Abstract
Introduction
Cannabinoids produce a spectrum of effects in humans including euphoria, cognitive impairments, psychotomimetic effects, and perceptual alterations. The extent to which dopaminergic systems contribute to the effects of Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ-9-THC) remains unclear. This study evaluated whether pretreatment with a dopamine receptor antagonist altered the effects of Δ-9-THC in humans.
Materials and methods
In a 2-test-day double-blind study, 28 subjects including healthy subjects (n = 17) and frequent users of cannabis (n = 11) were administered active (0.057 mg/kg) or placebo oral haloperidol in random order followed 90 and 215 min later by fixed order intravenous administration of placebo (vehicle) and active (0.0286 mg/kg) Δ-9-THC, respectively.
Results
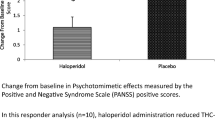
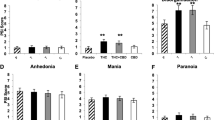
Consistent with previous reports, intravenous Δ-9-THC produced psychotomimetic effects, perceptual alterations, and subjective effects including “high.” Δ-9-THC also impaired verbal recall and attention. Haloperidol pretreatment did not reduce any of the behavioral effects of Δ-9-THC. Haloperidol worsened the immediate free and delayed free and cued recall deficits produced by Δ-9-THC. Haloperidol and Δ-9-THC worsened distractibility and vigilance. Neither drug impaired performance on a motor screening task, the Stockings of Cambridge task, or the delayed match to sample task. Frequent users had lower baseline plasma prolactin levels and blunted Δ-9-THC induced memory impairments.
Conclusions
The deleterious effects of haloperidol pretreatment on the cognitive effects of Δ-9-THC are consistent with the preclinical literature in suggesting crosstalk between DAergic and CBergic systems. However, it is unlikely that DA D2 receptor mechanisms play a major role in mediating the psychotomimetic and perceptual altering effects of Δ-9-THC. Further investigation is warranted to understand the basis of the psychotomimetic effects of Δ-9-THC and to better understand the crosstalk between DAergic and CBergic systems.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agurell S, Halldin M, Lindgren JE, Ohlsson A, Widman M, Gillespie H, Hollister L (1986) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of delta 1-tetrahydrocannabinol and other cannabinoids with emphasis on man. Pharmacol Rev 38:21–43
Aigner TG (1988) Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol impairs visual recognition memory but not discrimination learning in rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 95:507–511
Angrist BM, Gershon S (1970) The phenomenology of experimentally induced amphetamine psychosis–preliminary observations. Biol Psychiatry 2:95–107
Angrist B, Lee HK, Gershon S (1974a) The antagonism of amphetamine-induced symptomatology by a neuroleptic. Am J Psychiatry 131:817–819
Angrist B, Sathananthan G, Wilk S, Gershon S (1974b) Amphetamine psychosis: behavioral and biochemical aspects. J Psychiatr Res 11:13–23
Barnes TR (1989) A rating scale for drug-induced akathisia. Br J Psychiatry 154:672–676
Berk M, Brook S, Trandafir AI (1999) A comparison of olanzapine with haloperidol in cannabis-induced psychotic disorder: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 14:177–1780
Brandt J, Corwin J, Krafft L (1992) Is verbal recognition memory really different in Huntington’s and Alzheimer’s disease. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 14:773–784
Bremner JD, Krystal JH, Putnam FW, Southwick SM, Marmar C, Charney DS, Mazure CM (1998) Measurement of dissociative states with the Clinician-Administered Dissociative States Scale (CADSS). J Trauma Stress 11:125–136
Brunner E, Domhof S, Langer F (2002) Nonparametric analysis of longitudinal data in factorial experiments. Wiley, New York
Budney AJ, Moore BA, Vandrey RG, Hughes JR (2003) The time course and significance of cannabis withdrawal. J Abnorm Psychology 112:393–402
Bylsma FW, Rebok GW, Brandt J (1991) Long-term retention of implicit learning in Huntington’s disease. Neuropsychologia 29:1213–1221
Carlini EA, Hamaoui A, Bieniek D, Korte F (1970a) Effects of (−) delta-9-trans-tetrahydrocannabinol and a synthetic derivative on maze performance of rats. Pharmacology 4:359–368
Carlini EA, Santos M, Claussen U, Bieniek D, Korte F (1970b) Structure activity relationship of four tetrahydrocannabinols and the pharmacological activity of five semi-purified extracts of Cannabis sativa. Psychopharmacologia 18:82–93
Chen J, Paredes W, Lowinson JH, Gardner EL (1990a) Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol enhances presynaptic dopamine efflux in medial prefrontal cortex. Eur J Pharmacol 190:259–262
