Abstract
Rationale
Previous research suggests that the acute anorectic effect of cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist/inverse agonists may be secondary to response competition from the compulsive scratching and grooming syndrome characteristic of these agents.
Objectives
As the pruritic effect of rimonabant can be attenuated by the opioid receptor antagonist naloxone, these studies test the prediction that naloxone co-treatment should prevent acute rimonabant anorexia.
Methods
Two experiments comprehensively profiled the behavioural effects of an anorectic dose of rimonabant (1.5 mg/kg) in the absence or presence of naloxone (experiment 1: 0.01 or 0.1 mg/kg; experiment 2: 0.05 mg/kg).
Results
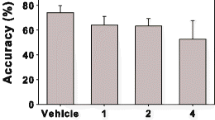
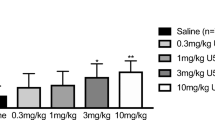
In both experiments, rimonabant not only significantly suppressed food intake and time spent eating but also induced compulsive scratching and grooming. In experiment 1, although the lower dose of naloxone seemed to weakly attenuate the effects of rimonabant both on ingestive and compulsive behaviours, the higher dose more strongly suppressed the compulsive elements but did not significantly affect the anorectic response. The results of experiment 2 showed that naloxone at a dose which markedly attenuated rimonabant-induced grooming and scratching did not alter the effects of the compound on food intake or time spent feeding. The apparent independence of the ingestive and compulsive effects of rimonabant was confirmed by the observation that despite a ‘normalising’ effect of naloxone co-treatment on behavioural structure (BSS), the opioid antagonist did not impact the suppressant effect of rimonabant on peak feeding.
Conclusion
The acute anorectic response to rimonabant would not appear to be secondary to compulsive scratching and grooming.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aceto MD, Scates SM, Lowe JA, Martin BR (1996) Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol: studies on precipitated and abrupt withdrawal. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:1290–1295
Addy C, Wright H, Van Laere K, Gantz I, Erondu N, Musser BJ, Lu K, Yuan J, Sanabria-Bohórquez SM, Stoch A, Stevens C, Fong TM, De Lepeleire I, Cilissen C, Cote J, Rosko K, Gendrano Iii IN, Nguyen AM, Gumbiner B, Rothenberg P, de Hoon J, Bormans G, Depré M, Eng W-s, Ravussin E, Klein S, Blundell J, Herman GA, Burns HD, Hargreaves RJ, Wagner J, Gottesdiener K, Amatruda JM, Heymsfield SB (2008) The acyclic CB1R inverse agonist taranabant mediates weight loss by increasing energy expenditure and decreasing caloric intake. Cell Metab 7:68–78
Akbas F, Gasteyger C, Sjodin A, Astrup A, Larsen TM (2009) A critical review of the cannabinoid receptor as a drug target for obesity management. Obes Rev 10:58–67
Alonso M, Serrano A, Vida M, Crespillo A, Hernandez-Folgado L, Jagerovic N, Goya P, Reyes-Cabello C, Perez-Valero V, Decara J, Macias-Gonzalez M, Bermudez-Silva FJ, Suarez J, Rodriquez de Fonseca F, Pavon FJ (2012) Anti-obesity efficacy of LH-21, a cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist with poor brain penetration, in diet-induced obese rats. Brit J Pharmacol 165:2274–2291
Arnone M, Maruani J, Chaperon F, Thiebot M-H, Poncelot M, Soubrié P, Le Fur G (1997) Selective inhibition of sucrose and ethanol intake by SR141716, an antagonist of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors. Psychopharmacology 132:104–106
Ballantyne JC, Loach AB, Carr DB (1988) Itching after epidural and spinal opiates. Pain 33:149–160
Bermudez-Silva FJ, Viveros MP, McPartland JM, Rodriguez de Fonseca F (2010) The endocannabinoid system, eating behavior and energy homeostasis: the end or a new beginning? Pharmacol Biochem Behav 95:375–382
