Abstract
Rationale
Antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism (AIP) is a severe adverse affect of neuroleptic treatment. Interindividual heterogeneity in AIP development and severity is associated with risk factors such as antipsychotic drug type, old age, and female gender. There is evidence for genetic predisposition to develop AIP but the variants that confer susceptibility or protection are mostly unknown.
Objective
To identify genes related to AIP susceptibility, we performed a pharmacogenomic genome-wide association study (GWAS) for AIP severity.
Methods
Three hundred ninety-seven American schizophrenia patients who participated in the Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE)-GWAS project were included in our analysis. Patients had been randomized to treatment with antipsychotic monotherapy for periods ranging from 2 weeks to 18 months during phase 1 of the CATIE trial. They were regularly assessed for AIP severity using the modified Simpson–Angus Scale (SAS). For statistical analysis, patients were dichotomized as cases (average SAS mean global score > 0.3 during CATIE phase 1, N = 199) or controls (average SAS mean global score 0, N = 198).
Results
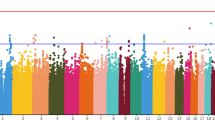
Using logistic regression and controlling for population stratification, age, gender, SAS score at baseline, and concomitant use of anticholinergic drugs, we identified several single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with AIP severity. Although none reached the GWAS significance level of P < 4.2 × 10−7, some promising candidate genes for further research on genetic predisposition to AIP were identified including EPF1, NOVA1, and FIGN.
Conclusions
Our finding may contribute to understanding of the pathophysiology of AIP as well as to a priori identification of patients vulnerable for development of AIP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Hadithy AF, Wilffert B, Stewart RE, Looman NM, Bruggeman R, Brouwers JR, Matroos GE, van Os J, Hoek HW, van Harten PN (2008) Pharmacogenetics of parkinsonism, rigidity, rest tremor, and bradykinesia in African–Caribbean inpatients: differences in association with dopamine and serotonin receptors. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B(6):890–897
Arranz MJ, de Leon J (2007) Pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics of schizophrenia: a review of last decade of research. Mol Psychiatry 12(8):707–747
Ayd F (1961) A survey of drug induced extrapyramidal reaction. JAMA 175:1054–1060
Basile VS, Masellis M, Potkin SG, Kennedy JL (2002) Pharmacogenomics in schizophrenia: the quest for individualized therapy. Hum Mol Genet 11(20):2517–2530
Bithell A, Alberta J, Hornby F, Stiles CD, Williams BP (2003) Expression of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor, mr-gef, is regulated during the differentiation of specific subsets of telencephalic neurons. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 146(1–2):107–118
Blanchet PJ (2003) Antipsychotic drug-induced movement disorders. Can J Neurol Sci Suppl 1:S101–S107
Bombin I, Arango C, Buchanan RW (2005) Significance and meaning of neurological signs in schizophrenia: two decades later. Schizophr Bull 31(4):962–977
Buckanovich RJ, Yang YY, Darnell RB (1996) The onconeural antigen Nova-1 is a neuron-specific RNA-binding protein, the activity of which is inhibited by paraneoplastic antibodies. J Neurosci 16(3):1114–1122
Caligiuri MP, Lohr JB (1997) Instrumental motor predictors of neuroleptic-induced parkinsonism in newly medicated schizophrenia patients. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 9(4):562–567
Caligiuri MP, Peavy G (2000) An instrumental study of the relationship between extrapyramidal signs and psychosis in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 12(1):34–39
Caligiuri MP, Lohr JB, Jeste DV (1993) Parkinsonism in neuroleptic–naive schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 150(9):1343–1348