Chen JP, Paredes W, Li J, Smith D, Lowinson J, Gardner EL (1990b) Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol produces naloxone-blockable enhancement of presynaptic basal dopamine efflux in nucleus accumbens of conscious, freely-moving rats as measured by intracerebral microdialysis. Psychopharmacology 102:156–162
Chen JP, Paredes W, Lowinson JH, Gardner EL (1991) Strain-specific facilitation of dopamine efflux by delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the nucleus accumbens of rat: an in vivo microdialysis study. Neurosci Lett 129:136–180
Compton WM, Grant BF, Colliver JD, Glantz MD, Stinson FS (2004) Prevalence of marijuana use disorders in the United States: 1991–1992 and 2001–2002. Jama 291:2114–2121
Curran HV, Brignell C, Fletcher S, Middleton P, Henry J (2002) Cognitive and subjective dose-response effects of acute oral Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in infrequent cannabis users. Psychopharmacology 164:61–70
D’Souza DC (2007) Cannabinoids and psychosis. Int Rev Neurobiol 78:289–326
D’Souza DC, Perry E, MacDougall L, Ammerman Y, Cooper T, Wu YT, Braley G, Gueorguieva R, Krystal JH (2004) The psychotomimetic effects of intravenous delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in healthy individuals: implications for psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1558–1572
D’Souza DC, Abi-Saab WM, Madonick S, Forselius-Bielen K, Doersch A, Braley G, Gueorguieva R, Cooper TB, Krystal JH (2005) Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol effects in schizophrenia: implications for cognition, psychosis, and addiction. Biol Psychiatry 57:594–608
D’Souza DC, Gil RB, Zuzarte E, MacDougall LM, Donahue L, Ebersole JS, Boutros NN, Cooper T, Seibyl J, Krystal JH (2006) Gamma-aminobutyric acid-serotonin interactions in healthy men: implications for network models of psychosis and dissociation. Biol Psychiatry 59:128–137
D’Souza DC, Ranganathan M, Braley G, Gueorguieva R, Zimolo Z, Cooper T, Perry E, Krystal J (2008) Blunted Psychotomimetic and Amnestic Effects of Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in Frequent Users of Cannabis. Neuropsychopharmacology (in press). DOI 10.1038/sj.npp.1301643
Diana M, Melis M, Gessa GL (1998) Increase in meso-prefrontal dopaminergic activity after stimulation of CB1 receptors by cannabinoids. Eur J Neurosci 10:2825–2830
Egerton A, Allison C, Brett RR, Pratt JA (2006) Cannabinoids and prefrontal cortical function: insights from preclinical studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:680–695
Fadda P, Scherma M, Spano MS, Salis P, Melis V, Fattore L, Fratta W (2006) Cannabinoid self-administration increases dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens. Neuroreport 17:1629–1632
Farde L, Nordstrom AL, Wiesel FA, Pauli S, Halldin C, Sedvall G (1992) Positron emission tomographic analysis of central D1 and D2 dopamine receptor occupancy in patients treated with classical neuroleptics and clozapine. Relation to extrapyramidal side effects. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:538–544
Fergusson DM, Poulton R, Smith PF, Boden JM (2006) Cannabis and psychosis. Bmj 332:172–175
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (2002) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I disorders—non-patient edition. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
French ED (1997) delta9-Tetrahydrocannabinol excites rat VTA dopamine neurons through activation of cannabinoid CB1 but not opioid receptors. Neurosci Lett 226:159–162
French ED, Dillon K, Wu X (1997) Cannabinoids excite dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmentum and substantia nigra. Neuroreport 8:649–652
Gardner EL (2005) Endocannabinoid signaling system and brain reward: emphasis on dopamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:263–284
Gessa GL, Melis M, Muntoni AL, Diana M (1998) Cannabinoids activate mesolimbic dopamine neurons by an action on cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 341:39–44
Goldman-Rakic PS (1996) Regional and cellular fractionation of working memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:13473–13480
Gordon M (1986) Microprocessor-based assessment of attention deficit disorders (ADD). Psychopharmacol Bull 22:288–290
Gregerson KA, Selmanoff M (1988) Selective effects of hyperprolactinemia on in vitro dopamine release from median eminence synaptosomes. J Neurosci 8:2477–2484
Griffith JD, Cavanaugh J, Held J, Oates JA (1972) Dextroamphetamine. Evaluation of psychomimetic properties in man. Arch Gen Psychiatry 26:97–100
Haertzen CA (1965) Addiction Research Center Inventory (ARCI): development of a general drug estimation scale. J Nerv Ment Dis 141:300–307
Haertzen CA (1966) Development of scales based on patterns of drug effects, using the addiction Research Center Inventory (ARCI). Psychol Rep 18:163–194
