Abstract
In vitro genotoxicity tests are known to suffer from several shortcomings, mammalian cell-based assays, in particular, from low specificities. Following a novel concept of genotoxicity detection, we developed a fluorescence-based method in living human cells. The assay quantifies DNA recombination events triggered by DNA double-strand breaks and damage-induced replication fork stalling predicted to detect a broad spectrum of genotoxic modes of action. To maximize sensitivities, we engineered a DNA substrate encompassing a chemoresponsive element from the human genome. Using this substrate, we screened various human tumor and non-transformed cell types differing in the DNA damage response, which revealed that detection of genotoxic carcinogens was independent of the p53 status but abrogated by apoptosis. Cell types enabling robust and sensitive genotoxicity detection were selected for the generation of reporter clones with chromosomally integrated DNA recombination substrate. Reporter cell lines were scrutinized with 21 compounds, stratified into five sets according to the established categories for identification of carcinogenic compounds: genotoxic carcinogens (“true positives”), non-genotoxic carcinogens, compounds without genotoxic or carcinogenic effect (“true negatives”) and non-carcinogenic compounds, which have been reported to induce chromosomal aberrations or mutations in mammalian cell-based assays (“false positives”). Our results document detection of genotoxic carcinogens in independent cell clones and at levels of cellular toxicities <60 % with a sensitivity of >85 %, specificity of ≥90 % and detection of false-positive compounds <17 %. Importantly, through testing cyclophosphamide in combination with primary hepatocyte cultures, we additionally provide proof-of-concept for the identification of carcinogens requiring metabolic activation using this novel assay system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler S, Basketter D, Creton S, Pelkonen O, van Benthem J, Zuang V, Andersen KE, Angers-Loustau A, Aptula A, Bal-Price A, Benfenati E, Bernauer U, Bessems J, Bois FY, Boobis A, Brandon E, Bremer S, Broschard T, Casati S, Coecke S, Corvi R, Cronin M, Daston G, Dekant W, Felter S, Grignard E, Gundert-Remy U, Heinonen T, Kimber I, Kleinjans J, Komulainen H, Kreiling R, Kreysa J, Leite SB, Loizou G, Maxwell G, Mazzatorta P, Munn S, Pfuhler S, Phrakonkham P, Piersma A, Poth A, Prieto P, Repetto G, Rogiers V, Schoeters G, Schwarz M, Serafimova R, Tähti H, Testai E, van Delft J, van Loveren H, Vinken M, Worth A, Zaldivar JM (2011) Alternative (non-animal) methods for cosmetics testing: current status and future prospects-2010. Arch Toxicol 85:367–485
Akyüz N, Wiesmüller L (2003) Proof of principle: Detection of genotoxicity by a fluorescence-based recombination test in mammalian cells. ALTEX 20:77–84
Akyüz N, Boehden GS, Süsse S, Rimek A, Preuss U, Scheidtmann KH, Wiesmüller L (2002) DNA substrate-dependence of p53-mediated regulation of double-strand-break-repair. Mol Cell Biol 22:6306–6317
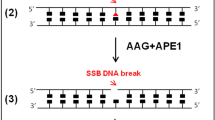
Allen C, Ashley AK, Hromas R, Nickoloff JA (2011) More forks on the road to replication stress recovery. J Mol Cell Biol 3:4–12
Billington N, Cahill P, Hughes C, Tate M, Walmsley RM (2010) A pre-validation transferability study of the GreenScreen HC GADD45a-GFP assay with a metabolic activation system (S9). Mutat Res 700:44–50
Birrell L, Cahill P, Hughes C, Tate M, Walmsley RM (2010) GADD45a-GFP GreenScreen HC assay results for the ECVAM recommended lists of genotoxic and non-genotoxic chemicals for assessment of new genotoxicity tests. Mutat Res 695:87–95
Boehden GS, Restle A, Marschalek R, Stocking C, Wiesmüller L (2004) Recombination at chromosomal sequences involved in leukaemogenic rearrangements is differentially regulated by p53. Carcinogenesis 8:1–9
Böhringer M, Wiesmüller L (2010) Fluorescence-based quantification of pathway-specific DNA double-strand break repair activities: a powerful method for the analysis of genome destabilizing mechanisms. Subcell Biochem 50:297–306
