Abstract
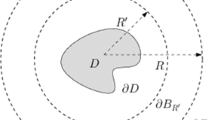
Consider the scattering of a time-domain acoustic plane wave by a bounded elastic obstacle which is immersed in a homogeneous air or fluid. This paper concerns the mathematical analysis of such a time-domain acoustic–elastic interaction problem. An exact transparent boundary condition (TBC) is developed to reduce the scattering problem from an open domain into an initial-boundary value problem in a bounded domain. The well-posedness and stability are established for the reduced problem. A priori estimates with explicit time dependence are achieved for the pressure of the acoustic wave field and the displacement of the elastic wave field. Our proof is based on the method of energy, the Lax–Milgram lemma, and the inversion theorem of the Laplace transform. In addition, a time-domain absorbing perfectly matched layer (PML) method is introduced to replace the nonlocal TBC by a Dirichlet boundary condition. A first order symmetric hyperbolic system is derived for the truncated PML problem. The well-posedness and stability are proved. The time-domain PML results are expected to be useful in the computational air/fluid–solid interaction problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelö, D.; Kreiss, G.: A new absorbing layer for elastic waves. J. Comput. Phys. 215(2), 642–660 (2006)
Berenger, J.-P.: A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves. J. Comput. Phys. 114(2), 185–200 (1994)
Bramble, J.H.; Pasciak, J.E.: Analysis of a finite PML approximation for the three dimensional time-harmonic Maxwell and acoustic scattering problems. Math. Comp. 76, 597–614 (2007)
Chen, Q.; Monk, P.: Discretization of the time domain CFIE for acoustic scattering problems using convolution quadrature. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 46(5), 3107–3130 (2014)
Chen, S.: Introduction to Modern Partial Differential Equations. Science Press, Beijing (2005)
Chen, Z.: Convergence of the time-domain perfectly matched layer method for acoustic scattering problems. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 6(1), 124–146 (2009)
Chen, Z.; Nédélec, J.-C.: On Maxwell's equations with the transparent boundary condition. J. Comput. Math. 26(3), 284–296 (2008)
Chen, Z.; Wu, X.: Long-time stability and convergence of the uniaxial perfectly matched layer method for time-domain acoustic scattering problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 50(5), 2632–2655 (2012)
Chen, Z.; Zheng, W.: Convergence of the uniaxial perfectly matched layer method for time-harmonic scattering problems in two-layered media. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 48(6), 2158–2185 (2010)
Chew, W.; Liu, Q.: Perfectly matched layers for elastodynamics: a new absorbing boundary condition. J. Comput. Acoust. 4(4), 341–359 (1996)
Chew, W.; Weedon, W.: A 3D perfectly matched medium for modified Maxwells equations with stretched coordinates. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 13, 599–604 (1994)
Cohen, A.M.: Numerical Methods for Laplace Transform Inversion, vol. 5. Numerical Methods and Algorithms. Springer, New York (2007)
Collino, F.; Monk, P.: The perfectly matched layer in curvilinear coordinates. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 19, 1061–1090 (1998)
Colton, D., Kress, R.: Inverse Acoustic and Electromagnetic Scattering Theory, vol. 93, Applied Mathematical Sciences, 3rd edn. Springer, New York, 2013
Courjon, D.: Near-Field Microscopy and Near-Field Optics, vol. 317. World Scientific, Singapore (2003)
Dallas, A.G.: Analysis of a Limiting-Amplitude Problem in Acousto-Elastic Interactions. Technical report, DTIC Document (1989)
De Hoop, A.T.; Van den Berg, P.M.; Remis, R.F.: Absorbing boundary conditions and perfectly matched layers-analytic time-domain performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Magn. 38(2), 657–660 (2002)
Diaz, J.; Joly, P.: A time domain analysis of PML models in acoustics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 195(29), 3820–3853 (2006)
Donea, J.; Giuliani, S.; Halleux, J.-P.: An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian finite element method for transient dynamic fluid-structure interactions. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 33(1–3), 689–723 (1982)
Estorff, O.V.; Antes, H.: On FEM-BEM coupling for fluid-structure interaction analyses in the time domain. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 31(6), 1151–1168 (1991)
Evans, L.C.: Partial Differential Equations, vol. 19, Graduate Studies in Mathematics, 2nd edn. American Mathematical Society, Providence, 2010
Fahy, F.J.; Gardonio, P.: Sound and Structural Vibration: Radiation. Transmission and Response. Academic Press, London (2007)
Fatemi, M., Greenleaf, J.F.: Ultrasound-Stimulated Vibro-Acoustic Spectrography. Science, 280(5360), 82–85, 1998