Haney M (2005) The marijuana withdrawal syndrome: diagnosis and treatment. Curr Psychiatry Rep 7:360–366
Haney M, Ward AS, Comer SD, Foltin RW, Fischman MW (1999a) Abstinence symptoms following oral THC administration to humans. Psychopharmacology 141:385–394
Haney M, Ward AS, Comer SD, Foltin RW, Fischman MW (1999b) Abstinence symptoms following smoked marijuana in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 141:395–404
Harclerode J (1984) Endocrine effects of marijuana in the male: preclinical studies. In: Braude MC, Ludford JP (eds) NIDA Research Monograph Series. National Institute on Drug Abuse, Rockville, MD, pp 45–114
Heishman SJ, Arasteh K, Stitzer ML (1997) Comparative effects of alcohol and marijuana on mood, memory, and performance. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 58:93–101
Henquet C, Murray R, Linszen D, van Os J (2005) The environment and schizophrenia: the role of Cannabis use. Schizophr Bull 31:608–612
Henquet C, Rosa A, Krabbendam L, Papiol S, Fananas L, Drukker M, Ramaekers JG, van Os J (2006) An experimental study of catechol-o-methyltransferase Val158Met moderation of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced effects on psychosis and cognition. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2748–2757
Hermann H, Marsicano G, Lutz B (2002) Coexpression of the cannabinoid receptor type 1 with dopamine and serotonin receptors in distinct neuronal subpopulations of the adult mouse forebrain. Neuroscience 109:451–460
Heyser CJ, Hampson RE, Deadwyler SA (1993) Effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on delayed match to sample performance in rats: alterations in short-term memory associated with changes in task specific firing of hippocampal cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:294–307
Jarrahian A, Watts VJ, Barker EL (2004) D2 dopamine receptors modulate Galpha-subunit coupling of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 308:880–886
Jentsch JD, Andrusiak E, Tran A, Bowers MB Jr., Roth RH (1997) Delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol increases prefrontal cortical catecholaminergic utilization and impairs spatial working memory in the rat: blockade of dopaminergic effects with HA966. Neuropsychopharmacology 16:426–432
Jentsch JD, Verrico CD, Le D, Roth RH (1998) Repeated exposure to delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol reduces prefrontal cortical dopamine metabolism in the rat. Neurosci Lett 246:169–172
Kapur S, Zipursky R, Roy P, Jones C, Remington G, Reed K, Houle S (1997) The relationship between D2 receptor occupancy and plasma levels on low dose oral haloperidol: a PET study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 131:148–152
Kapur S, Zipursky R, Jones C, Remington G, Houle S (2000) Relationship between dopamine D(2) occupancy, clinical response, and side effects: a double-blind PET study of first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 157:514–520
Kay SR, Opler LA, Lindenmayer JP (1989) The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS): rationale and standardisation. Br J Psychiatr Suppl 7:59–67
King DJ (1997) Guidelines for the use of antipsychotic drug studies in healthy volunteers. The BAP Consensus Group. J Psychopharmacol 11:201–209
Kinoshita H, Hasegawa T, Katsumata Y, Kameyama T, Yamamoto I, Nabeshima T (1994) Effect of dizocilpine (MK-801) on the catalepsy induced by delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol in mice. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 95:137–143
Kolb B, Gorny G, Limebeer CL, Parker LA (2006) Chronic treatment with Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol alters the structure of neurons in the nucleus accumbens shell and medial prefrontal cortex of rats. Synapse 60:429–436
Krystal JH, D’Souza DC, Karper LP, Bennett A, Abi-Dargham A, Abi-Saab D, Cassello K, Bowers MB Jr., Vegso S, Heninger GR, Charney DS (1999) Interactive effects of subanesthetic ketamine and haloperidol in healthy humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 145:193–204
Krystal JH, Perry EB Jr., Gueorguieva R, Belger A, Madonick SH, Abi-Dargham A, Cooper TB, Macdougall L, Abi-Saab W, D’Souza DC (2005) Comparative and interactive human psychopharmacologic effects of ketamine and amphetamine: implications for glutamatergic and dopaminergic model psychoses and cognitive function. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:985–994
Krystal JH, Madonick S, Perry E, Gueorguieva R, Brush L, Wray Y, Belger A, D’Souza DC (2006) Potentiation of low dose ketamine effects by naltrexone: potential implications for the pharmacotherapy of alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1793–1800
