Abstract
Rationale
5-HT6 receptor antagonists improve cognitive processes in rodents. However, their site(s) of action remains unexplored and their influence upon social memory has been little investigated.
Objectives
We examined the influence of 5-HT6 receptor ligands upon social memory in rats by use of systemic or local administration into the frontal cortex (FCX), striatum, or nucleus basalis magnocellularis (NBM).
Materials and methods
The social recognition test is based upon the ability of an adult rat to recognize a younger conspecific during the second of two 5-min sessions. In a procedure without an inter-session interval, the actions of drugs alone and the ability to reverse “amnesia” induced by the muscarinic antagonist, scopolamine (1.25 mg/kg, s.c.), were examined. The potential promnesic effect of drugs was also investigated in another procedure where a spontaneous deficit of recognition was induced by a 120-min inter-session interval.
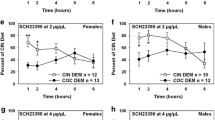
Results
The 5-HT6 receptor agonist, WAY-181187 (10.0 mg/kg, i.p.), significantly impaired social recognition. This effect was abolished by the 5-HT6 receptor antagonists, SB-271046 (20.0 mg/kg, i.p.) and SB-258585 (10.0 mg/kg, i.p.). These agents also abolished scopolamine-induced amnesia (10.0 and 2.5 mg/kg, i.p., respectively) and reversed the delay-induced deficit (10.0–20.0 and 2.5–10.0 mg/kg, i.p., respectively). WAY-181187 into the FCX significantly impaired social recognition (0.16–0.63 μg/side). Conversely, SB-271046 into the FCX (2.5–5.0 μg/side), but neither into the striatum nor the NBM, significantly reversed spontaneous deficit.
Conclusion
These results indicate that 5-HT6 receptors modulate social recognition by actions in the FCX and underpin their pertinence as targets for the treatment of psychiatric disorders in which cognitive function is compromised.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleman A, Hijman R, de Haan EHF, Kahn RS (1999) Memory impairment in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry 156:1358–1366
Bentley JC, Sleight AJ, Marsden CA, Fone KCF (1997) 5-HT6 antisense oligonucleotide I.C.V. affects rat performance in the water maze and feeding. J Psychopharmacol 11:255
Bert L, Favale D, Jego G, Greve P, Guilloux JP, Guiard BP, Gardier AM, Suaud-Chagny MF, Lestage P (2004) Rapid and precise method to locate microdialysis probe implantation in the rodent brain. J Neurosci Methods 140:53–57
Boess FG, Riemer C, Bos M, Bentley J, Bourson A, Sleight AJ (1998) The 5-hydroxytryptamine6 receptor-selective radioligand [3H]Ro 63–0563 labels 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor binding sites in rat and porcine striatum. Mol Pharmacol 54:577–583
Bonasera SJ, Chu HM, Brennan TJ, Tecott LH (2006) A null mutation of the serotonin 6 receptor alters acute responses to ethanol. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1801–1813
Bielsky IF, Young LJ (2004) Oxytocin, vasopressin, and social recognition in mammals. Peptides 25:1565–1574
Branchek TA, Blackburn TP (2000) 5-HT6 receptors as emerging targets for drug discovery. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 40:319–334
Bromidge SM, Brown AM, Clarke SE, Dodgson K, Gager T, Grassam HL, Jeffrey PM, Joiner GF, King FD, Middlemiss DN, Moss SF, Newman H, Riley G, Routledge C, Wyman P (1999) 5-chloro-N-(4-methoxy-3-piperazin-1-yl-phenyl)-3-methyl-2-benzothiophene-sulfonamide (SB-271046): a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable 5-HT6 receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 42:202–205
Callahan PM, Ilch CP, Rowe WB, Tehim A (2004) Characterization of the selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist SB 271046 in behavioral models of cognition. Soc Neurosci Abstr 30:776.19
Chudasama Y, Robbins TW (2004) Dopaminergic modulation of visual attention and working memory in the rodent prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1628–1636
Chudasama Y, Robbins TW (2006) Functions of frontostriatal systems in cognition: comparative neuropsychopharmacological studies in rats, monkeys and humans. Biol Psychol 73:19–38
Chudasama Y, Passetti F, Rhodes SEV, Lopian D, Desai A, Robbins TW (2003) Dissociable aspects of performance on the 5-choice serial reaction time task following lesions of the dorsal anterior cingulate, infralimbic and orbitofrontal cortex in the rat: differential effects on selectivity, impulsivity and compulsivity. Behav Brain Res 146:105–119
