Abstract
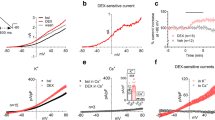
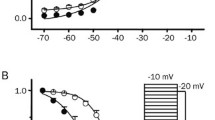
Phosphinotricin (L-PPT) is the active compound of a broad-spectrum herbicide. Acute poisoning with L-PPT has various clinical manifestations, including seizures and convulsions. However, the exact mechanism of L-PPT toxicity remains unclear. The present study addressed the role of L-PPT, in the excitability of striatal medium-sized spiny neurons (MSNs). In whole-cell current-clamp experiments, L-PPT increased the input resistance (Ri), decreased the rheobase and increased the firing frequency of action potentials. In voltage-clamp experiments, L-PPT inhibited the inward-rectifying potassium (Kir) currents. Finally, the effects of L-PPT mimicked the inhibition of Kir channels with Ba2+ on neuronal excitability. Altogether, these results suggest that the herbicide L-PPT is a modulator of Kir channels in MSNs. Thereby, Kir channels are potent regulators of the excitability of MSNs and reduced open probability of these channels would generate a powerful upregulation of neuronal output. This effect may represent a possible mechanism for L-PPT dependent neuronal toxicity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacci A et al (2002) Block of glutamate-glutamine cycle between astrocytes and neurons inhibits epileptiform activity in hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 88(5):2302–2310
Bak LK et al (2006) The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J Neurochem 98(3):641–653
Blomeley CP, Bracci E (2009) Serotonin excites fast-spiking interneurons in the striatum. Eur J Neurosci 29(8):1604–1614
Blumenfeld H et al (2009) Cortical and subcortical networks in human secondarily generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Brain 132(Pt 4):999–1012
Bouilleret V et al (2008) Basal ganglia involvement in temporal lobe epilepsy: a functional and morphologic study. Neurology 70(3):177–184
Calas AG et al (2008) Chronic exposure to glufosinate-ammonium induces spatial memory impairments, hippocampal MRI modifications and glutamine synthetase activation in mice. Neurotoxicology 29(4):740–747
Cepeda C et al (2008) Differential electrophysiological properties of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor-containing striatal medium-sized spiny neurons. Eur J Neurosci 27(3):671–682
D’Ambrosio R et al (2002) Differential role of KIR channel and Na(+)/K(+)-pump in the regulation of extracellular K(+) in rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 87(1):87–102
Eid T et al (2004) Loss of glutamine synthetase in the human epileptogenic hippocampus: possible mechanism for raised extracellular glutamate in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Lancet 363(9402):28–37
Fagg GE, Lanthorn TH (1985) Cl−/Ca2+ -dependent L-glutamate binding sites do not correspond to 2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoate-sensitive excitatory amino acid receptors. Br J Pharmacol 86(3):743–751
Faro LR et al (2013) Role of glutamate receptors and nitric oxide on the effects of glufosinate ammonium, an organophosphate pesticide, on in vivo dopamine release in rat striatum. Toxicology 311(3):154–161
Ferreira Nunes BV et al (2010) Evaluation of the effects and mechanisms of action of glufosinate, an organophosphate insecticide, on striatal dopamine release by using in vivo microdialysis in freely moving rats. Arch Toxicol 84(10):777–785
Gibor G et al (2004) External barium affects the gating of KCNQ1 potassium channels and produces a pore block via two discrete sites. J Gen Physiol 124(1):83–102
Graybiel AM et al (1994) The basal ganglia and adaptive motor control. Science 265(5180):1826–1831
John J, Manchanda R (2011) Modulation of synaptic potentials and cell excitability by dendritic KIR and KAs channels in nucleus accumbens medium spiny neurons: a computational study. J Biosci 36(2):309–328
Karschin C et al (1996) IRK(1-3) and GIRK(1-4) inwardly rectifying K+ channel mRNAs are differentially expressed in the adult rat brain. J Neurosci 16(11):3559–3570
Kehl SJ et al (2013) External Ba(2+) block of Kv4.2 channels is enhanced in the closed-inactivated state. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 304(4):C370–C381
Kimelberg HK, Norenberg MD (1989) Astrocytes. Sci Am 260(4):66–72
Klapstein GJ et al (2001) Electrophysiological and morphological changes in striatal spiny neurons in R6/2 Huntington’s disease transgenic mice. J Neurophysiol 86(6):2667–2677
Lamar C Jr, Sellinger OZ (1965) The inhibition in vivo of cerebral glutamine synthetase and glutamine transferase by the convulsant methionine sulfoximine. Biochem Pharmacol 14:489–506
Lantz SR et al (2014) Glufosinate binds N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors and increases neuronal network activity in vitro. Neurotoxicology 45:38–47