Lane SD, Cherek DR, Lieving LM, Tcheremissine OV (2005) Marijuana effects on human forgetting functions. J Exp Anal Behav 83:67–83
Laviolette SR, Grace AA (2006a) Cannabinoids Potentiate Emotional Learning Plasticity in Neurons of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex through Basolateral Amygdala Inputs. J Neurosci 26:6458–6468
Laviolette SR, Grace AA (2006b) The roles of cannabinoid and dopamine receptor systems in neural emotional learning circuits: implications for schizophrenia and addiction. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1597–1613
Leweke FM, Schneider U, Thies M, Munte TF, Emrich HM (1999) Effects of synthetic delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol on binocular depth inversion of natural and artificial objects in man. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 142:230–235
Lichtman AH, Martin BR (2005) Cannabinoid tolerance and dependence. Handb Exp Pharmacol 168:691–717
Lichtman AH, Dimen KR, Martin BR (1995) Systemic or intrahippocampal cannabinoid administration impairs spatial memory in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 119:282–290
Liegeois JF, Ichikawa J, Meltzer HY (2002) 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonism potentiates haloperidol-induced dopamine release in rat medial prefrontal cortex and inhibits that in the nucleus accumbens in a dose-dependent manner. Brain Res 947:157–165
Marchese G, Casti P, Ruiu S, Saba P, Sanna A, Casu G, Pani L (2003) Haloperidol, but not clozapine, produces dramatic catalepsy in delta9-THC-treated rats: possible clinical implications. Br J Pharmacol 140:520–526
Martin GW, Wilkinson DA, Kapur BM (1988) Validation of self-reported Cannabis use by urine analysis. Addict Behav 13:147–150
Meschler JP, Howlett AC (2001) Signal transduction interactions between CB1 cannabinoid and dopamine receptors in the rat and monkey striatum. Neuropharmacology 40:918–926
Miyamoto A, Yamamoto T, Ohno M, Watanabe S, Tanaka H, Morimoto S, Shoyama Y (1996) Roles of dopamine D1 receptors in delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced expression of Fos protein in the rat brain. Brain Res 710:234–240
Moghaddam B, Bunney BS (1990) Acute effects of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on the release of dopamine from prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and striatum of the rat: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurochem 54:1755–1760
Moghaddam B, Roth RH, Bunney BS (1990) Characterization of dopamine release in the rat medial prefrontal cortex as assessed by in vivo microdialysis: comparison to the striatum. Neuroscience 36:669–676
Murphy BL, Arnsten AF, Goldman-Rakic PS, Roth RH (1996) Increased dopamine turnover in the prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance in rats and monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:1325–1329
Murphy LL, Munoz RM, Adrian BA, Villanua MA (1998) Function of cannabinoid receptors in the neuroendocrine regulation of hormone secretion. Neurobiol Dis 5:432–446
Nagai H, Egashira N, Sano K, Ogata A, Mizuki A, Mishima K, Iwasaki K, Shoyama Y, Nishimura R, Fujiwara M (2006) Antipsychotics improve Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced impairment of the prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 84:330–336
Ng Cheong Ton JM, Gerhardt GA, Friedemann M, Etgen AM, Rose GM, Sharpless NS, Gardner EL (1988) The effects of delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol on potassium-evoked release of dopamine in the rat caudate nucleus: an in vivo electrochemical and in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res 451:59–68
Owen AM, Downes JJ, Sahakian BJ, Polkey CE, Robbins TW (1990) Planning and spatial working memory following frontal lobe lesions in man. Neuropsychologia 28:1021–1034
Patel S, Hillard CJ (2003) Cannabinoid-induced Fos expression within A10 dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res 963:15–25
Pistis M, Ferraro L, Pira L, Flore G, Tanganelli S, Gessa GL, Devoto P (2002) Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol decreases extracellular GABA and increases extracellular glutamate and dopamine levels in the rat prefrontal cortex: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res 948:155–158
Ramaekers JG, Kauert G, van Ruitenbeek P, Theunissen EL, Schneider E, Moeller MR (2006) High-potency marijuana impairs executive function and inhibitory motor control. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2296–2303
Ranganathan M, D’Souza D (2006) the acute effects of cannabinoids on memory in humans: a review. Psychopharmacology 188:425–444
Ranganathan M, Perry E, Braley G, Cooper T, Gueorguieva R, Krystal J, D’Souza DC (2007) Blunted “negative” but not “positive” effects of thc in cannabis abusers: implications for cannabis use in schizophrenia. In: Schulz CTaC (ed) International Congress on Schizophrenia Research. Schizophrenia Bulletin, Colorado Springs, p 477
