Abstract
Rationale and objective
Performance on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST), which requires patients to ‘shift attention’ between stimulus dimensions (sorting categories), is impaired in diseases such as schizophrenia. The rat attentional set shifting task is an analogue of the WCST. Given that 5-HT6 receptor antagonists improve cognitive performance and influence cortical neurochemistry in rats, the present study investigated the effects of 5-HT6 receptor antagonists upon attentional set shifting in rats.
Methods
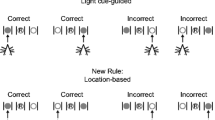
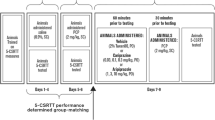
Rats were tested in this paradigm following sub-chronic SB-399885-T or SB-271046-A (both 10 mg kg−1 bid, p.o. for 8 days prior to testing and either 4 or 2 h prior to testing on day 9, respectively). Rats were trained to dig in baited bowls for a food reward and to discriminate based on odour or digging media (Habituation, day 8). In a single session (day 9), rats performed a series of discriminations, including reversals (REV), intra-dimensional (ID) and extra-dimensional (ED) shifts.
Results
Neither compound altered performance during Habituation. On the test day, both SB-399885-T and SB-271046-A reduced the total trials to reach criterion and the total errors made when data were collapsed across all discriminations (P<0.05–0.01). Further, both compounds significantly reduced the trials to criterion for REV-1 (P<0.05–0.01) and abolished the ID/ED shift. SB-399885-T, but not SB-271046-A, reduced trials required to complete the ED shift (P<0.05) and the number of errors made during completion of the ID (P<0.05) and ED shifts (P<0.01).
Conclusion
5-HT6 receptor antagonists improved performance in the attentional set shifting task and may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of disorders where cognitive deficits are a feature, including schizophrenia.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barense MD, Fox MT, Baxter MG (2002) Aged rats are impaired on an attentional set-shifting task sensitive to medial frontal cortex damage in young rats. Learn Mem 9:191–201
Barnes NM, Sharp T (1999) A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 38:1083–1152
Bentley JC, Sleight AJ, Marsden CA, Fone KCF (1997) 5-HT6 antisense oligonucleotide i.c.v. affects rat performance in the water maze and feeding. J Psychopharmacol 11:A64
Bentley JC, Bourson A, Boess FG, Fone KCF, Marsden CA, Petit N, Sleight AJ (1999) Investigation of stretching behaviour induced by the selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist RE 04-6790 in rats. Br J Pharmacol 126:1537–1542
Berg EA (1948) A simple objective treatment for measuring flexibility in thinking. J Gen Psychol 39:15–22
Birrell JM, Brown VJ (2000) Medial frontal cortex mediates perceptual attentional set shifting in the rat. J Neurosci 20(11):4320–4324
Bourson A, Borroni E, Austin RH, Monsma F Jr, Sleight AJ (1995) Determination of the role of the 5-HT6 receptor in the rat brain: a study using antisense oligonucleotides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:173–180
Bourson A, Boess FG, Bos M, Sleight AJ (1998) Involvement of 5-HT6 receptors in nigro-striatal function in rodents. Br J Pharmacol 125:1562–1566
Bromidge SM, Brown AM, Clarke SE, Dodgson K, Gager T, Grassam HL, Jeffrey PM, Joiner GF, King FD, Middlemiss DN, Moss SF, Newman H, Riley G, Routledge C, Wyman P (1999) 5-Chloro-N-(4-methoxy-3-piperazin-1-yl-phenyl)-3-methyl-2-benzothiophenesulfonamide (SB-271046): a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable 5-HT6 receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 42(2):202–205
Foley AG, Murphey KJ, Hirst WD, Gallagher HC, Hagan JJ, Upton N, Walsh FS, Regan CM (2004) The 5-HT6 receptor antagonist SB-271046 reverses scopolamine-disrupted consolidation of a passive avoidance task and ameliorates spatial task deficits in aged rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 29(1):93–100
Fox MT, Barense MD, Baxter MG (2003) Perceptual attentional set-shifting is impaired in rats with neurotoxic lesions of the posterior parietal cortex. J Neurosci 23(2):676–681
Frederick JA, Meador-Woodruff JH (1999) Effects of clozapine and haloperidol on 5-HT6 receptor mRNA levels in the rat brain. Schizophr Res 38:7–12
Gerard C, El Mestikawy S, Lebrand C, Adrien J, Ruat M, Traiffort B, Hamon M, Martres MP (1996) Quantitative RT-PCR distribution of serotonin 5-HT6 receptor mRNA in the central nervous system of control or 5,7-dihydroxytruptamine-treated rats. Synapse 23(3):164–173
Gerard C, Martres MP, Lefevre K, Miquel MC, Verge D, Lanfumey L, Doucet E, Hamon M, El Mestikawy S (1997) Immuno-localization of serotonin 5-HT6 receptor-like material in the rat central nervous system. Brain Res 746:207–219
Hamon M, Doucet E, Lefevre K, Miquel MC, Lanfumey L, Insausti R, Frechilla D, Del Rio J, Verge D (1999) Antibodies and antisense oligonucleotide for probing the distribution and putative functions of central 5-HT6 receptor. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:68–76
Hatcher PD, Brown VJ, Tait DS, Jones DNC (2002) 5-HT6 receptor antagonists improve performance in an attentional set shifting task. J Psychopharmacol 16(3):A16
