Abstract
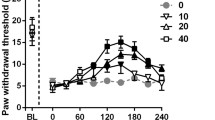
We studied nociceptive behavior and the effects of analgesics in Wistar (Wist) and Sprague Dawley (SPD) rats and in CB1 receptor-deficient mice with neuropathic pain experimentally. Neuropathic pain was induced by loose ligation of the sciatic nerve (chronic constriction injury, CCI). In CCI rats from both strains, cold allodynia and a reduced thermal pain threshold were detected, whereas no effect was found in the hot plate test. Thermal pain threshold was used to study the antinociceptive effects of morphine, gabapentin, and parecoxib 5 days after surgery. Doses of gabapentin and morphine which had no effect on sham-operated animals provoked antinociceptive activity in CCI rats from both strains. An antinociceptive effect of parecoxib was only found in CCI Wist rats. No pharmacokinetic differences were detected between the two strains in parecoxib metabolism. Antinociceptive activity caused by parecoxib was attenuated by the CB1 antagonist rimonabant. To further clarify parecoxib—CB1 interaction, the effect of parecoxib was investigated in CB1-deficient mice and wild-type animals. CCI did not affect thermal pain threshold and mechanical pain threshold was decreased. Parecoxib normalized the altered mechanical pain threshold in CCI wild-type animals, whereas it had only a marginal effect in CB1 receptor deficient mice. Receptor binding experiments showed increased CB1 binding in parecoxib-treated CCI Wist rats. Levels of the CB1 receptor mRNA remained constant in both strains of rats 5 days after surgery. Differences in antinociceptive activity might be due to modification of the cannabinoid system.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson BJ (2008) Paracetamol (acetaminophen): mechanisms of action. Paediatr Anaesth 18:915–921
Asato F, Butler M, Blomberg H, Gordh T (2000) Variation in rat sciatic nerve anatomy: implications for a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Peripher Nerv Syst 5:19–21
Ballesta JJ, Cremades J, Rodriguez-Munoz M, Garzon J, Faura CC (2012) Sensitivity to mu opioid receptor mediated antinociception is determined by cross-regulation between mu and delta opioid receptors at supraspinal level. Br J Pharmacol 166:309–326
Bär KJ, Brehm S, Boettger MK, Boettger S, Wagner G, Sauer H (2005) Pain perception in major depression depends on pain modality. Pain 117:97–103
Bär KJ, Brehm S, Boettger MK, Wagner G, Boettger S, Sauer H (2006) Decreased sensitivity to experimental pain in adjustment disorder. Eur J Pain 10:467–471
Becker A, Grecksch G, Bernstein HG, Höllt V, Bogerts B (1999) Social behaviour in rats lesioned with ibotenic acid in the hippocampus: quantitative and qualitative analysis. Psychopharmacology (Berlin) 144:333–338
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33:87–107
Beyer CE, Dwyer JM, Piesla MJ, Platt BJ, Shen R, Rahman Z, Chan K, Manners MT, Samad TA, Kennedy JD, Bingham B, Whiteside GT (2010) Depression-like phenotype following chronic CB1 receptor antagonism. Neurobiol Dis 39:148–155
Bishay P, Schmidt H, Marian C, Haussler A, Wijnvoord N, Ziebell S, Metzner J, Koch M, Myrczek T, Bechmann I, Kuner R, Costigan M, Dehghani F, Geisslinger G, Tegeder I (2010) R-flurbiprofen reduces neuropathic pain in rodents by restoring endogenous cannabinoids. PLoS One 5:e10628
Braida D, Iosue S, Pegorini S, Sala M (2004) Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced conditioned place preference and intracerebroventricular self-administration in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 506:63–69
Calignano A, La RG, Giuffrida A, Piomelli D (1998) Control of pain initiation by endogenous cannabinoids. Nature 394:277–281
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63
Chapman V (1999) The cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, SR141716A, selectively facilitates nociceptive responses of dorsal horn neurones in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 127:1765–1767
Dani M, Guindon J, Lambert C, Beaulieu P (2007) The local antinociceptive effects of paracetamol in neuropathic pain are mediated by cannabinoid receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 573:214–215
