Abstract
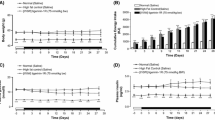
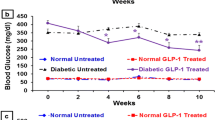
The frog skin host-defence peptide hymenochirin-1B has been shown to stimulate insulin release in vitro from isolated pancreatic islets and BRIN-BD11 clonal β-cells. This study examines the effects of 28-day administration of a more potent analogue [P5K]hymenochirin-1B ([P5K]hym-1B) (75 nmol·kg−1 body weight) to high-fat-fed mice with obesity, glucose intolerance and insulin resistance. Treatment with [P5K]hym-1B significantly decreased plasma glucose concentrations and improved glucose tolerance, insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity and increased the magnitude of the incretin effect (difference in response to oral vs intraperitoneal glucose loads). Responses to established insulin secretagogues were greater in islets isolated from treated animals compared with saline-treated controls. [P5K]hym-1B administration significantly decreased total islet area and β- and α-cell areas, and resulted in lower concentrations of circulating triglycerides and plasma and pancreatic glucagon. Peptide treatment had no effect on food intake, body weight, indirect calorimetry or circulating concentrations of amylase and marker enzymes of liver and kidney function. RT-PCR demonstrated that the Insr (insulin receptor) gene and genes involved in insulin signalling (Slc2a4, Irs1, Pik3ca, Akt1 and Pkd1) were significantly up-regulated in skeletal muscle from animals treated with [P5K]hym-1B. Expression of the Glp1r (GLP-1 receptor) and Gipr (GIP receptor) genes was significantly elevated in islets from peptide-treated mice. These data suggest that [P5K]hym-1B shows potential for development into an agent for treating patients with type 2 diabetes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attoub S, Arafat H, Mechkarska M, Conlon JM (2013) Anti-tumour activities of the host-defense peptide hymenochirin-1B. Regul Pept 187:51–56
Cerf ME (2013) Beta cell dysfunction and insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol 4:1–12
Conlon JM, Mechkarska M, Lukic ML, Flatt PR (2014) Potential therapeutic applications of multifunctional host-defense peptides from frog skin as anti-cancer, anti-viral, immunomodulatory, and anti-diabetic agents. Peptides 57:67–77
Cryer PE (2012) Glucagon in the pathogenesis of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in diabetes. Endocrinology 153:1039–1048
Derosa G, Carbone A, D’Angelo A, Querci F, Fogari E, Cicero AF, Maffioli P (2012) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial evaluating sitagliptin action on insulin resistance parameters and β-cell function. Expert Opin Pharmacother 13:2433–2442
Flatt PR, Bailey CJ (1981) Abnormal plasma glucose and insulin responses in heterozygous lean (ob/+) mice. Diabetologia 20:573–577
Fröjdö S, Vidal H, Pirola L (2009) Alterations of insulin signaling in type 2 diabetes: a review of the current evidence from humans. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792:83–92
Garg R, Chen W, Pendergrass M (2010) Acute pancreatitis in type 2 diabetes treated with exenatide or sitagliptin. A retrospective observational pharmacy claims analysis. Diabetes Care 33:2349–2354
Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 (2015) Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet 386:743–800
Goto M, Maki T, Kiyoizumi T, Satomi S, Monaco AP (1985) An improved method for isolation of mouse pancreatic islets. Transplantation 40:437–438
Holst JJ, Knop FK, Vilsboll T, Krarup T, Madsbad S (2011) Loss of incretin effect is a specific, important, and early characteristic of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 34:S251–S257
Hull RL, Andrikopoulos S, Verchere CB, Vidal J, Wang F, Cnop M, Prigeon RL, Kahn SE (2003) Increased dietary fat promotes islet amyloid formation and β-cell secretory dysfunction in a transgenic mouse model of islet amyloid. Diabetes 52:372–379
Imai Y, Patel HR, Doliba NM, Matschinsky FM, Tobias JW, Ahima RS (2008) Analysis of gene expression in pancreatic islets from diet-induced obese mice. Physiol Genomics 36:43–51
Iyer S, Drake JA 3rd, West R, Mendez C, Tanenberg R (2011) Case report of acute necrotizing pancreatitis associated with combination treatment of sitagliptin and exenatide. Endocr Pract 18:e10–e13
Johnson R, McNutt P, MacMahon S, Robson R (1997) Use of the Friedewald formula to estimate LDL-cholesterol in patients with chronic renal failure on dialysis. Clin Chem 43:2183–2184
Kahn SE, Hull RL, Utzschneider KM (2006) Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 444:840–846
Kazakos K (2011) Incretin effect: GLP-1, GIP, DPP4. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 93:S32–S36
Marshall JA, Bessesen DH (2002) Dietary fat and the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 25:620–622
Martin CMA, Gault VA, McClean S, Flatt PR, Irwin N (2012) Degradation, insulin secretion, glucose-lowering and GIP additive actions of palmitate-derivatised analogues of xenin-25. Biochem Pharmacol 84:312–319
Mechkarska M, Prajeep M, Coquet L, Leprince J, Jouenne T, Vaudry H, King JD, Conlon JM (2012) The hymenochirins: a family of host-defense peptides from the Congo dwarf clawed frog Hymenochirus boettgeri (Pipidae). Peptides 35:269–275