Casey DE (2004) Pathophysiology of antipsychotics drug-induced movement disorders. J Clin Psychiatry 65(supp):25–28
Chakos MH, Mayerhoff DI, Loebel AD, Alvir JM, Lieberman JA (1992) Incidence and correlates of acute extrapyramidal symptoms in first episode of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacol Bull 28(1):81–86
Chatterjee A, Chakos M, Koreen A, Geisler S, Sheitman B, Woerner M, Kane JM, Alvir J, Lieberman JA (1995) Prevalence and clinical correlates of extrapyramidal signs and spontaneous dyskinesia in never-medicated schizophrenic patients. Am J Psychiatry 152(12):1724–1729
Cichon S, Craddock N, Daly M, Faraone SV, Gejman PV, Kelsoe J, Lehner T, Levinson DF, Moran A, Sklar P, Sullivan PF, Psychiatric GWAS Consortium Coordinating Committee (2009)Genomewide association studies: history, rationale, and prospects for psychiatric disorders. Am J Psychiatry 166(5):540–556
Cox GA, Mahaffey CL, Nystuen A, Letts VA, Frankel WN (2000) The mouse fidgetin gene defines a new role for AAA family proteins in mammalian development. Nat Genet 26(2):198–202
Crowley JJ, Sullivan PF, McLeod HL (2009) Pharmacogenomic genome-wide association studies: lessons learned thus far. Pharmacogenomics 10(2):161–163
Dolzan V, Plesnicar BK, Serretti A, Mandelli L, Zalar B, Koprivsek J, Breskvar K (2007) Polymorphisms in dopamine receptor DRD1 and DRD2 genes and psychopathological and extrapyramidal symptoms in patients on long-term antipsychotic treatment. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 144B(6):809–815
Ebadi M, Srinivasan SK (1995) Pathogenesis, prevention, and treatment of neuroleptic-induced movement disorders. Pharmacol Rev 47(4):575–604
Freimer N, Sabatti C (2004) The use of pedigree, sib-pair and association studies of common diseases for genetic mapping and epidemiology. Nat Genet 36(10):1045–1051
Freyhan FA (1959) Therapeutic implications of differential effects of new phenothiazine compounds. Am J Psychiatry 115:577–585
Garcia-Dominguez M, Poquet C, Garel S, Charnay P (2003) Ebf gene function is required for coupling neuronal differentiation and cell cycle exit. Development 130(24):6013–6025
Geddes J, Freemantle N, Harrison P, Bebbington P (2000) Atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia: systematic overview and meta-regression analysis. BMJ 321(7273):1371–1376
Greenbaum L, Strous RD, Kanyas K, Merbl Y, Horowitz A, Karni O, Katz E, Kotler M, Olender T, Deshpande SN, Lancet D, Ben-Asher E, Lerer B (2007) Association of the RGS2 gene with extrapyramidal symptoms induced by treatment with antipsychotic medication. Pharmacogenet Genomics 17(7):519–528
Greenbaum L, Smith RC, Rigbi A, Strous R, Teltsh O, Kanyas K, Korner M, Lancet D, Ben-Asher E, Lerer B (2009) Further evidence for association of the RGS2 gene with antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism: protective role of a functional polymorphism in the 3′-untranslated region. Pharmacogenomics J 9(2):103–110
Gunes A, Dahl ML, Spina E, Scordo MG (2008) Further evidence for the association between 5-HT2C receptor gene polymorphisms and extrapyramidal side effects in male schizophrenic patients. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 64(5):477–482
Güzey C, Scordo MG, Spina E, Landsem VM, Spigset O (2007) Antipsychotic-induced extrapyramidal symptoms in patients with schizophrenia: associations with dopamine and serotonin receptor and transporter polymorphisms. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 63(3):233–241
Haddad PM, Dursun SM (2008) Neurological complications of psychiatric drugs: clinical features and management. Hum Psychopharmacol 23(Suppl 1):15–26
Hansen TE, Casey DE, Hoffman WF (1997) Neuroleptic intolerance. Schizophr Bull 23(4):567–582
Hirose G (2006) Drug induced parkinsonism: a review. J Neurol 253(Suppl 3):iii22–iii24
Janno S, Holi M, Tuisku K, Wahlbeck K (2004) Prevalence of neuroleptic-induced movement disorders in chronic schizophrenia inpatients. Am J Psychiatry 161(1):160–163
Janno S, Holi MM, Tuisku K, Wahlbeck K (2005) Validity of Simpson–Angus Scale (SAS) in a naturalistic schizophrenia population. BMC Neurol 5(1):5