Dauri M, Faria S, Gatti A, Celidonio L, Carpenedo R, Sabato AF (2009) Gabapentin and pregabalin for the acute post-operative pain management. a systematic-narrative review of the recent clinical evidences. Curr Drug Targets 10:716–733
De la O-Arciniega M, Diaz-Reval MI, Cortes-Arroyo AR, Dominguez-Ramirez AM, Lopez-Munoz FJ (2009) Anti-nociceptive synergism of morphine and gabapentin in neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:457–464
Deiana S, Fattore L, Spano MS, Cossu G, Porcu E, Fadda P, Fratta W (2007) Strain and schedule-dependent differences in the acquisition, maintenance and extinction of intravenous cannabinoid self-administration in rats. Neuropharmacology 52:646–654
Eggan SM, Stoyak SR, Verrico CD, Lewis DA (2010) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor immunoreactivity in the prefrontal cortex: comparison of schizophrenia and major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:2060–2071
Elmer GI, Pieper JO, Negus SS, Woods JH (1998) Genetic variance in nociception and its relationship to the potency of morphine-induced analgesia in thermal and chemical tests. Pain 75:129–140
Fattore L, Spano MS, Altea S, Angius F, Fadda P, Fratta W (2007) Cannabinoid self-administration in rats: sex differences and the influence of ovarian function. Br J Pharmacol 152:795–804
Finnerup NB, Sindrup SH, Jensen TS (2007) Chronic neuropathic pain: mechanisms, drug targets and measurement. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 21:129–136
Fuchs A, Rigaud M, Hogan QH (2007) Painful nerve injury shortens the intracellular Ca2+ signal in axotomized sensory neurons of rats. Anesthesiology 107:106–116
Gallinat J, Rentzsch J, Roser P (2012) Neurophysiological effects of cannabinoids: implications for psychosis research. Curr Pharm Des 18:4938–4949
Goto M, Miyahara I, Hirotsu K, Conway M, Yennawar N, Islam MM, Hutson SM (2005) Structural determinants for branched-chain aminotransferase isozyme-specific inhibition by the anticonvulsant drug gabapentin. J Biol Chem 280:37246–37256
Gotta AW (2002) Valdecoxib (Pharmacia). Curr Opin Investig Drugs 3:240–245
Grecksch G, Bernstein HG, Becker A, Hollt V, Bogerts B (1999) Disruption of latent inhibition in rats with postnatal hippocampal lesions. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:525–532
Grecksch G, Zhou D, Franke C, Schroder U, Sabel B, Becker A, Huether G (1997) Influence of olfactory bulbectomy and subsequent imipramine treatment on 5-hydroxytryptaminergic presynapses in the rat frontal cortex: behavioural correlates. Br J Pharmacol 122:1725–1731
Hahm TS, Ahn HJ, Bae CD, Kim HS, Lim SW, Cho HS, Lee SM, Sim WS, Kim JA, Gwak MS, Choi SJ (2009) Protective effects of gabapentin on allodynia and alpha 2 delta 1-subunit of voltage-dependent calcium channel in spinal nerve-ligated rats. J Korean Med Sci 24:146–151
Hama AT, Borsook D (2005) The effect of antinociceptive drugs tested at different times after nerve injury in rats. Anesth Analg 101:175–179
Helme RD (2006) How useful are currently available tools for pain evaluation in elderly people with dementia? Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2:474–475
Hooley JM, Delgado ML (2001) Pain insensitivity in the relatives of schizophrenia patients. Schizophr Res 47:265–273
Jhaveri MD, Richardson D, Chapman V (2007) Endocannabinoid metabolism and uptake: novel targets for neuropathic and inflammatory pain. Br J Pharmacol 152:624–632
Jochum T, Letzsch A, Greiner W, Wagner G, Sauer H, Bar KJ (2006) Influence of antipsychotic medication on pain perception in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 142:151–156
Keilhoff G, Becker A, Grecksch G, Bernstein HG, Wolf G (2006) Cell proliferation is influenced by bulbectomy and normalized by imipramine treatment in a region-specific manner. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1165–1176
Kelly S, Chapman V (2001) Selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor activation inhibits spinal nociceptive transmission in vivo. J Neurophysiol 86:3061–3064