Bigliardi PL, Stammer H, Jost G, Rufli T, Buchner S, Bigliardi-Qi M (2007) Treatment of pruritus with topically applied opiate receptor antagonist. J Am Acad Dermatol 56:979–988
Carai MAM, Colombo G, Gessa GL (2005) Rimonabant: the first therapeutically relevant cannabinoid antagonist. Life Sci 77:2339–2350
Chambers AP, Sharkley KA, Koopmans HS (2004) Cannabinoid (CB)1 receptor antagonist, AM251, causes a sustained reduction of daily food intake in the rat. Physiol Behav 82:863–869
Chambers AP, Koopmans HS, Pittman QJ, Sharkley KA (2006) AM 251 produces sustained reductions in food intake and body weight that are resistant to tolerance and conditioned taste aversion. Brit J Pharmacol 147:109–116
Chen RZ, Huang R-RC, Shen C-Y, MacNeil DJ, Fong TM (2004) Synergistic effects of cannabinoid inverse agonist AM251 and opioid antagonist nalmefene on food intake in mice. Brain Res 999:227–230
Chen W, Tang H, Liu H, Long L, Gong Z, Zheng J, Chi M, Xie Y, Zheng Z, Li S, Wang L (2010) Novel selective antagonist of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor, MJ15, with prominent anti-obesity effect in rodent models. Eur J Pharmacol 637:178–185
Cies JJ, Giamalis JN (2007) Treatment of cholestatic pruritus in children. Am J Health-Syst Pharm 64:1157–1162
Cluny NL, Vemuri VK, Chambers AP, Limebeer CL, Bedard H, Wood JT, Lutz B, Zimmer A, Parker LA, Makriyannis A, Sharkey KA (2010) A novel peripherally-restricted cannabinoid receptor antagonist, AM6545, reduces food intake and body weight, but does not cause malaise, in rodents. Brit J Pharmacology 161:629–642
Cluny NL, Chambers AP, Vemuri VK, Wood JT, Eller LK, Freni C, Reimer RA, Makriyannis A, Sharkey KA (2011) The neutral cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist AM4113 regulates body weight through changes in energy intake in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97:537–543
Colombo G, Agabio R, Diaz G, Lobina C, Reali R, Gessa GL (1998) Appetite suppression and weight loss after the cannabinoids antagonist SR141716A. Life Sci 63:PL113–PL117
Cook SA, Lowe JA, Martin BR (1998) CB1 receptor antagonist precipitates withdrawal in mice exposed to Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J Pharmacol Exper Ther 285:1150–1156
Cota D, Tschöp M, Horvath TL, Levine AS (2006) Cannabinoids, opioids and eating behavior: The molecular face of hedonism? Brain Res Revs 51:85–107
Darmani NA, Pandya DK (2000) Involvement of other neurotransmitters in behaviors induced by the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR 141716A in naïve mice. J Neural Transm 107:931–945
de Fonseca FR, Carrera MRA, Navarro M, Koob GF, Weiss F (1997) Activation of corticotropin-releasing factor in the limbic system during cannabinoid withdrawal. Science 276:2050–2054
De Vry J, Schrieber R, Eckel G, Jentzsch KR (2004) Behavioral mechanisms underlying inhibition of food-maintained responding by the cannabinoid receptor antagonist/inverse agonist SR141716A. Eur J Pharmacol 483:55–63
DiMarzo V (2008) Targeting the endocannabinoid system: to enhance or reduce? Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:438–455
DiPatrizio NV, Astarita G, Schwartz G, Li X, Piomelli D (2011) Endocannabinoid signal in the gut controls dietary fat intake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:12904–12908
European Medicines Agency (2008) Acomplia: European public assessment reports. European Medicines Agency London
Freedland CS, Poston JS, Porrino LJ (2000) Effects of SR141716A, a central cannabinoid receptor antagonist, on food-maintained responding. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:265–270
Friedman JD, Dello Buono FA (2001) Opioid antagonists in the treatment of opioid-induced constipation and pruritus. Ann Pharmacother 35:85–91
Gallate JE, Saharov T, Mallet PE, McGregor IS (1999) Increased motivation for beer in rats following administration of a cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 370:233–240