Flemisch, B.; Kaltenbacher, M.; Wohlmuth, B.I.: Elasto-acoustic and acoustic-acoustic coupling on non-matching grids. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 67(13), 1791–1810 (2006)
Gao, Y.; Li, P.: Analysis of time-domain scattering by periodic structures. J. Differ. Equ. 261(9), 5094–5118 (2016)
Gustafsson, B.; Kreiss, H.O.; Oliger, J.: Time Dependent Problems and Difference Methods. Wiley, New York (1995)
Hagstrom, T.: Radiation boundary conditions for the numerical simulation of waves. Acta Numer. 8, 47–106 (1999)
Hamdi, M., Jean, P.: A Mixed Functional for the Numerical Resolution of Fluid-Structure Interaction Problems, Aero-and Hydro-Acoustics, pp. 269–276. Springer, Berlin, 1986
Hsiao, G.C.: On the Boundary-Field Equation Methods for Fluid-Structure Interactions, Problems and Methods in Mathematical Physics, vol. 134, Teubner-Texte Mathematics, pp. 79–88. Teubner, Stuttgart, 1994
Hsiao, G.C., Kleinman, R.E., Schuetz, L.S.: On Variational Formulations of Boundary Value Problems for Fluid–Solid Interactions, Elastic Wave Propagation, vol. 35, North-Holland Series Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, pp. 321–326. North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1989
Hu, G.; Kirsch, A.; Yin, T.: Factorization method in inverse interaction problems with bi-periodic interfaces between acoustic and elastic waves. Inverse Probl. Imaging 10(1), 103–129 (2016)
Jin, J.-M.; Riley, D.J.: Finite Element Analysis of Antennas and Arrays. Wiley, New York (2009)
Kucukcoban, S.; Kallivokas, L.: Mixed perfectly-matched-layers for direct transient analysis in 2D elastic heterogeneous media. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 200(1), 57–76 (2011)
Li, J.; Huang, Y.: Time-Domain Finite Element Methods for Maxwell's Equations in Metamaterials, vol. 43. Springer Series in Computational Mathematics. Springer, Heidelberg (2013)
Li, P.; Wang, L.-L.; Wood, A.: Analysis of transient electromagnetic scattering from a three-dimensional open cavity. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 75(4), 1675–1699 (2015)
Luke, C.J.; Martin, P.A.: Fluid-solid interaction: acoustic scattering by a smooth elastic obstacle. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 55(4), 904–922 (1995)
Morand, H.J.-P.; Ohayon, R.: Fluid Structure Interaction. Wiley, New York (1995)
Nédélec, J.-C.: Acoustic and Electromagnetic Equations Integral Representations for Harmonic Problems, vol. 144. Applied Mathematical Sciences. Springer, New York (2001)
Ohayon, R.; Soize, C.: Structural Acoustics and Vibration: Mechanical Models. Variational Formulations and Discretization. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1997)
Qi, Q.; Geers, T.L.: Evaluation of the perfectly matched layer for computational acoustics. J. Comput. Phys. 139(1), 166–183 (1998)
Riley, D.J.; Jin, J.-M.: Finite-element time-domain analysis of electrically and magnetically dispersive periodic structures. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 56(11), 3501–3509 (2008)
Shirron, J.J.; Giddings, T.E.: A finite element model for acoustic scattering from objects near a fluid-fluid interface. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 196(1), 279–288 (2006)
Soares, D.; Mansur, W.: Dynamic analysis of fluid-soil-structure interaction problems by the boundary element method. J. Comput. Phys. 219(2), 498–512 (2006)
Trèves, F.: Basic Linear Partial Differential Equations, vol. 62. Pure and Applied Mathematics. Academic Press, New York (1975)
Turkel, E.; Yefet, A.: Absorbing PML boundary layers for wave-like equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 27, 533–557 (1998)
Uhlmann, G.: Inside Out: Inverse Problems and Applications, vol. 47. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Wang, B.; Wang, L.: On \(L^2\)-stability analysis of time-domain acoustic scattering problems with exact nonreflecting boundary conditions. J. Math. Study 1(1), 65–84 (2014)
Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.: Fast and accurate computation of time-domain acoustic scattering problems with exact nonreflecting boundary conditions. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 72(6), 1869–1898 (2012)
Yin, T.; Hu, G.; Xu, L.; Zhang, B.: Near-field imaging of obstacles with the factorization method: fluid-solid interaction. Inverse Probl. 32(1), 01500329 (2016)
Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.: Unsplit complex frequency-shifted pml implementation using auxiliary differential equations for seismic wave modeling. Geophysics 75(4), T141–T154 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Lin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, G., Gao, Y. & Li, P. Time-Domain Analysis of an Acoustic–Elastic Interaction Problem. Arch Rational Mech Anal 229, 835–884 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00205-018-1228-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00205-018-1228-2