Brennan RJ, Schiestl RH (2004) Detecting carcinogens with the yeast DEL assay. Methods Mol Biol 262:111–124
Concin N et al (2003) Comparison of p53 mutational status with mRNA and protein expression in a panel of 24 human breast carcinoma cell lines. Breast Cancer Res Treat 79:37–46
Corvi R, Aardema MJ, Gribaldo L, Hayashi M, Hoffmann S, Schechtman L, Vanparys P (2012) ECVAM prevalidation study on in vitro cell transformation assays: general outline and conclusions of the study. Mutat Res 744:12–19
Danesi CC, Bellagamba BC, Dihl RR, de Andrade HH, Cunha KS, Lehmann M (2010) Evaluation of the genotoxicity of cisplatin, paclitaxel and 5-fluorouracil combined treatment in the Drosophila wing-spot test. Food Chem Toxicol 48:3120–3124
Digue L, Orsière T, De Méo M, Mattéi MG, Depetris D, Duffaud F, Favre R, Botta A (1999) Evaluation of the genotoxic activity of paclitaxel by the in vitro micronucleus test in combination with fluorescent in situ hybridization of a DNA centromeric probe and the alkaline single cell gel electrophoresis technique (comet assay) in human T-lymphocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen 34:269–278
Elhajouji A, Likamowicz M, Cammerer Z, Kirsch-Volders M (2011) Potential thresholds for genotoxic effect by micronucleus scoring. Mutagenesis 26:199–204
Essmann F, Engels IH, Totzke G, Schulze-Osthoff K, Jänicke RU (2004) Apoptosis resistance of MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells to ionizing radiation is independent of p53 and cell cycle control but caused by the lack of caspase-3 and a caffeine-inhibitable event. Cancer Res 64:7065–7072
Filipič M (2012) Mechanisms of cadmium induced genomic instability. Mutat Res 733:69–77
Fowler P, Smith R, Smith K, Young J, Jeffrey L, Kirkland D, Pfuhler S, Carmichael P (2012) Reduction of misleading (“false”) positive results in mammalian cell genotoxicity assays. II. Importance of accurate toxicity measurement. Mutat Res 747:104–117
Gallagher CM, Chen JJ, Kovach JS (2010) Environmental cadmium and breast cancer risk. Aging 2:804–814
Gebel TW, Leister M, Schumann W, Hirsch-Ernst K (2002) Low-level self-tolerance to arsenite in human HepG2 cells is associated with a depressed induction of micronuclei. Mutat Res 514:245–255
Godoy P et al (2013) Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME. Arch Toxicol 87:1315–1530
Hartwig A (2013) Metal interaction with redox regulation: an integrating concept in metal carcinogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med 55:63–72
Hastwell PW, Chai LL, Roberts KJ, Webster TW, Harvey JS, Rees RW, Walmsley RM (2006) High-specificity and high-sensitivity genotoxicity assessment in a human cell line: validation of the GreenScreen HC GADD45a-GFP genotoxicity assay. Mutat Res 607:160–175
Hastwell PW, Webster TW, Tate M, Billinton N, Lynch AM, Harvey JS, Rees RW, Walmsley RM (2009) Analysis of 75 marketed pharmaceuticals using the GADD45a-GFP “GreenScreen HC” genotoxicity assay. Mutagenesis 24:455–463
Hengstler JG, Utesch D, Steinberg P, Platt KL, Diener B, Ringel M, Swales N, Fischer T, Biefang K, Gerl M, Böttger T, Oesch F (2000a) Cryopreserved primary hepatocytes as a constantly available in vitro model for the evaluation of human and animal drug metabolism and enzyme induction. Drug Metab Rev 32:81–118
Hengstler JG, Ringel M, Biefang K, Hammel S, Milbert U, Gerl M, Klebach M, Diener B, Platt KL, Böttger T, Steinberg P, Oesch F (2000b) Cultures with cryopreserved hepatocytes: applicability for studies of enzyme induction. Chem Biol Interact 125:51–73
Hewitt NJ, Lechón MJ, Houston JB, Hallifax D, Brown HS, Maurel P, Kenna JG, Gustavsson L, Lohmann C, Skonberg C, Guillouzo A, Tuschl G, Li AP, LeCluyse E, Groothuis GM, Hengstler JG (2007) Primary hepatocytes: current understanding of the regulation of metabolic enzymes and transporter proteins, and pharmaceutical practice for the use of hepatocytes in metabolism, enzyme induction, transporter, clearance, and hepatotoxicity studies. Drug Metab Rev 39:159–234
Jagger C, Tate M, Cahill PA, Hughes C, Knight AW, Billinton N, Walmsley RM (2009) Assessment of the genotoxicity of S9-generated metabolites using the GreenScreen HC GADD45a-GFP assay. Mutagenesis 24:35–50