Consolo S, Ramponi S, Ladinsky H, Baldi G (1996) A critical role for D1 receptors in the 5-HT1A-mediated facilitation of in vivo acetylcholine release in the rat frontal cortex. Brain Res 707:320–323
Dalley JW, Cardinal RN, Robbins TW (2004) Prefrontal executive and cognitive functions in rodents: neural and neurochemical substrates. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28:771–784
Daly DA, Moghaddam B (1993) Actions of clozapine and haloperidol on the extracellular levels of excitatory amino acids in the prefrontal cortex and striatum of conscious rats. Neurosci Lett 152:61–64
Dantzer R, Bluthe RM, Koob GF, Le Moal M (1987) Modulation of social memory in male rats by neurohypophyseal peptides. Psychopharmacology 91:363–368
Davis RL (2004) Olfactory learning. Neuron 44:31–38
Dawson LA, Nguyen HQ, Li P (2000) In vivo effects of the 5-HT6 antagonist SB-271046 on striatal and frontal cortex extracellular concentrations of noradrenaline, dopamine, 5-HT, glutamate and aspartate. Br J Pharmacol 130:23–26
Dawson LA, Nguyen HQ, Li P (2001) The 5-HT6 receptor antagonist SB-271046 selectively enhances excitatory neurotransmission in the rat frontal cortex and hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 25:662–668
Di Cara B, Panayi F, Gobert A, Dekeyne A, Sicard D, De Groote L, Millan MJ (2007) Activation of dopamine D1 receptors enhances cholinergic transmission and social cognition: a parallel dialysis and behavioural study in rats. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10:383–399
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1997) Central cholinergic systems and cognition. Annu Rev Psychol 48:649–684
Foley AG, Murphy KJ, Hirst WD, Gallagher HC, Hagan JJ, Upton N, Walsh FS, Regan CM (2004) The 5-HT6 receptor antagonist SB-271046 reverses scopolamine-disrupted consolidation of a passive avoidance task and ameliorates spatial task deficits in aged rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:93–100
Gallese V, Keysers C, Rizzolatti G (2004) A unifying view of the basis of social cognition. Trends Cogn Sci 8:396–403
Gérard C, Martres MP, Lefèvre K, Miquel MC, Vergé D, Lanfumey L, Doucet E, Hamon M, El Mestikawy S (1997) Immuno-localization of serotonin 5-HT6 receptor-like material in the rat central nervous system. Brain Res 746:207–219
Hatcher PD, Brown VJ, Tait DS, Bate S, Overend P, Hagan JJ, Jones DNC (2005) 5-HT6 receptor antagonists improve performance in an attentional set shifting task in rats. Psychopharmacology 181:253–259
Hirst WD, Minton JAL, Bromidge SM, Moss SF, Latter AJ, Riley G, Routledge C, Middlemiss DN, Price GW (2000) Characterization of [125I]-SB-258585 binding to human recombinant and native 5-HT6 receptors in rat, pig and human brain tissue. Br J Pharmacol 130:1597–1605
Hirst WD, Stean TO, Rogers DC, Sunter D, Pugh P, Moss SF, Bromidge SM, Riley G, Smith DR, Barlett S, Heidbreder CA, Atkins AR, Lacroix LP, Dawson LA, Foley AG, Regan CM, Upton N (2006) SB-399885 is a potent, selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist with cognitive enhancing properties in aged rat water maze and novel object recognition models. Eur J Pharmacol 553:109–119
King MV, Sleight AJ, Woolley ML, Topham IA, Marsden CA, Fone KCF (2004) 5-HT6 receptor antagonists reverse delay-dependent deficits in novel object discrimination by enhancing consolidation - an effect sensitive to NMDA receptor antagonism. Neuropharmacology 47:195–204
King MV, Sleight AJ, Fone KCF, Marsden CA (2006) A 5-HT6 receptor agonist prolongs memory in the novel object discrimination (NOD) task. J Psychopharmacol 20:A66
Kuperberg G, Heckers S (2000) Schizophrenia and cognitive function. Curr Opin Neurobiol 10:205–210
Lacroix LP, Dawson LA, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA (2004) 5-HT6 receptor antagonist SB-271046 enhances extracellular levels of monoamines in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Synapse 51:158–164
Lee KH, Brown WH, Egleston PN, Green RDJ, Farrow TFD, Hunter MD, Parks RW, Wilkinson ID, Spence SA, Woodruff PWR (2006) A functional magnetic resonance imaging study of social recognition in schizophrenia during an acute episode and after recovery. Am J Psychiatry 163:1926–1933