Robbins TW, James M, Owen AM, Sahakian BJ, McInnes L, Rabbitt P (1994) Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB): a factor analytic study of a large sample of normal elderly volunteers. Dementia 5:266–281
Rodriguez De Fonseca F, Fernandez-Ruiz JJ, Murphy LL, Cebeira M, Steger RW, Bartke A, Ramos JA (1992) Acute effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol on dopaminergic activity in several rat brain areas. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 42:269–275
Saeedi H, Remington G, Christensen BK (2006) Impact of haloperidol, a dopamine D2 antagonist, on cognition and mood. Schizophr Res 85:222–231
Sahakian BJ, Owen AM (1992) Computerized assessment in neuropsychiatry using CANTAB: discussion paper. J R Soc Med 85:399–402
SAMHSA (2004) Results from the 2003 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: national findings. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services AdministrationRockville, MD
Schotte A, Janssen PF, Gommeren W, Luyten WH, Van Gompel P, Lesage AS, De Loore K, Leysen JE (1996) Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 124:57–73
Selmanoff M (1981) The lateral and medial median eminence: distribution of dopamine, norepinephrine, and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone and the effect of prolactin on catecholamine turnover. Endocrinology 108:1716–1722
Simpson GM, Angus JW (1970) A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 212:11–19
Sobell LC, Sobell MB (1992) Timeline follow-back: a technique for assessing self-reported alcohol consumption. In: Litten R, Allen J (eds) Measuring alcohol consumption. Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp 41–72
Spitzer RL, Williams JBW, Gibbon M, First MB (1990) Structured clinical interview for DSM-III-R-patient edition (SCID-P, version 1.0). American Psychiatric, Washington, DC
Tanda G, Pontieri FE, Di Chiara G (1997a) Cannabinoid and heroin activation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission by a common mu1 opioid receptor mechanism. Science 276:2048–2050
Tanda G, Pontieri FE, Di Chiara G (1997b) Cannabinoid and heroin activation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission by a common mu1 opioid receptor mechanism [comment]. Science 276:2048–2050
Verrico CD, Jentsch JD, Roth RH (2003) Persistent and anatomically selective reduction in prefrontal cortical dopamine metabolism after repeated, intermittent cannabinoid administration to rats. Synapse 49:61–66
Wachtel SR, ElSohly MA, Ross SA, Ambre J, de Wit H (2002) Comparison of the subjective effects of Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol and marijuana in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 161:331–339
Wall ME, Brine DR, Perez-Reyes M (1976) Metabolism of cannabinoids in man. In: Braude MC, Szara S (eds) Pharmacology of marihuana. vol. 1. Raven, New York (536pp.)
Winsauer PJ, Lambert P, Moerschbaecher JM (1999) Cannabinoid ligands and their effects on learning and performance in rhesus monkeys. Behav Pharmacol 10:497–511
Zahrt J, Taylor JR, Mathew RG, Arnsten AF (1997) Supranormal stimulation of D1 dopamine receptors in the rodent prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance. J Neurosci 17:8528–8535
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the critical clinical research contributions of the Biological Studies Unit, VA Connecticut Healthcare System, including Elizabeth O’Donell, R.N; Angelina Genovese, R.N.; Sonah Yoo, R.Ph.; Robert Sturwold, R.Ph., and Mr. Willie Ford. This study was supported by the National Institute of Drug Abuse (DA12382-01 to DCD). In addition, the authors acknowledge support from the (1) Department of Veterans Affairs Schizophrenia Biological Research Center (John Krystal), (2) National Institute of Mental Health (MH61019-02 to DCD), (3) National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (R03 AA11413-02 to DCD), (4) Stanley Medical Research Institute (DCD), and (5) Donaghue Foundation (DCD).
Disclosure/Conflict of interest
None of the authors have any potential conflict/s of interest relating to the subject of the report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
Motor results (means [±SD]) (DOC 36.0 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D’Souza, D.C., Braley, G., Blaise, R. et al. Effects of haloperidol on the behavioral, subjective, cognitive, motor, and neuroendocrine effects of Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol in humans. Psychopharmacology 198, 587–603 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-1042-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-1042-2