Kaiser R, Tremblay PB, Klufmöller F, Roots I, Brockmöller J (2002) Relationship between adverse effects of antipsychotic treatment and dopamine D(2) receptor polymorphisms in patients with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 7(7):695–705
Khaitovich P, Kelso J, Franz H, Visagie J, Giger T, Joerchel S, Petzold E, Green RE, Lachmann M, Pääbo S (2006) Functionality of intergenic transcription: an evolutionary comparison. PLoS Genet 2(10):e171
Kindmark A, Jawaid A, Harbron CG, Barratt BJ, Bengtsson OF, Andersson TB, Carlsson S, Cederbrant KE, Gibson NJ, Armstrong M, Lagerström-Fermér ME, Dellsén A, Brown EM, Thornton M, Dukes C, Jenkins SC, Firth MA, Harrod GO, Pinel TH, Billing-Clason SM, Cardon LR, March RE (2008) Genome-wide pharmacogenetic investigation of a hepatic adverse event without clinical signs of immunopathology suggests an underlying immune pathogenesis. Pharmacogenomics J 8(3):186–195
Koning JP, Tenback DE, van Os J, Aleman A, Kahn RS, van Harten PN. (2008) Dyskinesia and parkinsonism in antipsychotic-naive patients with schizophrenia, first-degree relatives and healthy controls: a meta-analysis. Schizophr Bull. [Epub ahead of print]
Lencz T, Morgan TV, Athanasiou M, Dain B, Reed CR, Kane JM, Kucherlapati R, Malhotra AK (2007) Converging evidence for a pseudoautosomal cytokine receptor gene locus in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 12(6):572–580
Lesage S, Brice A (2009) Parkinson's disease: from monogenic forms to genetic susceptibility factors. Hum Mol Genet 18(R1):R48–R59
Lerner V, Libov I, Kaptsan A, Miodownik C, Dwolatzky T, Levine J (2007) The prevalence of neuroleptic drug-induced tardive movement subsyndromes among schizophrenic and schizoaffective patients residing in the southern region of Israel. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci 44(1):20–28
Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO, Keefe RS, Davis SM, Davis CE, Lebowitz BD, Severe J, Hsiao JK (2005) Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) investigators. Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med 353(12):1209–1223
Lindenmayer JP, Eerdekens E, Berry SA, Eerdekens M (2004) Safety and efficacy of long-acting risperidone in schizophrenia: a 12-week, multicenter, open-label study in stable patients switched from typical and atypical oral antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 65(8):1084–1089
Link E, Parish S, Armitage J, Bowman L, Heath S, Matsuda F, Gut I, Lathrop M, Collins R (2008) SLCO1B1 variants and statin-induced myopathy—a genomewide study. N Engl J Med 359(8):789–799
Liu YZ, Pei YF, Guo YF, Wang L, Liu XG, Yan H, Xiong DH, Zhang YP, Levy S, Li J, Haddock CK, Papasian CJ, Xu Q, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Recker RR, Li MD, Deng HW (2009) Genome-wide association analyses suggested a novel mechanism for smoking behavior regulated by IL15. Mol Psychiatry. 14:668–680
Lobo MK, Yeh C, Yang XW (2008) Pivotal role of early B-cell factor 1 in development of striatonigral medium spiny neurons in the matrix compartment. J Neurosci Res 86(10):2134–2146
Martens JA, Wu PY, Winston F (2005) Regulation of an intergenic transcript controls adjacent gene transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev 19(22):2695–2704
McCreadie RG, Thara R, Kamath S, Padmavathy R, Latha S, Mathrubootham N, Menon MS (1996) Abnormal movements in never-medicated Indian patients with schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 168(2):221–226
Medinar C, Kramer MD, Kurland AA (1962) Biperiden in the treatment of phenothiazine-induced extrapyramidal reactions. JAMA 182:1127–1128
Miyamoto S, Duncan GE, Marx CE, Lieberman JA (2005) Treatments for schizophrenia: a critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs. Mol Psychiatry 10(1):79–104
Modestin J, Wehrli MV, Stephan PL, Agarwalla P (2008) Evolution of neuroleptic-induced extrapyramidal syndromes under long-term neuroleptic treatment. Schizophr Res 100(1–3):97–107