Lieben CKJ, Blokland A, Sik A, Sung E, van Nieuwenhuizen P, Schreiber R (2005) The selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist Ro4368554 restores memory performance in cholinergic and serotonergic models of memory deficiency in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:2169–2179
Lindner MD, Hodges DB, Hogan JB, Orie AF, Corsa JA, Barten DM, Polson C, Robertson BJ, Guss VL, Gillman KW, Starrett JE, Gribkoff VK (2003) An assessment of the effects of serotonin6 (5-HT6) receptor antagonists in rodent models of learning. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307:682–691
Loiseau F, Millan MJ, Dekeyne A (2007) The D1 receptor agonist, SKF81297, and the D3 receptor antagonist, S33084, enhance social recognition in rat: implication of the frontal cortex. Behav Pharmacol 18:S50–S51
Manoach DS (2003) Prefrontal cortex dysfunction during working memory performance in schizophrenia: reconciling discrepant findings. Schizophr Res 60:285–298
Marcos B, Gil-Bea J, Hirst WD, Garcia-Alloza M, Ramirez MJ (2006) Lack of localization of 5-HT6 receptors on cholinergic neurons: implication of multiple neurotransmitter systems in 5-HT6 receptor-mediated acetylcholine release. Eur J Neurosci 24:1299–1306
Meneses A (2001) Effects of the 5-HT6 receptor antagonist Ro 04-6790 on learning consolidation. Behav Brain Res 118:107–110
Millan MJ, Lejeune F, Gobert A (2000) Reciprocal autoreceptor and heteroreceptor control of serotonergic, dopaminergic, and noradrenergic transmission in the frontal cortex: relevance to the actions of antidepressant agents. J Psychopharmacol 14:114–138
Millan MJ, Gobert A, Roux S, Porsolt RD, Meneses A, Carli M, Di Cara B, Jaffard R, Rivet J-M, Lestage P, Mocaer E, Péglion JL, Dekeyne A (2004) The serotonin1A receptor partial agonist, S15535 [4-(benzodioxan-5-yl)1-(indan-2-yl)piperazine], enhances cholinergic transmission and cognitive function in rodents: a combined neurochemical and behavioral analysis. J Pharm Exp Ther 311:190–203
Millan MJ, Di Cara B, Dekeyne A, Gobert A (2007) Selective blockade of dopamine D3 versus D2 receptors enhances cholinergic transmission and social memory in rats: a parallel neurochemical and behavioural analysis. J Neurochem 100:954–963
Mitchell ES, Neumaier JF (2005) 5-HT6 receptors: a novel target for cognitive enhancement. Pharmacol Ther 108:320–333
Mitchell ES, Hoplight BJ, Lear SP, Neumaier JF (2006) BGC20–761, a novel tryptamine analog, enhances memory consolidation and reverses scopolamine-induced memory deficit in social and visuospatial memory tasks through a 5-HT6 receptor-mediated mechanism. Neuropharmacology 50:412–420
Mitchell ES, Sexton T, Neumaier JF (2007) Increased expression of 5-HT6 receptors in the rat dorsomedial striatum impairs instrumental learning. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1520–1530
Monsma FJ, Shen Y, Ward RP, Hamblin MW, Sibley DR (1993) Cloning and expression of a novel serotonin receptor with high affinity for tricyclic psychotropic drugs. Mol Pharmacol 43:320–327
Passetti F, Chudasama Y, Robbins TW (2002) The frontal cortex of the rat and visual attention performance: dissociable functions of distinct medial prefrontal subregions. Cereb Cortex 12:1254–1268
Paxinos G, Watson W (1994) The rat brain stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, Sydney
Perez-García G, Meneses A (2005) Oral administration of the 5-HT6 receptor antagonists SB-357134 and SB-399885 improves memory formation in an autoshaping learning task. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:673–682
Perio A, Terranova JP, Worms P, Bluthe RM, Dantzer R, Biziere K (1989) Specific modulation of social memory in rats by cholinomimetic and nootropic drugs, by benzodiazepine inverse agonists, but not by psychostimulants. Psychopharmacology 97:262–268
Prast H, Argyriou A, Philippu A (1996) Histaminergic neurons facilitate social memory in rats. Brain Res 734:316–318
Prediger RDS, Takahashi RN (2003) Ethanol improves short-term social memory in rats. Involvement of opioid and muscarinic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 462:115–123
Raggazino ME, Adams S, Kesner RP (1998) Differential involvement of the dorsal anterior cingulate and prelimbic-infralimbic areas of the rodent prefrontal cortex in spatial working memory. Behav Neurosci 112:293–303