Keimling M, Wiesmüller L (2009) DNA double-strand break repair activities in mammary epithelial cells-influence of endogenous p53 variants. Carcinogenesis 30:1260–1268
Kern JC, Kehrer JP (2002) Acrolein/induced cell death: a caspase-influenced decision between apoptosis and oncosis/necrosis. Chem Biol Interact 139:79–95
Khoury L, Zalko D, Audebert M (2013) Validation of high-throughput assay screening using γH2AX In-cell western assay on HepG2 cells. Environ Mol Mutagen 54:737–746
Kirkland D, Aardema M, Henderson L, Muller L (2005) Evaluation of the ability of a battery of three in vitro genotoxicity tests to discriminate rodent carcinogens and non-carcinogens I. Sensitivity, specificity and relative productivity. Mutat Res 584:1–256
Kirkland D, Pfuhler S, Tweats D, Aardema M, Corvi R, Darroudi F, Elhajouji A, Glatt H, Hastwell P, Hayashi M, Kasper P, Kirchner S, Lynch A, Marzin D, Maurici D, Meunier JR, Müller L, Nohynek G, Parry J, Parry E, Thybaud V, Tice R, van Benthem J, Vanparys P, White P (2007) How to reduce false positive results when undertaking in vitro genotoxicity testing and thus avoid unnecessary follow-up animal tests: report of an ECVAM workshop. Mutat Res 628:31–55
Kirkland D, Kasper P, Müller L, Corvi R, Speit G (2008) Recommended lists of genotoxic and non-genotoxic chemicals for assessment of the performance of new or improved genotoxicity tests: a follow-up to an ECVAM workshop. Mutat Res 653:99–108
Kirkland D, Reeve L, Gatehouse D, Vanparys P (2011) A core in vitro genotoxicity battery comprising the Ames test plus the in vitro micronucleus test is sufficient to detect rodent carcinogens and in vivo genotoxins. Mutat Res 721:27–73
Kirpnick Z, Homiski M, Rubitski E, Repnevskaya M, Howlett N, Aubrecht J, Schiestl RH (2005) Yeast DEL assay detects clastogens. Mutat Res 582:116–134
Komissarova EV, Saha SK, Rossman TG (2005) Dead or dying: the importance of time in cytotoxicity assays using arsenite as an example. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 202:99–107
Lacroix M, Robert-Alain Toillon RA, Leclercq G (2006) p53 and breast cancer, an update. Endocr Relat Cancer 13:293–325
Law JC, Ritke MK, Yalowich JC, Leder GH, Ferrell RE (1993) Mutational inactivation of the p53 gene in the human erythroid leukemic K562 cell line. Leuk Res 17:1045–1050
Levy JA, Virolainen M, Defendi V (1968) Human lymphoblastoid lines from lymph node and spleen. Cancer 22:517–524
Lozzio CB, Lozzio BB (1975) Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood 45:321–344
Lynch A, Sasaki J, Elespuru R (2011) New and emerging technologies for genetic toxicity testing. Environ Mol Mutagen 52:205–223
Mahdi T, Alcalay D, Cognard C, Tanzer J, Kitzis A (1998) Rescue of K562 cells from MDM2-modulated p53-dependent apoptosis by growth factor-induced differentiation. Biol Chem 90:15–27
McGahon A, Bissonnette R, Schmitt M, Cotter KM, Green DR, Cotter TG (1994) BCR-ABL maintains resistance of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells to apoptotic cell death. Blood 83:1179–1187
Meyer C et al (2013) The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias in 2013. Leukemia 27:2165–2176
Mirault ME, Boucher P, Tremblay A (2006) Nucleotide-resolution mapping of topoisomerase-mediated and apoptotic DNA strand scissions at or near an MLL translocation hotspot. Am J Hum Genet 79:779–791
Mondal S, Bhattacharya K, Mallick A, Sangwan R, Mandal C (2012) Bak compensated for Bax in p53-null cells to release cytochrome c for the initiation of mitochondrial signaling during withanolide D-induced apoptosis. PLoS ONE 7:e34277
Muntean AG, Hess JL (2012) The pathogenesis of mixed-lineage leukemia. Annu Rev Pat 7:283–301
Nagai S, Heun P, Gasser SM (2010) Roles for nuclear organization in the maintenance of genome stability. Epigenomics 2:289–305
O′Donovan M (2012) A critique of methods to measure cytotoxicity in mammalian cell genotoxicity assays. Mutagenesis 27:615–621
Olaharski A, Albertini S, Kirchner S, Platz S, Uppal H, Lin H, Kolaja K (2009) Evaluation of the GreenScreen GADD45α-GFP indicator assay with non-proprietary and proprietary compounds. Mutat Res 627:10–16