Gomez R, Navarro M, Ferrer B, Trigo JM, Bilbao A, Del Arco I, Cippitelli A, Nava F, Piomelli D, de Fonseca FR (2002) A peripheral mechanism for CB1 cannabinoid receptor-dependent modulation of feeding. J Neurosci 22:9612–9617
Griebel G, Stemmelin J, Scatton B (2005) Effects of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant in models of emotional reactivity in rodents. Biol Psychiatr 57:261–267
Halford JCG, Wanninayake SCD, Blundell JE (1998) Behavioral satiety sequence (BSS) for the diagnosis of drug action on food intake. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:159–168
Halford JCG, Boyland EJ, Blundell JE, Kirkham TC, Harrold JA (2010) Pharmacological management of appetite expression in obesity. Nature Revs Endocrinol 6:255–269
Higgs S, Williams CM, Kirkham TC (2003) Cannabinoid influences on palatability: microstructural analysis of sucrose drinking after Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, anandamide, 2-arachidonoyl glycerol and SR141716. Psychopharmacology 165:370–377
Hodge J, Bow JP, Plyer KS, Vemuri VK, Wisniecki A, Salamone JD, Makriyannis A, McLaughlin PJ (2008) The cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonist AM 251 and antagonist AM 4113 procedure similar effects on the behavioral satiety sequence in rats. Behav Brain Res 193:298–305
Janoyan JJ, Crim JL, Darmani NA (2002) Reversal of SR 141716A-induced head-twitch and ear-scratch responses in mice by Δ-9-THC and other cannabinoids. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:155–162
Järbe TUC, Andrzejewski ME, DiPatrizio NV (2002) Interactions between the CB1 receptor agonist Δ9–THC and the CB1 receptor antagonist SR-141716 in rats: open-field revisited. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:911–919
Järbe TUC, DiPatrizio NV, Lu D, Makriyannis A (2003) The cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR-141716 does not readily antagonise open-field effects induced by the cannabinoid receptor agonist (R)-methanandamide in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:809–821
Järbe TUC, DiPatrizio NV, Lu D, Makriyannis A (2004) (−)-Adamantyl-Δ8-tetrahydrocannabinol (AM-411), a selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor agonist: effects on open field behaviors and antagonism by SR-141716 in rats. Behav Pharmacol 15:517–521
Järbe TUC, Ross T, DiPatrizion NV, Pandarinathan L, Makriyannis A (2006) Effects of CB1R agonist WIN-55,212-2 and the CB1R antagonists SR-141716 and AM-1387: open-field examination in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85:243–252
Järbe TUC, LeMay BJ, Olszewska T, Vemuri VK, Wood JT, Makriyannis A (2008) Intrinsic effects of AM4113, a putative neutral CB1 receptor selective antagonist, on open field behaviors in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:84–90
Kennett GA, Clifton PG (2010) New approaches to the pharmacological treatment of obesity: Can they break through the efficacy barrier? Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97:63–83
Kirkham TC (2009) Cannabinoids and appetite: food craving and food pleasure. Int Rev Psychiatr 21:163–171
Kirkham TC, Williams CM (2001) Synergistic effects of opioid and cannabinoid antagonists on food intake. Psychopharmacology 153:267–270
Kunos G, Osei-Hyiaman D, Batkai S, Sharkey KA, Makriyannis A (2008) Should peripheral CB1 cannabinoid receptors be selectively targeted for therapeutic gain? TIPS 30:1–7
Kuraishi Y, Yamaguchi T, Miyamoto T (2000) Itch-scratch responses induced by opioids through central mu opioid receptors in mice. J Biomed Sci 7:248–252
Limebeer CL, Vemuri VK, Bedard H, Lang ST, Ossenkopp KP, Makriyannis A, Parker LA (2010) Inverse agonism of cannabinoid CB1 receptors potentiates LiCl-induced nausea in the conditioned gaping model in rats. Brit J Pharmacol 161:3336–3349