Riemer C, Borroni E, Levet-Trafit B, Martin JR, Poli S, Porter RHP, Bös M (2003) Influence of the 5-HT6 receptor on acetylcholine release in the cortex: pharmacological characterization of 4-(2-bromo-6-pyrrolidin-1-ylpyridine-4-sulfonyl)phenylamine, a potent and selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 46:1273–1276
Rogers DC, Hagan JJ (2001) 5-HT6 receptor antagonists enhance retention of a water maze task in the rat. Psychopharmacology 158:114–119
Ruat MT, Traiffort E, Arrang JM, Tardivel-Lacombe J, Diaz J, Leurs R (1993) A novel rat serotonin (5-HT6) receptor: molecular cloning, localization and stimulation of cAMP accumulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 193:268–276
Russell MGN, Dias R (2002) Memories are made of this (perhaps): a review of serotonin 5-HT6 receptor ligands and their biological functions. Curr Top Med Chem 2:643–654
Sarter M, Nelson CL, Bruno JP (2005) Cortical cholinergic transmission and cortical information processing in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 31:117–138
Schechter LE, Li Q, Smith DL, Zhang G, Shan Q, Platt B, Brandt MR, Dawson LA, Cole D, Bernotas R, Robichaud A, Rosenzweig-Lipson S, Beyer CE (2007) Neuropharmacological profile of novel and selective 5-HT6 receptor agonists: WAY-181187 and WAY-208466. Neuropsychopharmacology (in press) DOI 10.1038/sj.npp-1301503
Schreiber R, Vivian J, Hedley L, Szczepanski K, Secchi RL, Zuzow M, van Laarhoven S, Moreau JL, Martin JR, Sik A, Blokland A (2006) Effects of the novel 5-HT6 receptor antagonist Ro4368554 in rat models for cognition and sensorimotor gating. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 30:2169–2179
Seamans JK, Yang CR (2004) The principal features and mechanisms of dopamine modulation in the prefrontal cortex. Prog Neurobiol 71:1–58
Seamans JK, Floresco SB, Phillips AG (1995) Functional differences between the prelimbic and anterior cingulate regions of the rat prefrontal cortex. Behav Neurosci 109:1063–1073
Slassi A, Isaac M, O’Brien A (2002) Recent progress in 5-HT6 receptor antagonists for the treatment of CNS diseases. Expert Opin Ther Patents 12:513–527
Steckler T, Drinkenburg WH, Sahgal A, Aggleton JP (1998) Recognition memory in rats - II. Neuroanatomical substrates. Prog Neurobiol 54:313–332
Terranova JP, Storme JJ, Lafon N, Perio A, Rinaldi-Carmona M, Le Fur G, Soubrié P (1996) Improvement of memory in rodents by the selective CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonist, SR 141716. Psychopharmacology 126:165–172
Tollefson GD (1996) Cognitive function in schizophrenic patients. J Clin Psychiatry 57:31–39
van Kampen M, Selbach K, Schneider R, Schiegel E, Boess F, Schreiber R (2004) AR-R 17779 improves social recognition in rats by activation of nicotinic α7 receptors. Psychopharmacology 172:375–383
Weinberger DR, Egan MF, Bertolino A, Callicott JH, Mattay VS, Lipska BK, Berman KF, Golberg TE (2001) Prefrontal neurons and the genetics of schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 50:825–844
Winslow JT, Camacho F (1995) Cholinergic modulation of a decrement in social investigation following repeated contacts between mice. Psychopharmacology 121:164–172
Woolley ML, Bentley JC, Sleight AJ, Marsden CA, Fone KC (2001) A role for 5-HT6 receptors in retention of spatial memory in the Morris Water maze. Neuropharmacology 41:210–219
Woolley ML, Marsden CA, Sleight AJ, Fone KC (2003) Reversal of a cholinergic-induced deficit in a rodent model of recognition memory by the selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, Ro 04–6790. Psychopharmacology 170:358–367
Woolley ML, Marsden CA, Fone KC (2004) 5-ht6 receptors. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 3:59–79
Yoshioka M, Matsumoto M, Tagashi H, Mori K, Saito H (1998) Central distribution and function of 5-HT6 receptor subtype in the rat brain. Life Sci 62:1473–1477
Acknowledgments
We thank Rodolphe Billiras for excellent technical assistance with the microinjection procedure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loiseau, F., Dekeyne, A. & Millan, M.J. Pro-cognitive effects of 5-HT6 receptor antagonists in the social recognition procedure in rats: implication of the frontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 196, 93–104 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0934-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0934-5