Olaharski AJ, Albertini S, Mueller L, Zeller A, Struwe M, Gocke E, Kolaja K (2011) GADD45α induction in the GreenScreen HC indicator assay does not occur independently of cytotoxicity. Environ Mol Mutagen 52:28–34
Pfuhler S, Fellows M, van Benthem J, Corvi R, Curren R, Dearfield K, Fowler P, Frötschl R, Elhajouji A, Hégarat Le L, Kasamatsu T, Kojima H, Ouédraogo G, Scott A, Speit G (2011) In vitro genotoxicity test approaches with better predictivity: summary of an IWGT workshop. Mutat Res 723:101–107
Restle A, Färber M, Baumann C, Böhringer M, Scheidtmann KH, Müller-Tidow C, Wiesmüller L (2008) Dissecting the role of p53 phosphorylation in homologous recombination provides new clues for gain-of-function mutants. Nucleic Acids Res 36:5362–5375
Rothkamm K, Krüger I, Thompson LH, Löbrich M (2003) Pathways of DNA double-strand break repair during the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol 23:5706–5715
Schaap MM, Zwart EP, Wackers PF, Huijskens I, van de Water B, Breit TM, van Steeg H, Jonker MJ, Luijten M (2012) Dissecting modes of action of non-genotoxic carcinogens in primary mouse hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 86:1717–1727
Schiestl RH (1989) Nonmutagenic carcinogens induce intrachromosomal recombination in yeast. Nature 337:285–288
Scott D, Galloway SM, Marshall RR, Ishidate M Jr, Brusick D, Ashby J, Myhr BC (1991) International commission for protection against environmental mutagens and carcinogens. Genotoxicity under extreme culture conditions. A report from ICPEMC Task Group 9. Mutat Res 257:147–205
Sim SP, Liu LF (2001) Nucleolytic cleavage of the mixed lineage leukemia breakpoint cluster region during apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276:31590–31595
Thybaud V, Aardema M, Casciano D, Dellarco V (2007) Relevance and follow-up of positive results in in vitro genetic toxicity assays: an ILSI-HESI initiative. Mutat Res 633:67–79
Tsamou M, Jennen DG, Claessen SM, Magkoufopoulou C, Kleinjans JC, van Delft JH (2012) Performance of in vitro γH2AX assay in HepG2 cells to predict in vivo genotoxicity. Mutagenesis 27:645–652
Un F (2007) G1 arrest induction represents a critical determinant for cisplatin cytotoxicity in G1 checkpoint-retaining human cancers. Anticancer Drugs 18:411–417
Valenci-Quintana R, Gómez-Arroyo S, Waliszewski SM (2012) Evaluation of the genotoxic potential of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in meristematic cells of the root of Vicia faba. Toxicol Environ Health Sci 4:154–160
Wilkening S, Stahl F, Bader A (2003) Comparison of primary human hepatocytes and hepatoma cell line Hepg2 with regard to their biotransformation properties. Drug Metab Dispos 31:1035–1042
Yvon AM, Wadsworth P, Jordan MA (1999) Taxol suppresses dynamics of individual microtubules in living human tumor cells. Mol Biol Cell 10:947–959
Zhang F, Gu W, Hurles ME, Lupski JR (2009) Copy number variation in human health, disease, and evolution. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 10:451–481
Zhang QX, Yang GY, Li JT, Li WX, Zhang B, Zhu W (2011) Melamine induces sperm DNA damage and abnormality, but not genetic toxicity. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 60:144–150
Acknowledgments
We thank Thomas Friedl, Ulm University, for help with the statistical evaluation of the data, and Günter Speit, Ulm University, for extremely helpful discussions and expert advice regarding genotoxicity testing. We thank Ms. Georgia Günther for competent support with isolation and cultivation of primary hepatocytes. This work was supported by the German state of Baden-Württemberg, Ministry of Nutrition and Agriculture, grant #315E, by the German Research Foundation (DFG, WI 3099/7-1 and -2) and by the FP7 EU projects DETECTIVE and NOTOX.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ireno, I.C., Baumann, C., Stöber, R. et al. Fluorescence-based recombination assay for sensitive and specific detection of genotoxic carcinogens in human cells. Arch Toxicol 88, 1141–1159 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1229-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1229-3