Lockie SH, Czyzyk TA, Chaudhary N, Perez-Tilve D, Woods SC, Oldfield BJ, Statnick MA, Tschöp MH (2011) CNS opioid signaling separates cannabinoid receptor 1-mediated effects on body weight and mood-related behavior in mice. Endocrinology 152:3661–3667
Manzanares J, Corchero J, Romero J, Fernandez-Ruiz JJ, Ramos JA, Fuentes JA (1999) Pharmacological and biochemical interactions between opioids and cannabinoids. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:287–294
Marco EM, Romero-Zerbo SY, Viveros M-P, Bermudez-Silva F-J (2012) The role of the endocannabinoid system in eating disorders: pharmacological implications. Behav Pharmacol 23:526–536
McLaughlin PJ (2012) Reports of the death of CB1 antagonists have been greatly exaggerated: recent preclinical findings predict improved safety in the treatment of obesity. Behav Pharmacol 23:537–550
McLaughlin PJ, Winston K, Swezey L, Wisniecki A, Aberman J, Tardif DJ, Betz AJ, Ishwari K, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2003) The cannabinoid CB1 antagonists SR 141716A and AM 251 suppress food intake and food-reinforced behavior in a variety of tasks in rats. Behav Pharmacol 14:583–588
McLaughlin PJ, Winston KM, Limebeer CL, Parker LA, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2005) The cannabinoid CB1 antagonist AM 251 produces food avoidance and behaviors associated with nausea but does not impair feeding efficiency in rats. Psychopharmacology 180:286–293
McLaughlin PJ, Quan L, Wood JT, Wisniecki A, Winston KM, Swezey LA, Ishiwari K, Betz AJ, Pandarinathan L, Xu W, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2006) Suppression of food intake and food-reinforced behavior produced by the novel CB1 receptor antagonist/inverse agonist AM 1387. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 83:396–402
Miyamoto T, Nojima H, Shinkado T, Nakahashi T, Kuraishi Y (2002) Itch-associated response induced by experimental dry skin in mice. Jpn J Pharmacol 88:285–292
Navarro M, Carrera MRA, Fratta W, Valverde O, Cossu G, Fattore L, Chowen JA, Gomez R, del Arco I, Villanua MA, Maldonado R, Koob GF, Rodriguez de Fonseca F (2001) Functional interaction between opioid and cannabinoid receptors in drug self-administration. J Neurosci 21:5344–5350
Pavon FJ, Bilbao A, Hernandez-Folgado L, Cippitelli A, Jagerovic N, Abellan G, Rodriguez-Franco MI, Serrano A, Macias M, Gomez R, Navarro M, Goya P, de Fonseca FR (2006) Antiobesity effects of the novel in vivo neutral cannabinoid receptor antagonist 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-3-hexyl-1H-1,2,4-trazole–LH21. Neuropharmacology 51:358–366
Phan NQ, Bernhard JD, Luger TA, Stander S (2010) Antipruritic treatment with systemic μ-opioid receptor antagonists: a review. J Am Acad Dermatol 63:680–688
Pietras TA, Rowland NE (2002) Effect of opioid and cannabinoid receptor antagonism on orphanin FQ-induced hyperphagia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 442:237–239
Plieth J (2008) Obesity: what next after the CB1 antagonists' failure. Scrip, November 2008, 44–47
Randall PA, Vemuri VK, Segovia KN, Torres EF, Hosmer S, Nunes EJ, Santerre JL, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2010) The novel cannabinoid CB1 antagonist AM6545 suppresses food intake and food-reinforced behavior. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97:179–184
Rios CD, Jordan BA, Gomes I, Devi LA (2001) G-protein-coupled receptor dimerization: modulation of receptor function. Pharmacol Ther 92:71–87
Rios CD, Gomes I, Devi LA (2006) μ-Opioid and CB1 cannabinoid receptor interactions: reciprocal inhibition of receptor signaling and neuritogenesis. Br J Pharmacol 148:387–395
Rodgers RJ, Holch P, Tallett AJ (2010) Behavioural satiety sequence (BSS): separating wheat from chaff in the behavioural pharmacology of appetite. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97:3–14
