtis JJ (2004) Increased anticholinergic challenge-induced memory impairment associated with the APOE-epsilon4 allele in the elderly: a controlled pilot study. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:403–409
Rasch BH, Born J, Gais S (2006) Combined blockade of cholinergic receptors shifts the brain from stimulus encoding to memory consolidation. J Cogn Neurosci 18:793–802
Riedel WJ, Klaassen T, Deutz NE, van Someren A, van Praag HM (1999) Tryptophan depletion in normal volunteers produces selective impairment in memory consolidation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 141:362–369
Robbins TW, Semple J, Kumar R, Truman MI, Shorter J, Ferraro A, Fox B, McKay G, Matthews K (1997) Effects of scopolamine on delayed-matching-to-sample and paired associates tests of visual memory and learning in human subjects: comparison with diazepam and implications for dementia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 134:95–106
Rock PL, Roiser JP, Riedel WJ, Blackwell AD (2014) Cognitive impairment in depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol Med 44:2029–2040
Rodriguez JJ, Noristani HN, Verkhratsky A (2012) The serotonergic system in ageing and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 99:15–41
Sambeth A, Blokland A, Harmer CJ, Kilkens TOC, Nathan PJ, Porter RJ, Schmitt JAJ, Scholtissen B, Sobczak S, Young AH, Riedel WJ (2007) Sex differences in the effect of acute tryptophan depletion on declarative episodic memory: a pooled analysis of nine studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 31:516–529
Sambeth A, Riedel WJ, Tillie DE, Blokland A, Postma A, Schmitt JA (2009) Memory impairments in humans after acute tryptophan depletion using a novel gelatin-based protein drink. J Psychopharmacol 23:56–64
Schwarz S, Froelich L, Burns A (2012) Pharmacological treatment of dementia. Curr Opin Psychiatr 25:542–550
Seyedabadi M, Fakhfouri G, Ramezani V, Mehr SE, Rahimian R (2014) The role of serotonin in memory: interactions with neurotransmitters and downstream signaling. Exp Brain Res 232:723–738
Sherman SJ, Atri A, Hasselmo ME, Stern CE, Howard MW (2003) Scopolamine impairs human recognition memory: data and modeling. Behav Neurosci 117:526–539
Snyder PJ, Bednar MM, Cromer JR, Maruff P (2005) Reversal of scopolamine-induced deficits with a single dose of donepezil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Alzheimers Dement 1:126–135
Sperling R, Greve D, Dale A, Killiany R, Holmes J, Rosas HD, Cocchiarella A, Firth P, Rosen B, Lake S, Lange N, Routledge C, Albert M (2002) Functional MRI detection of pharmacologically induced memory impairment. PNAS 99:455–460
Stancampiano R, Cocco S, Cugusi C, Sarais L, Fadda F (1999) Serotonin and acetylcholine release response in the rat hippocampus during a spatial memory task. Neuroscience 89:1135–1143
Steckler T, Sahgal A (1995) The role of serotonergic-cholinergic interactions in the mediation of cognitive behaviour. Behav Brain Res 67:165–199
Toda N, Kaneko T, Kogen H (2010) Development of an efficient therapeutic agent for Alzheimer’s disease: design and synthesis of dual inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase and serotonin transporter. Chem Pharm Bull 58:273–287
Trillo L, Das D, Hsieh W, Medina B, Moghadam S, Lin B, Dang V, Sanchez MM, De Miguel Z, Ashford JW, Salehi A (2013) Ascending monoaminergic systems alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Translating basic science into clinical care. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37:1363–1379
Tune L, Carr S, Hoag E, Cooper T (1992) Anticholinergic effects of drugs commonly prescribed for the elderly: potential means for assessing risk of delirium. Am J Psychiatr 149:1393–1394
Van Harten J (1993) Clinical pharmacokinetics of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet 24:203–220
Van Ruitenbeek P, Vermeeren A, Riedel WJ (2008) Histamine H1-receptor blockade in humans affects psychomotor performance but not memory. J Psychopharmacol 22:663–672
Van Strien JW, Verkoeijen PP, Van der Meer N, Franken IH (2007) Electrophysiological correlates of word repetition spacing: ERP and induced band power old/new effects with massed and spaced repetitions. Int J Psychophysiol 66:205–214
Wezenberg E, Verkes RJ, Sabbe BG, Ruigt GS, Hulstijn W (2005) Modulation of memory and visuospatial processes by biperiden and rivastigmine in elderly healthy subjects. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 181:582–594
Woolley ML, Marsden CA, Sleight AJ, Fone KCF (2003) Reversal of a cholinergic-induced deficit in a rodent model of recognition memory by the selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, Ro 04-6790. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 170:358–367
Xu Y, Yan J, Zhou P, Li J, Gao H, Xia Y, Wang Q (2012) Neurotransmitter receptors and cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neurobiol 97:1–13
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Eini Knuutinen for her assistance in data acquisition. This study was sponsored by the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research, grant number 451-07-011.
Conflict of interest
Wim J. Riedel was also employed by Cambridge Cognition Ltd., Cambridge, UK, while remaining affiliated to Maastricht University, during the last few years. This raises no conflict of interest. There were no commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sambeth, A., Riedel, W.J., Klinkenberg, I. et al. Biperiden selectively induces memory impairment in healthy volunteers: no interaction with citalopram. Psychopharmacology 232, 1887–1897 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3822-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3822-9