Hirst WD, Stean TO, Rogers DC, Sunters D, Pugh P, Moss SF, Bromidge SM, Riley G, Smith DR, Barlett S, Heidbreder CA, Atkins AR, Lacroix LP, Dawson LA, Foley AG, Regan CM, Upton N. SB-399885 is a potent, selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist active in rat water maze and novel object recognition models, Br J Pharmacol (personal communication)
Jay TM (2003) Dopamine: a potential substrate for synaptic plasticity and memory mechanisms. Prog Neurobiol 69(6):375–390
Kolb B, Wilshaw IQ (1983) Performance of schizophrenic patients on tests sensitive to left or right frontal temporal, or parietal function in neurological patients. J Nerv Ment Dis 171:435–443
Lacroix LP, Dawson LA, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA (2004) 5-HT6 receptor antagonist SB-271046 enhances extracellular levels of monoamines in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Synapse 51(2):158–164
Lindner MD, Hodges DB, Hogan JB, Orie AF, Corsa JA, Barten DM, Polson C, Robertson BJ, Guss VL, Gillman KW, Starrett JE, Gribkoff VK (2003) An assessment of the effects of serotonin 6 (5-HT6) receptor antagonists in rodent models of learning. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 307(2):682–691
McAlonan K, Brown VJ (2003) Orbital prefrontal cortex mediates reversal learning and not attentional set shifting in the rat. Behav Brain Res 146(1–2):97–103
Meltzer HY, McGurk SR (1999) The effects of clozapine, risperidone, and olanzapine on cognitive function in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 25(2):233–255
Meneses A (2001) Effects of the 5-HT6 receptor antagonist RO 04-6790 on learning consolidation. Behav Brain Res 118:107–110
Pantelis C, Barber FZ, Barnes TRE, Nelson HE, Owen AM, Robbins TW (1999) Comparison of set shifting ability in patients with chronic schizophrenia and frontal lobe damage. Schizophr Res 37:251–270
Pare D (2003) Role of the basolateral amygdala in memory consolidation. Prog Neurobiol 70(5):409–420
Ragozzino ME, Wilcox C, Raso M, Kesner RP (1999) Involvement of rodent prefrontal cortex subregions in strategy switching. Behav Neurosci 113:32–41
Regan CM, Foley AG, Murphy KJ, Hirst WD, Gallagher HC, Hagan JJ, Upton N, Walsh FS (2003) The 5-HT6 receptor antagonists SB-271046 and SB-399885 increase basal and learning induced NCAM-polysialylation in the rat dentate gyrus. Society for Neuroscience No. 835.21
Riemer C, Borroni E, Levet-Treafit B, Martin JR, Poli S, Porter RHP, Bos M (2003) Influence of the 5-HT6 receptor on acetylcholine release in the cortex: pharmacological characterisation 4-(2-Bromo-6-pyrrolidin-1-ylpyridine-4-sulfonyl)phenylamine, a potent and selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 46:1273–1276
Roberts AC, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (1988) The effects of intradimensional and extra-dimensional shifts on visual discrimination learning in humans and non-human primates. Q J Exp Psychol 40B:321–341
Rogers DC, Hagan JJ (2001) 5-HT6 receptor antagonists enhance retention of a water maze task in the rat. Psychopharmacology 158(2):114–119
Roth BL, Criago SC, Choudhary MS, Uluer A, Monsma FJ, Shen Y, Meltzer HY, Sibley DR (1994) Binding of typical and atypical antipsychotic agents to 5-HT6 and 5-HT7 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 268:1403–1410
Roth BL, Sheffler DJ, Kroeze WK (2004) Magic shotgun versus magic bullets: selectively non-selective drugs for mood disorders and schizophrenia. Nat Rev 3:353–359
Routledge C, Bromidge SM, Moss SF, Price GW, Hirst WD, Newman H, Riley G, Gager T, Stean TO, Upton N, Clarke SE, Brown AM, Middlemiss DN (2000) Characterisation of SB-271046-A: a potent, selective and orally active 5-HT6 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol 130:1606–1612
Ruat M, Traiffort E, Arrang JM, Tardivel-Lacombe J, Diaz J, Leurs Schwartz JC (1993) A novel rat serotonin (5-HT6) receptor: molecular cloning, localization and stimulation of cAMP accumulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 193(1):268–276
Ward RP, Hamblin MW, Lachowicz JE, Hoffman BJ, Sibleys DR, Dorsa DM (1995) Localization of serotonin subtype 6 receptor messenger RNA in the rat brain by in situ hybridization histochemistry. Neuroscience 64(4):1105–1111
Woolley ML, Marsden CA, Sleight AJ, Fone KCF (2000) Reversal of a scopolamine-induced deficit in object discrimination by a selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, RO-06790, in rats. Br J Pharmacol 129:64P
Woolley ML, Bentley JC, Sleight AJ, Marsden CA, Fone KCF (2001) A role for 5-HT6 receptors in retention of spatial learning in the Morris water maze. Neuropharmacology 41:210–219
Woolley ML, Marsden CA, Sleight AJ, Fone KCF (2003) Reversal of a cholinergic-induced deficit in a rodent model of recognition memory by the selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist, Ro 04-6790. Psychopharmacology 170(4):358–367
Woolley ML, Marsden CA, Fone KCF (2004) 5HT6 receptors. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 3:59–79
Zhukovshaya NL, Neumaier JF (2000) Clozapine downregulates 5-HT6 and upregulates 5-HT7 receptors in HeLa cells. Neurosci Lett 288:236–240
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatcher, P.D., Brown, V.J., Tait, D.S. et al. 5-HT6 receptor antagonists improve performance in an attentional set shifting task in rats. Psychopharmacology 181, 253–259 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2261-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2261-z