Rodgers RJ, Tschöep MH, Wilding JPH (2012) Anti-obesity drugs: past, present and future. Dis Model Mech, in press
Rowland NE, Mukherjee M, Roberston K (2001) Effects of the cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR141716, alone and in combination with dexfenfluramine or naloxone, on food intake in rats. Psychopharmacology 159:111–116
Rubino T, Patrini G, Massi P, Fuzio D, Vigano D, Giagnoni G, Parolaro D (1998) Cannabinoid-precipitated withdrawal: a time-course study of the behavioral aspect and its correlation with cannabinoid receptors and G protein expression. J Pharmacol Exper Ther 285:813–819
Schlosburg JE, Boger DL, Cravatt BF, Lichtman AH (2009) Endocannabinoid modulation of a scratching response in an acute allergenic model: a new prospective neural therapeutic target for pruritus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329:314–323
Schlosburg JE, O'Neal ST, Conrad DH, Lichtman AH (2011) CB1 receptors mediate rimonabant-induced pruritic responses in mice: investigation of locus of action. Psychopharmacology 216:323–331
Schoffelmeer ANM, Hogenboom F, Wardeh G, De Vries TJ (2006) Interactions between CB1 cannabinoid and μ opioid receptors mediating inhibition of neurotransmitter release in rat nucleus accumbens core. Neuropharmacology 51:773–781
Shearman LP, Rosko KM, Fleischer R, Wang J, Xu S, Tong XS, Rocha BA (2003) Antidepressant-like and anorectic effects of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonist AM251 in mice. Behav Pharmacol 14:573–582
Sink KS, McLaughlin PJ, Wood JAT, Brown C, Fan P, Vemuri KV, Pang Y, Olszewska T, Thakur GA, Makriyannis A, Parker LA, Salamone JD (2008a) The novel cannabinoid CB1 receptor neutral antagonist AM4113 suppressed food intake and food-reinforced behavior but does not induce signs of nausea in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:946–955
Sink KS, Vemuri VK, Olszewska T, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2008b) Cannabinoid CB1 antagonists and dopamine antagonists produce different effects on a task involving response allocation and effort-related choice in food-seeking behavior. Psychopharmacology 196:565–574
Sink KS, Vemuri VK, Wood J, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2009) Oral bioavailability of the novel cannabinoid CB1 anatgonist AM6527: effects on food-reinforced behavior and comparisons with AM4113. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:303–306
Skelly MJ, Guy EG, Howlett AC, Pratt WE (2010) CB1 receptors modulate the intake of a sweetened-fat diet in response to mu-opioid receptor stimulation of the nucleus accumbens. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97:144–151
Ständer S, Schmelz M, Metze D, Luger T, Rukwied R (2005) Distribution of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and 2 (CB2) on sensory nerve fibres and adnexal structures in the human skin. J Derm Sci 38:177–188
Tallett AJ, Blundell JE, Rodgers RJ (2007a) Grooming, scratching and feeding: role of response competition in acute anorectic response to rimonabant in male rats. Psychopharmacology 195:27–39
Tallett AJ, Blundell JE, Rodgers RJ (2007b) Acute anorectic response to cannabinoid receptor antagonist/inverse agonist AM 251 in rat: indirect behavioural mediation. Behav Pharmacol 18:591–600
Tallett AJ, Blundell JE, Rodgers RJ (2008a) Endogenous opioids and cannabinoids: system interactions in the regulation of appetite, grooming and scratching. Physiol Behav 94:422–431
Tallett AJ, Blundell JE, Rodgers RJ (2008b) Behaviourally-selective hypophagic effects of naloxone in non-deprived male rats presented with palatable food. Behav Brain Res 187:417–427
Tallett AJ, Blundell JE, Rodgers RJ (2009a) Effects of acute low dose combined treatment with naloxone and AM 251 on food intake, feeding behaviour and weight gain in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:358–366