Kim J, Alger BE (2004) Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 potentiates retrograde endocannabinoid effects in hippocampus. Nat Neurosci 7:697–698
Kinsey SG, Long JZ, O’Neal ST, Abdullah RA, Poklis JL, Boger DL, Cravatt BF, Lichtman AH (2009) Blockade of endocannabinoid-degrading enzymes attenuates neuropathic pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 330:902–910
Lee BH, Won R, Baik EJ, Lee SH, Moon CH (2000) An animal model of neuropathic pain employing injury to the sciatic nerve branches. Neuroreport 11:657–661
Lee DH, Chung K, Chung JM (1997) Strain differences in adrenergic sensitivity of neuropathic pain behaviors in an experimental rat model. Neuroreport 8:3453–3456
Lipska BK, Weinberger DR (1995) Genetic variation in vulnerability to the behavioral effects of neonatal hippocampal damage in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:8906–8910
Lovell JA, Stuesse SL, Cruce WL, Crisp T (2000) Strain differences in neuropathic hyperalgesia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 65:141–144
Martin WJ, Loo CM, Basbaum AI (1999) Spinal cannabinoids are anti-allodynic in rats with persistent inflammation. Pain 82:199–205
Mehta V, Johnston A, Cheung R, Bello A, Langford RM (2008) Intravenous parecoxib rapidly leads to COX-2 inhibitory concentration of valdecoxib in the central nervous system. Clin Pharmacol Ther 83:430–435
Myers RR, Heckman HM, Rodriguez M (1996) Reduced hyperalgesia in nerve-injured WLD mice: relationship to nerve fiber phagocytosis, axonal degeneration, and regeneration in normal mice. Exp Neurol 141:94–101
O’Mahony CM, Clarke G, Gibney S, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2011) Strain differences in the neurochemical response to chronic restraint stress in the rat: relevance to depression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97:690–699
Ottani A, Leone S, Sandrini M, Ferrari A, Bertolini A (2006) The analgesic activity of paracetamol is prevented by the blockade of cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 531:280–281
Padi SS, Jain NK, Singh S, Kulkarni SK (2004) Pharmacological profile of parecoxib: a novel, potent injectable selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor. Eur J Pharmacol 491:69–76
Pamplona FA, Menezes-de-Lima O Jr, Takahashi RN (2010) Aspirin-triggered lipoxin induces CB1-dependent catalepsy in mice. Neurosci Lett 470:33–37
Paunescu H, Coman OA, Coman L, Ghita I, Georgescu SR, Draghia F, Fulga I (2011) Cannabinoid system and cyclooxygenases inhibitors. J Med Life 4:11–20
Petrosino S, Di Marzo V (2010) FAAH and MAGL inhibitors: therapeutic opportunities from regulating endocannabinoid levels. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 11:51–62
Portenoy RK, Hagen NA (1990) Breakthrough pain: definition, prevalence and characteristics. Pain 41:273–281
Potvin S, Marchand S (2008) Hypoalgesia in schizophrenia is independent of antipsychotic drugs: a systematic quantitative review of experimental studies. Pain 138:70–78
Potvin S, Stip E, Tempier A, Pampoulova T, Bentaleb LA, Lalonde P, Lipp O, Goffaux P, Marchand S (2008) Pain perception in schizophrenia: no changes in diffuse noxious inhibitory controls (DNIC) but a lack of pain sensitization. J Psychiatr Res 42:1010–1016
Przewlocki R, Przewlocka B (2001) Opioids in chronic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 429:79–91
Rigaud M, Gemes G, Barabas ME, Chernoff DI, Abram SE, Stucky CL, Hogan QH (2008) Species and strain differences in rodent sciatic nerve anatomy: implications for studies of neuropathic pain. Pain 136:188–201
Robinson I, Meert TF (2005) Stability of neuropathic pain symptoms in partial sciatic nerve ligation in rats is affected by suture material. Neurosci Lett 373:125–129
Rode F, Thomsen M, Brolos T, Jensen DG, Blackburn-Munro G, Bjerrum OJ (2007) The importance of genetic background on pain behaviours and pharmacological sensitivity in the rat spared serve injury model of peripheral neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 564:103–111
