Abstract
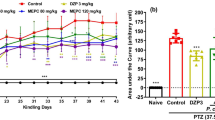
The goal of this study was to investigate the effects of rosmarinic acid (RA) and caffeic acid (CA) in the acute pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) and pilocarpine (PIL) seizure models. We also evaluated the effect of RA and CA on the diazepam (DZP)-induced sleeping time test and its possible neuroprotective effect against the genotoxic damage induced by PTZ and PIL. Mice were treated intraperitoneally (i.p.) with saline, RA (2 or 4 mg/kg), or CA (4 or 8 mg/kg) alone or associated to low-dose DZP. After, mice received a single dose of PTZ (88 mg/kg) or PIL (250 mg/kg) and were monitored for the percentage of seizures and the latency to first seizure (LFS) >3 s. Vigabatrin and DZP were used as positive controls. In the DZP-induced sleeping time test, mice were treated with RA and CA and 30 min after receiving DZP (25 mg/kg, i.p.). The alkaline comet assay was performed after acute seizure tests to evaluate the antigenotoxic profiles of RA and CA. The doses of RA and CA tested alone did not reduce the occurrence of seizures induced by PTZ or PIL. The association of 4 mg/kg RA + low-dose DZP was shown to increase LFS in the PTZ model, compared to the group that received only the DZP. In the DZP-induced sleeping time test, the latency to sleep was reduced by 4 mg/kg RA and 8 mg/kg CA. The PTZ-induced genotoxic damage was not prevented by RA or CA, but the PIL-induced genotoxic damage was decreased by pretreatment with 4 mg/kg RA (in cortex) and 4 mg/kg CA (in hippocampus). In conclusion, RA and CA presented neuroprotective effect against PIL-induced genotoxic damage and reduced the latency to DZP-induced sleep. Of the rosmarinic acid, 4 mg/kg enhanced the DZP effect in the increase of latency to clonic PTZ-induced seizures.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar CC, Almeida AB, Araújo PV, de Abreu RN, Chaves EM, do Vale OC, Macêdo DS, Woods DJ, Fonteles MM, Vasconcelos SM (2012) Oxidative stress and epilepsy: literature review. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2012:1–12. doi:10.1155/2012/795259
Ahmadiani A, Mandgary A, Sayyah M (2003) Anticonvulsant effect of flutamide on seizures induced by pentylenetetrazole: involvement of benzodiazepine receptors. Epilepsia 44:629–635. doi:10.1046/j.1528-1157.2003.36402.x
Asadi-Shekaari M, Eslami A, Kalantaripour T, Joukar S (2014) Potential mechanisms involved in the anticonvulsant effect of walnut extract on pentylenetetrazole-induced seizure. Med Princ Pract 23:538–542. doi:10.1159/000365759
Awad R, Muhammad A, Durst T, Trudeau VL, Arnason JT (2009) Bioassay-guided fractionation of lemon balm (Melissa officinalis L.) using an in vitro measure of GABA transaminase activity. Phytother Res 23:1075–1081. doi:10.1002/ptr.2712
Ben-Menachem E (2011) Mechanism of action of vigabatrin: correcting misperceptions. Acta Neurol Scand 192:5–15. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2011.01596.x
Chindo BA, Ya’U J, Danjuma NM, Okhale SE, Gamaniel KS, Becker A (2014) Behavioral and anticonvulsant effects of the standardized extract of Ficus platyphylla stem bark. J Ethnopharmacol 154:351–360. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.061
Coelho VR, Vieira CG, de Souza LP, Moysés F, Basso C, Papke DK, Pires TR, Siqueira IR, Picada JN, Pereira P (2015) Antiepileptogenic, antioxidant and genotoxic evaluation of rosmarinic acid and its metabolite caffeic acid in mice. Life Sci 122:65–71. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2014.11.009
Costa JP, Ferreira PB, De Sousa DP, Jordan J, Freitas RM (2012) Anticonvulsant effect of phytol in a pilocarpine model in mice. Neurosci Lett 523:115–118. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.06.055
Curia G, Longo D, Biagini G, Jones RS, Avoli M (2008) The pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci Methods 172:143–157. doi:10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.04.019
Da Silva LF, Pereira P, Elisabetsky E (1998) A neuropharmacological analysis of PTZ-induced kindling in mice. Gen Pharmacol 31:47–50. doi:10.1016/S0306-3623(97)00423-0
De Oliveira NC, Sarmento MS, Nunes EA, Porto CM, Rosa DP, Bona SR, Rodrigues G, Marroni NP, Pereira P, Picada JN, Ferraz AB, Thiesen FV, Da Silva J (2012) Rosmarinic acid as a protective agent against genotoxicity of ethanol in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 50:1208–1214. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2012.01.028
Elger CE, Schmidt D (2008) Modern management of epilepsy: a practical approach. Epilepsy Behav 12:501–539. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2008.01.003
Fisher RS, van Emde BW, Blume W, Elger C, Genton P, Lee P, Engel J Jr (2005) Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: definitions proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE). Epilepsia 46:470–472. doi:10.1111/j.0013-9580.2005.66104.x