Nakazono Y, Abe H, Murakami H, Koyabu N, Isaka Y, Nemoto Y, Murata S, Tsutsumi Y, Ohtani H, Sawada Y (2005) Association between neuroleptic drug-induced extrapyramidal symptoms and dopamine D2-receptor polymorphisms in Japanese schizophrenic patients. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 43(4):163–171
Park S, Ross-Degnan D, Adams AS, Sabin J, Kanavos P, Soumerai SB (2005) Effect of switching antipsychotics on antiparkinsonian medication use in schizophrenia: population-based study. Br J Psychiatry 187:137–142
Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D (2006) Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet 38(8):904–909
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, Maller J, Sklar P, de Bakker PI, Daly MJ, Sham PC (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81(3):559–575
Reich D, Price AL, Patterson N (2008) Principal component analysis of genetic data. Nat Genet 40(5):646–649
Rochon PA, Stukel TA, Sykora K, Gill S, Garfinkel S, Anderson GM, Normand SL, Mamdani M, Lee PE, Li P, Bronskill SE, Marras C, Gurwitz JH (2005) Atypical antipsychotics and parkinsonism. Arch Intern Med 165(16):1882–1888
Ruggiu M, Herbst R, Kim N, Jevsek M, Fak JJ, Mann MA, Fischbach G, Burden SJ, Darnell RB (2009) Rescuing Z+agrin splicing in Nova null mice restores synapse formation and unmasks a physiologic defect in motor neuron firing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(9):3513–3518
Simpson G, Angus MP (1970) Scale for assessment extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand 212:11–19
Stephen PJ, Williamson J (1984) Drug-induced parkinsonism in the elderly. Lancet 2(8411):1082–1083
Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Byerly MJ, Glick ID, Canive JM, McGee MF, Simpson GM, Stevens MC, Lieberman JA (2003) The National Institute of Mental Health Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness (CATIE) project: schizophrenia trial design and protocol development. Schizophr Bull 29(1):15–31
Sullivan PF, Lin D, Tzeng JY, van den Oord E, Perkins D, Stroup TS, Wagner M, Lee S, Wright FA, Zou F, Liu W, Downing AM, Lieberman J, Close SL (2008) Genomewide association for schizophrenia in the CATIE study: results of stage 1. Mol Psychiatry 13(6):570–584
Tenback DE, van Harten PN, Slooff CJ, van Os J (2006) Evidence that early extrapyramidal symptoms predict later tardive dyskinesia: a prospective analysis of 10,000 patients in the European Schizophrenia Outpatient Health Outcomes (SOHO) study. Am J Psychiatry 163(8):1438–1440
Whitty PF, Owoeye O, Waddington JL (2009) Neurological signs and involuntary movements in schizophrenia: intrinsic to and informative on systems pathobiology. Schizophr Bull 35(2):415–424
Yang Y, Mahaffey CL, Bérubé N, Frankel WN (2006) Interaction between fidgetin and protein kinase A-anchoring protein AKAP95 is critical for palatogenesis in the mouse. J Biol Chem 281(31):22352–22359
Yin M, Liu S, Yin Y, Li S, Li Z, Wu X, Zhang B, Ang SL, Ding Y, Zhou J (2009) Ventral mesencephalon-enriched genes that regulate the development of dopaminergic neurons in vivo. J Neurosci 29(16):5170–5182
Acknowledgement
The principal investigators of the CATIE (Clinical Antipsychotic Trials of Intervention Effectiveness) trial were Jeffrey A. Lieberman, M.D., T. Scott Stroup, M.D., M.P.H., and Joseph P. McEvoy, M.D. The CATIE trial was funded by a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (N01 MH900001) along with MH074027 (PI PF Sullivan). Genotyping was funded by Eli Lilly and Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Ana Alkelai and Lior Greenbaum contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 1
(DOC 56 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alkelai, A., Greenbaum, L., Rigbi, A. et al. Genome-wide association study of antipsychotic-induced parkinsonism severity among schizophrenia patients. Psychopharmacology 206, 491–499 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1627-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1627-z