Rosenthal SH, Porter KA, Coffey B (1990) Pain insensitivity in schizophrenia. Case report and review of the literature. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 12:319–322
Rupp A, Schmahl W, Lederer W, Matiasek K (2007) Strain differences in the branching of the sciatic nerve in rats. Anat Histol Embryol 36:202–208
Sagar DR, Kelly S, Millns PJ, O’Shaughnessey CT, Kendall DA, Chapman V (2005) Inhibitory effects of CB1 and CB2 receptor agonists on responses of DRG neurons and dorsal horn neurons in neuropathic rats. Eur J Neurosci 22:371–379
Scholl JL, Renner KJ, Forster GL, Tejani-Butt S (2010) Central monoamine levels differ between rat strains used in studies of depressive behavior. Brain Res 1355:41–51
Schröder H, Höllt V, Becker A (2011) Parecoxib and its metabolite valdecoxib directly interact with cannabinoid binding sites in CB1-expressing HEK 293 cells and rat brain tissue. Neurochem Int 58:9–13
Singh MK, Giles LL, Nasrallah HA (2006) Pain insensitivity in schizophrenia: trait or state marker? J Psychiatr Pract 12:90–102
Slanina KA, Schweitzer P (2005) Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 elicits a CB1-mediated decrease of excitatory transmission in rat CA1 hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 49:653–659
Sommer C, Schafers M (1998) Painful mononeuropathy in C57BL/Wld mice with delayed wallerian degeneration: differential effects of cytokine production and nerve regeneration on thermal and mechanical hypersensitivity. Brain Res 784:154–162
Stichtenoth DO (2004) The second generation of COX-2 inhibitors: clinical pharmacological point of view. Mini Rev Med Chem 4:617–624
Telleria-Diaz A, Schmidt M, Kreusch S, Neubert AK, Schache F, Vazquez E, Vanegas H, Schaible HG, Ebersberger A (2010) Spinal antinociceptive effects of cyclooxygenase inhibition during inflammation: Involvement of prostaglandins and endocannabinoids. Pain 148:26–35
Treede RD, Jebseb TS, Campbell JN, Cruccu G, Dostrovsky JO, Gruffin JW, Hansson P, Hughes R, Nurmikko T, Serra J (2007) Neuropathic pain. Redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research porposes. Neurology 70:1630–1635
Vinod KY, Xie S, Psychoyos D, Hungund BL, Cooper TB, Tejani-Butt SM (2012) Dysfunction in fatty acid amide hydrolase is associated with depressive-like behavior in Wistar Kyoto rats. PLoS One 7:e36743
Vissers K, De JR, Hoffmann V, Heylen R, Crul B, Meert T (2003) Internal and external factors affecting the development of neuropathic pain in rodents. Is it all about pain? Pain Pract 3:326–342
Vukojevic K, Lovric-Kojundzic S, Sapunar D (2007) Hyperalgesia-type response reveals no difference in pain-related behavior between Wistar and Sprague–Dawley rats. Bosn J Basic Med Sci 7:121–126
Yeomans DC, Proudfit HK (1996) Nociceptive responses to high and low rates of noxious cutaneous heating are mediated by different nociceptors in the rat: electrophysiological evidence. Pain 68:141–150
Yoon YW, Lee DH, Lee BH, Chung K, Chung JM (1999) Different strains and substrains of rats show different levels of neuropathic pain behaviors. Exp Brain Res 129:167–171
Zhang RX, Lao L, Qiao JT, Ruda MA (2003) Strain differences in pain sensitivity and expression of preprodynorphin mRNA in rats following peripheral inflammation. Neurosci Lett 353:213–216
Zimmer A, Zimmer AM, Hohmann AG, Herkenham M, Bonner TI (1999) Increased mortality, hypoactivity, and hypoalgesia in cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:5780–5785
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Michaela Böx, Petra Dehmel, Cathleen Knape, Dana Meyer, Gabriele Schulze, Helga Tischmeyer, and Carlo Angioni for their expert technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest related to this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, A., Geisslinger, G., Murín, R. et al. Cannabinoid-mediated diversity of antinociceptive efficacy of parecoxib in Wistar and Sprague Dawley rats in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 386, 369–382 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0839-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-013-0839-2