Hansen SL, Sperling BB, Sánchez C (2004) Anticonvulsant and antiepileptogenic effects of GABAA receptor ligands in pentylenetetrazole-kindled mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28:105–113. doi:10.1016/j.pnpbp.2003.09.026
Huang RQ, Bell-Horner CL, Dibas MI, Covey DF, Drewe JA, Dillon GH (2001) Pentylenetetrazole-induced inhibition of recombinant gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA(A) receptors: mechanism and site of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:986–995
Hui Yin Y, Ahmad N, Makmor-Bakry M (2013) Pathogenesis of epilepsy: challenges in animal models. Iran. Basic Med Sci 11:1119–1132
Johnston GA, Hanrahan JR, Chebib M, Duke RK, Mewett KN (2006) Modulation of ionotropic GABA receptors by natural products of plant origin. Adv Pharmacol 54:285–316. doi:10.1016/S1054-3589(06)54012-8
Kelsey NA, Wilkins HM, Linseman DA (2010) Nutraceutical antioxidants as novel neuroprotective agents. Molecules 15:7792–7814. doi:10.3390/molecules15117792
Khamse S, Sadr SS, Roghani M, Hasanzadeh G, Mohammadian M (2015) Rosmarinic acid exerts a neuroprotective effect in the kainate rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy: underlying mechanisms. Pharm Biol 53:1818–1825. doi:10.3109/13880209.2015.1010738
Koriem KM, Abdelhamid AZ, Younes HF (2013) Caffeic acid protects tissue antioxidants and DNA content in methamphetamine induced tissue toxicity in Sprague Dawley rats. Toxicol Mech Methods 23:134–143. doi:10.3109/15376516.2012.730561
Kupferberg H (2001) Animal models used in the screening of antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia 42:7–12. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2001.00002.x
Larsson OM, Gram L, Schousboe I, Schousboe A (1986) Differential effect of gamma-vinyl GABA and valproate on GABA-transaminase from cultured neurones and astrocytes. Neuropharmacology 25:617–625. doi:10.1016/0028-3908(86)90214-5
Li C, Yan Z, Yang J, Chen H, Li H, Jiang Y, Zhang Z (2010) Neuroprotective effects of resveratrol on ischemic injury mediated by modulating the release of neurotransmitter and neuromodulator in rats. Neurochem Int 56:495–500. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2009.12.009
Löscher W (2011) Critical review of current animal models of seizures and epilepsy used in the discovery and development of new antiepileptic drugs. Seizure 20:359–368. doi:10.1016/j.seizure.2011.01.003
Löscher W, Klitgaard H, Twyman RE, Schmidt D (2013) New avenues for anti-epileptic drug discovery and development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12:757–776. doi:10.1038/nrd4126
Martinc B, Grabnar I, Vovk T (2014) Antioxidants as a preventive treatment for epileptic process: a review of the current status. Curr Neuropharmacol 12:527–550. doi:10.2174/1570159X12666140923205715
Matos G, Ribeiro DA, Alvarenga TA, Hirotsu C, Scorza FA, Le Sueur-Maluf L, Noguti J, Cavalheiro EA, Tufik S, Andersen ML (2012) Behavioral and genetic effects promoted by sleep deprivation in rats submitted to pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Neurosci Lett 515:137–140. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.03.030
Moon DO, Kim MO, Lee JD, Choi YH, Kim GY (2010) Rosmarinic acid sensitizes cell death through suppression of TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation and ROS generation in human leukemia U937 cells. Cancer Lett 288:183–191. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2009.06.033
Nugroho A, Kim M, Choi J, Choi JS, Jung WT, Lee K, Park H (2012) Phytochemical studies of the phenolic substances in Aster glehni extract and its sedative and anticonvulsant activity. Arch Pharm Res 35:423–430. doi:10.1007/s12272-012-0304-7
Oliveira PA, Lino FL, Cappelari SE, Da Silva Brum LF, Picada JN, Pereira P (2008) Effects of gamma-decanolactone on seizures induced by PTZ-kindling in mice. Exp Brain Res 187:161–166. doi:10.1007/s00221-008-1295-y
Pereira P, Tysca D, Oliveira P, Da Silva Brum LF, Picada JN, Ardenghi P (2005) Neurobehavioral and genotoxic aspects of rosmarinic acid. Pharmacol Res 52:199–203. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2005.03.003
Pereira P, Oliveira PA, Ardenghi P, Rotta L, Henriques JA, Picada JN (2006) Neuropharmacological analysis of caffeic acid in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 99:374–378. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2006.pto_533.x
Pereira MB, Freitas RL, Assis MA, Silva RF, Fonteles MM, Freitas RM, Takahashi RN (2007) Study pharmacologic of the GABAergic and glutamatergic drugs on seizures and status epilepticus induced by pilocarpine in adult Wistar rats. Neurosci Lett 419:253–257. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.04.021
Qiao S, Li W, Tsubouchi R, Haneda M, Murakami K, Takeuchi F, Nisimoto Y, Yoshino M (2005) Rosmarinic acid inhibits the formation of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in RAW264.7 macrophages. Free Radic Res 39:995–1003. doi:10.1080/10715760500231836
Ramos AA, Azqueta A, Pereira-Wilson C, Collins AR (2010) Polyphenolic compounds from salvia species protect cellular DNA from oxidation and stimulate DNA repair in cultured human cells. J Agric Food Chem 58:7465–7471. doi:10.1021/jf100082p