Tallett AJ, Blundell JE, Rodgers RJ (2009b) Night and day: diurnal differences in the behavioural satiety sequence in male rats. Physiol Behav 97:125–130
Tanda G, Goldberg SR (2003) Cannabinoids: reward, dependence and underlying mechanisms—a review of recent preclinical data. Psychopharmacology 169:115–134
Terra SG, Tsunoda SM (1998) Opioid antagonists in the treatment of pruritus from cholestatic liver disease. Ann Pharmacother 32:1228–1230
Thornton-Jones ZD, Kennett GA, Benwell KR, Revell DF, Misra A, Sellwood DM, Vickers SP, Clifton PG (2006) The cannabinoid CB1 receptor inverse agonist, rimonabant, modifies body weight and adiponectin function in diet-induced obese rats as a consequence of reduced food intake. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 84:353–359
Trojniar W, Wise RA (1991) Faciliatory effect of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol on hypothalamically induced feeding. Psychopharmacology 103:172–176
Tucci SA, Halford JCG, Harrold JA, Kirkham TC (2006) Therapeutic potential of targeting the endocannabinoids: implications for the treatment of obesity, metabolic syndrome, drug abuse and smoking cessation. Curr Med Chem 13:2669–2680
Vemuri VK, Janero DR, Makriyannis A (2008) Therapeutic targeting of the endocannabinoid signaling system: drugs for obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Physiol Behav 93:671–686
Verty AN, McGregor IS, Mallet PE (2004) Consumption of high carbohydrate, high fat, and normal chow is equally suppressed by a cannabinoid receptor antagonist in non-deprived rats. Neurosci Letts 354:217–220
Vickers SP, Cheetham SC (2007) Preclinical developments in antiobesity drugs. In: Kirkham TC, Cooper SJ (eds) Appetite and body weight. Integrative systems and the development of anti-obesity drugs. Academic, London, pp 323–336
Vickers SP, Webster LJ, Wyatt A, Dourish CT, Kennett GA (2003) Preferential effects of the cannabinoids CB1 receptor antagonist, SR141716, on food intake and body weight gain of obese (fa/fa) compared to lean Zucker rats. Psychopharmacology 167:103–111
Vickers SP, Jackson HC, Cheetham SC (2011) The utility of animal models to evaluate novel anti-obesity agents. Br J Pharmacol 164:1248–1262
Webster LJ, Kennett GA, Vickers SP (2003) Effect of the CB1 receptor antagonist SR 141716 on food intake, bodyweight and the behavioural satiety sequence in obese (fa/fa) Zucker rats. Brit J Pharmacol 138:106P
Weiss SM (1995) Pharmacological and behavioural examination of the defensive reactions of laboratory mice to the calls of the Tawny owl. PhD thesis, School of Psychology, University of Leeds
Werner NA, Koch JE (2003) Effects of the cannabinoid antagonists AM281 and AM630 on deprivation-induced intake in Lewis rats. Brain Res 967:2290–2292
Wiley JL, Burston JJ, Leggett DC, Alekseeva OO, Razdan RK, Mahadevan A, Martin BR (2005) CB1 cannabinoid receptor-mediated modulation of food intake in mice. Brit J Pharmacol 145:293–300
Williams CM, Kirkham TC (2000) Reversal of cannabinoid hyperphagia by naloxone but not dexfenfluramine. Appetite 35:317
Williams CM, Kirkham TC (2002) Reversal of Δ9-THC hyperphagia by SR141716 and naloxone but not dexfenfluramine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:341–348
Yamamoto A, Sugimoto Y (2010) Involvement of peripheral mu opioid receptors in scratching behavior in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 649:336–341
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Professor John Blundell for stimulating discussions leading to the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, F.L., Rodgers, R.J. Low dose naloxone attenuates the pruritic but not anorectic response to rimonabant in male rats. Psychopharmacology 226, 415–431 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2916-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2916-5