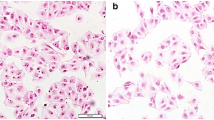
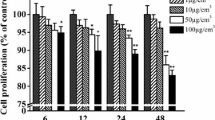
Abstract
Nanosized copper oxide (nano-CuO) has been widely used in many fields. Recent studies have shown that nano-CuO has toxic effects on various organs, but the effects of nano-CuO on kidney remain unclear. The aim of this study was to assess whether nano-CuO can induce the apoptosis of podocytes. The result of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay indicated that nano-CuO decreased podocyte viability in a concentration-dependent and time-dependent manner. The apoptotic assay by flow cytometry showed that nano-CuO induced podocyte apoptosis significantly. Meanwhile, the result of flow cytometric assay gave a clear indication that nano-CuO increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) level. The measurement of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA) showed that nano-CuO decreased SOD and increased MDA levels in podocytes. These results may provide basic information for the safe application of nano-CuO in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamed M, Alsalhi MS, Siddiqui MK (2010a) Silver nanoparticle applications and human health. Clin Chim Acta 411(23–24):1841–1848. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2010.08.016
Ahamed M, Posgai R, Gorey TJ, Nielsen M, Hussain SM, Rowe JJ (2010b) Silver nanoparticles induced heat shock protein 70, oxidative stress and apoptosis in Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 242(3):263–269. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2009.10.016
Ahamed M, Siddiqui MA, Akhtar MJ, Ahmad I, Pant AB, Alhadlaq HA (2010c) Genotoxic potential of copper oxide nanoparticles in human lung epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 396(2):578–583. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.156
Akhtar MJ, Ahamed M, Kumar S, Siddiqui H, Patil G, Ashquin M, Ahmad I (2010) Nanotoxicity of pure silica mediated through oxidant generation rather than glutathione depletion in human lung epithelial cells. Toxicology 276(2):95–102. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2010.07.010
Akhtar MJ, Ahamed M, Fareed M, Alrokayan SA, Kumar S (2012) Protective effect of sulphoraphane against oxidative stress mediated toxicity induced by CuO nanoparticles in mouse embryonic fibroblasts BALB 3T3. J Toxicol Sci 37(1):139–148
Binder CJ, Weiher H, Exner M, Kerjaschki D (1999) Glomerular overproduction of oxygen radicals in Mpv17 gene-inactivated mice causes podocyte foot process flattening and proteinuria: a model of steroid-resistant nephrosis sensitive to radical scavenger therapy. Am J Pathol 154(4):1067–1075. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65359-X
Chen Z, Meng H, Xing G, Chen C, Zhao Y, Jia G, Wang T, Yuan H, Ye C, Zhao F, Chai Z, Zhu C, Fang X, Ma B, Wan L (2006) Acute toxicological effects of copper nanoparticles in vivo. Toxicol Lett 163(2):109–120. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2005.10.003
Denizot F, Lang R (1986) Rapid colorimetric assay for cell growth and survival. Modifications to the tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and reliability. J Immunol Methods 89(2):271–277
Fahmy B, Cormier SA (2009) Copper oxide nanoparticles induce oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in airway epithelial cells. Toxicol In Vitro 23(7):1365–1371. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2009.08.005
Greiber S, Munzel T, Kastner S, Muller B, Schollmeyer P, Pavenstadt H (1998) NAD(P)H oxidase activity in cultured human podocytes: effects of adenosine triphosphate. Kidney Int 53(3):654–663. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00796.x
Hoshi S, Shu Y, Yoshida F, Inagaki T, Sonoda J, Watanabe T, Nomoto K, Nagata M (2002) Podocyte injury promotes progressive nephropathy in zucker diabetic fatty rats. Lab Invest 82(1):25–35
Inoue M, Nishikawa M, Sato E, Matsuno K, Sasaki J (1999) Synthesis of superoxide dismutase derivative that specifically accumulates in renal proximal tubule cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 368(2):354–360. doi:10.1006/abbi.1999.1329