Ramos AA, Pedro D, Collins AR, Pereira-Wilson C (2012) Protection by salvia extracts against oxidative and alkylation damage to DNA in human HCT15 and CO115 cells. J Toxic Environ Health A 75:765–775. doi:10.1080/15287394.2012.689804
Rapacz A, Rybka S, Obniska J, Salat K, Powraznik B, Pekala E, Filipek B (2015) Evaluation of anticonvulsant and antinociceptive properties of new N-Mannich bases derived from pyrrolidine-2,5-dione and 3-methylpyrrolidine-2,5-dione. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. doi:10.1007/s00210-015-1194-2
Russo E, di Paola ED, Gareri P, Siniscalchi A, Labate A, Gallelli L, Citraro R, De Sarro G (2013) Pharmacodynamic potentiation of antiepileptic drugs’ effects by some HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors against audiogenic seizures in DBA/2 mice. Pharmacol Res 70:1–12. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2012.12.002
Saha L, Chakrabarti A (2014) Understanding the anti-kindling role and its mechanism of resveratrol in pentylenetetrazole induced-kindling in a rat model. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 120:57–64. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2014.01.010
Sayin U, Timmerman W, Westerink BHC (1995) The significance of extracellular GABA in the substantia nigra of the rat during seizures and anticonvulsant treatments. Brain Res 669:67–72. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(94)01240-I
Sefil F, Kahraman I, Dokuyucu R, Gokce H, Ozturk A, Tutuk O, Aydin M, Ozkan U, Pinar N (2014) Ameliorating effect of quercetin on acute pentylenetetrazole induced seizures in rats. Int J Clin Exp Med 7:2471–2477
Sevgi K, Tepe B, Sarikurkcu C (2015) Antioxidant and DNA damage protection potentials of selected phenolic acids. Food Chem Toxicol 77:12–21. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2014.12.006
Smolders I, Khan GM, Lindekens H, Prikken S, Marvin CA, Manil J, Ebinger G, Michotte Y (1997) Effectiveness of vigabatrin against focally evoked pilocarpine-induced seizures and concomitant changes in extracellular hippocampal and cerebellar glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid and dopamine levels, a microdialysis-electrocorticography study in freely moving rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:1239–1248
Sucher NJ, Carles MC (2015) A pharmacological basis of herbal medicines for epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 52:308–318. doi:10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.05.012
Sueishi Y, Hori M, Ishikawa M, Matsu-Ura K, Kamogawa E, Honda Y, Kita M, Ohara K (2014) Scavenging rate constants of hydrophilic antioxidants against multiple reactive oxygen species. J Clin Biochem Nutr 54:67–74. doi:10.3164/jcbn.13-53
Takeda H, Tsuji M, Miyamoto J, Masuya J, Iimori M, Matsumiya T (2003) Caffeic acid produces antidepressive- and/or anxiolytic-like effects through indirect modulation of the alpha 1A-adrenoceptor system in mice. Neuroreport 14:1067–1070. doi:10.1097/01.wnr.0000073427.02536.b0
Tice RR, Agurell E, Anderson D, Burlinson B, Hartmann A, Kobayashi H, Miyamae Y, Rojas E, Ryu JC, Sasaki YF (2000) Single cell gel/comet assay: guidelines for in vitro and in vivo genetic toxicology testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 35:206–221. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-2280(2000)35:3<206::AID-EM8>3.0.CO;2-J
Turski L, Ikonomidou C, Turski WA, Bortolotto ZA, Cavalheiro EA (1989) Review: cholinergic mechanisms and epileptogenesis. Seizures Induc Pilocarpine: a Nov Exp Model Intractable epilepsy Synapse 3:154–171. doi:10.1002/syn.890030207
Villalpando-Vargas F, Medina-Ceja L (2015) Effect of sparteine on status epilepticus induced in rats by pentylenetetrazole, pilocarpine and kainic acid. Brain Res 1624:59–70. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2015.07.017
Woodbury A, Yu SP, Wei L, García P (2013) Neuro-modulating effects of honokiol: a review. Front Neurol 4:1–6. doi:10.3389/fneur.2013.00130
Yang J, Sykora P, Wilson DM, Mattson MP, Bohr VA (2011) The excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate stimulate DNA repair to increase resiliency. Mech Ageing Dev 132:405–411. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2011.06.005
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by FAPERGS (Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul) (grant number 002100-2551/13-9) and CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico; fellowships), Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coelho, V.R., Vieira, C.G., de Souza, L.P. et al. Behavioral and genotoxic evaluation of rosmarinic and caffeic acid in acute seizure models induced by pentylenetetrazole and pilocarpine in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 389, 1195–1203 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1281-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1281-z