Lapouble E et al (2002) Phosphinothricin induces epileptic activity via nitric oxide production through NMDA receptor activation in adult mice. Brain Res 957(1):46–52
Lee HY et al (2009) Vasogenic edema in striatum following ingestion of glufosinate-containing herbicide. J Clin Neurosci 16(10):1372–1373
Meme W et al (2004) ATP-induced inhibition of gap junctional communication is enhanced by interleukin-1 beta treatment in cultured astrocytes. Neuroscience 126(1):95–104
Meme S et al (2009a) MRI characterization of structural mouse brain changes in response to chronic exposure to the glufosinate ammonium herbicide. Toxicol Sci 111(2):321–330
Meme W et al (2009b) Electrical coupling between hippocampal astrocytes in rat brain slices. Neurosci Res 63(4):236–243
Mermelstein PG et al (1998) Inwardly rectifying potassium (IRK) currents are correlated with IRK subunit expression in rat nucleus accumbens medium spiny neurons. J Neurosci 18(17):6650–6661
Motte J et al (1998) Spatial and temporal evolution of neuronal activation, stress and injury in lithium-pilocarpine seizures in adult rats. Brain Res 793(1–2):61–72
Nakaki T et al (2000) Glufosinate ammonium stimulates nitric oxide production through N-methyl d-aspartate receptors in rat cerebellum. Neurosci Lett 290(3):209–212
Nisenbaum ES, Wilson CJ (1995) Potassium currents responsible for inward and outward rectification in rat neostriatal spiny projection neurons. J Neurosci 15(6):4449–4463
Norenberg MD, Martinez-Hernandez A (1979) Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res 161(2):303–310
O’Donnell P, Grace AA (1993) Physiological and morphological properties of accumbens core and shell neurons recorded in vitro. Synapse 13(2):135–160
Park HY et al (2006) Anterograde amnesia with hippocampal lesions following glufosinate intoxication. Neurology 67(5):914–915
Podda MV et al (2010) Dopamine D1-like receptor activation depolarizes medium spiny neurons of the mouse nucleus accumbens by inhibiting inwardly rectifying K+ currents through a cAMP-dependent protein kinase A-independent mechanism. Neuroscience 167(3):678–690
Pruss H et al (2003) Kir2 potassium channels in rat striatum are strategically localized to control basal ganglia function. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 110(2):203–219
Shen W et al (2005) Cholinergic suppression of KCNQ channel currents enhances excitability of striatal medium spiny neurons. J Neurosci 25(32):7449–7458
Shen W et al (2007) Cholinergic modulation of Kir2 channels selectively elevates dendritic excitability in striatopallidal neurons. Nat Neurosci 10(11):1458–1466
Slaght SJ et al (2002) Functional organization of the circuits connecting the cerebral cortex and the basal ganglia: implications for the role of the basal ganglia in epilepsy. Epileptic Disord 4(Suppl 3):S9–22
Steffens M et al (2005) Unchanged glutamine synthetase activity and increased NMDA receptor density in epileptic human neocortex: implications for the pathophysiology of epilepsy. Neurochem Int 47(6):379–384
Talley EM et al (2001) Cns distribution of members of the two-pore-domain (KCNK) potassium channel family. J Neurosci 21(19):7491–7505
Turski L et al (1988) Dopamine-sensitive anticonvulsant site in the rat striatum. J Neurosci 8(11):4027–4037
Turski L et al (1989) The basal ganglia, the deep prepyriform cortex, and seizure spread: bicuculline is anticonvulsant in the rat striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86(5):1694–1697
Uchimura N, North RA (1990) Muscarine reduces inwardly rectifying potassium conductance in rat nucleus accumbens neurones. J Physiol 422:369–380
van der Hel WS et al (2005) Reduced glutamine synthetase in hippocampal areas with neuron loss in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 64(2):326–333
Wilson CJ (2005) The mechanism of intrinsic amplification of hyperpolarizations and spontaneous bursting in striatal cholinergic interneurons. Neuron 45(4):575–585
Yu W et al (2013) Deconstructing the neural and ionic involvement of seizure-like events in the striatal network. Neurobiol Dis 52:128–136
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor T. Gefflault (University of Clermont-Ferrand) for providing us with L-PPT. This work was funded by the French National Research Agency (ANR) and the National Center for Scientific Research (CNRS). As part of the PhD studies of L.D., it was also supported by the French Ministry of Education and Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domingos, L., Desrus, A., Même, S. et al. L-Phosphinothricin modulation of inwardly rectifying K+ channels increased excitability in striatal medium-sized spiny neurons. Arch Toxicol 90, 1719–1727 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1721-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-016-1721-z