Mechkarska M, Prajeep M, Radosavljevic GD, Jovanovic IP, Al Baloushi A, Sonnevend A, Lukic ML, Conlon JM (2013) An analog of the host-defense peptide hymenochirin-1B with potent broad-spectrum activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria and immunomodulatory properties. Peptides 50:153–159
Mezza T, Muscogiuri G, Sorice GP, Clemente G, Hu J, Pontecorvi A, Holst JJ, Giaccari A, Kulkarni RN (2014) Insulin resistance alters islet morphology in non-diabetic humans. Diabetes 63:995–1007
Moffett RC, Irwin N, Francis JM, Flatt PR (2013) Alterations of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and expression of genes involved in mammary gland and adipose tissue lipid metabolism during pregnancy and lactation. PLoS One 8:e78560
Moffett RC, Vasu S, Thorens B, Drucker DJ, Flatt PR (2014) Incretin receptor null mice reveal key role of GLP-1 but not GIP in pancreatic beta cell adaptation to pregnancy. PLoS One 9:e96863
Moffett RC, Patterson S, Irwin N, Flatt PR (2015) Positive effects of GLP-1 receptor activation with liraglutide on pancreatic islet morphology and metabolic control in C57BL/KsJ db/db mice with degenerative diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 31:248–255
Nauck MA, Friedrich N (2013) Do GLP-1–based therapies increase cancer risk? Diabetes Care 36:S245–S252
Obanda DN, Ribnicky D, Yu Y, Stephens J, Cefalu WT (2016) An extract of Urtica dioica L. mitigates obesity induced insulin resistance in mice skeletal muscle via protein phosphatase 2 A (PP2A). Sci Rep 6:22222
Ojo OO, Conlon JM, Flatt PR, Abdel-Wahab YHA (2013) Frog skin peptides (tigerinin-1R, magainin-AM1, −AM2, CPF-AM1, and PGla-AM1) stimulate secretion of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) by GLUTag cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 431:14–18
Ojo OO, Srinivasan DK, Owolabi BO, Conlon JM, Flatt PR, Abdel-Wahab YHA (2015a) Magainin-AM2 improves glucose homeostasis and beta cell function in high-fat fed mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1850:80–87
Ojo OO, Srinivasan DK, Owolabi BO, Flatt PR, Abdel-Wahab YHA (2015b) Beneficial effects of tigerinin-1R on glucose homeostasis and beta cell function in mice with diet-induced obesity-diabetes. Biochimie 109:18–26
O’Neill S, O’Driscoll L (2015) Metabolic syndrome: a closer look at the growing epidemic and its associated pathologies. Obes Rev 16:1–12
Østergaard L, Frandsen CS, Madsbad S (2016) Treatment potential of the GLP-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a review. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 9:241–265
Owolabi BO, Ojo OO, Srinivasan DK, Conlon JM, Flatt PR, Abdel-Wahab YHA (2016) In vitro and in vivo insulinotropic properties of the multifunctional frog skin peptide hymenochirin-1B: a structure-activity study. Amino Acids 48:535–547
Poletto AC, Furuya DT, David-Silva A, Ebersbach-Silva P, Santos CL, Correa-Giannella ML, Passarelli M, Machado UF (2015) Oleic and linoleic fatty acids downregulate Slc2a4/GLUT4 expression via NFKB and SREBP1 in skeletal muscle cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 401:65–72
Roat R, Rao V, Doliba NM, Matschinsky FM, Tobias JW, Garcia E, Ahima RS, Imai Y (2014) Alterations of pancreatic islet structure, metabolism and gene expression in diet-induced obese C57BL/6 J mice. PLoS One 9:e86815
Rouse R, Xu L, Stewart S, Zhang J (2014) High fat diet and GLP-1 drugs induce pancreatic injury in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 276:104–114
Srinivasan DK, Ojo OO, Owolabi BO, Conlon JM, Flatt PR, Abdel-Wahab YHA (2015) The frog skin host-defense peptide CPF-SE1 improves glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and islet function and decreases plasma lipids in high-fat fed mice. Eur J Pharmacol 764:38–47
Turner N, Zeng XY, Osborne B, Rogers S, Ye JM (2016) Repurposing drugs to target the diabetes epidemic. Trends Pharmacol Sci. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2016.01.007
Vangoitsenhoven R, Mathieu C, Van der Schueren B (2012) GLP1 and cancer: friend or foe? Endocr Relat Cancer 19:F77–F88
Weyer C, Funahashi T, Tanaka S, Hotta K, Matsuzawa Y, Pratley RE, Tataranni PA (2001) Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity and type 2 diabetes: close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1930–1935
Winzell MS, Ahren B (2004) The high-fat diet-fed mouse: a model for studying mechanisms and treatment of impaired glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 53:S215–S219
Ye J (2013) Mechanisms of insulin resistance in obesity. Front Med 7:14–24
Younan SM, Rashed LA (2007) Impairment of the insulinotropic effect of gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) in obese and diabetic rats is related to the down-regulation of its pancreatic receptors. Gen Physiol Biophys 26:181–193
Acknowledgments
Funding for this study was provided by a project grant from Diabetes UK (grant number 12/0004457) and an award of a University Vice Chancellor Research Studentship to DKS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Owolabi, B.O., Ojo, O.O., Srinivasan, D.K. et al. Glucoregulatory, endocrine and morphological effects of [P5K]hymenochirin-1B in mice with diet-induced glucose intolerance and insulin resistance. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 389, 769–781 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1243-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-016-1243-5