Jiang LC, Zhang WD (2010) A highly sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on CuO nanoparticles-modified carbon nanotube electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 25(6):1402–1407. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2009.10.038
Kang BP, Frencher S, Reddy V, Kessler A, Malhotra A, Meggs LG (2003) High glucose promotes mesangial cell apoptosis by oxidant-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284(3):F455–F466. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00137.2002
Karlsson HL, Cronholm P, Gustafsson J, Moller L (2008) Copper oxide nanoparticles are highly toxic: a comparison between metal oxide nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Chem Res Toxicol 21(9):1726–1732. doi:10.1021/tx800064j
Kretzler M, Koeppen-Hagemann I, Kriz W (1994) Podocyte damage is a critical step in the development of glomerulosclerosis in the uninephrectomised-desoxycorticosterone hypertensive rat. Virchows Arch 425(2):181–193
Kriz W, Gretz N, Lemley KV (1998) Progression of glomerular diseases: is the podocyte the culprit? Kidney Int 54(3):687–697. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00044.x
Kuwabara M, Asanuma T, Niwa K, Inanami O (2008) Regulation of cell survival and death signals induced by oxidative stress. J Clin Biochem Nutr 43(2):51–57. doi:10.3164/jcbn.2008045
Li N, Hao M, Phalen RF, Hinds WC, Nel AE (2003) Particulate air pollutants and asthma. A paradigm for the role of oxidative stress in PM-induced adverse health effects. Clin Immunol 109(3):250–265
Liu Z, Liu S, Ren G, Zhang T, Yang Z (2011) Nano-CuO inhibited voltage-gated sodium current of hippocampal CA1 neurons via reactive oxygen species but independent from G-proteins pathway. J Appl Toxicol 31(5):439–445. doi:10.1002/jat.1611
Meng H, Chen Z, Xing G, Yuan H, Chen C, Zhao F, Zhang C, Zhao Y (2007) Ultrahigh reactivity provokes nanotoxicity: explanation of oral toxicity of nano-copper particles. Toxicol Lett 175(1–3):102–110. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2007.09.015
Meyer TW, Bennett PH, Nelson RG (1999) Podocyte number predicts long-term urinary albumin excretion in Pima Indians with Type II diabetes and microalbuminuria. Diabetologia 42(11):1341–1344. doi:10.1007/s001250051447
Mundel P, Reiser J, Zuniga Mejia Borja A, Pavenstadt H, Davidson GR, Kriz W, Zeller R (1997) Rearrangements of the cytoskeleton and cell contacts induce process formation during differentiation of conditionally immortalized mouse podocyte cell lines. Exp Cell Res 236(1):248–258
Nel A, Xia T, Madler L, Li N (2006) Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 311(5761):622–627. doi:10.1126/science.1114397
Nishino Y, Takemura S, Minamiyama Y, Hirohashi K, Ogino T, Inoue M, Okada S, Kinoshita H (2003) Targeting superoxide dismutase to renal proximal tubule cells attenuates vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Free Radic Res 37(4):373–379
Oberdorster G, Oberdorster E, Oberdorster J (2005) Nanotoxicology: an emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ Health Perspect 113(7):823–839
Oktem F, Arslan MK, Ozguner F, Candir O, Yilmaz HR, Ciris M, Uz E (2005) In vivo evidences suggesting the role of oxidative stress in pathogenesis of vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity: protection by erdosteine. Toxicology 215(3):227–233. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2005.07.009
Pavenstadt H, Kriz W, Kretzler M (2003) Cell biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol Rev 83(1):253–307. doi:10.1152/physrev.00020.2002
Powers SK, Quindry JC, Kavazis AN (2008) Exercise-induced cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Free Radic Biol Med 44(2):193–201. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.02.006
Ren G, Huynh C, Bijian K, Cybulsky AV (2008) Role of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 in complement-mediated glomerular epithelial cell injury. Mol Immunol 45(8):2236–2246. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2007.11.013
Schiffer M, Bitzer M, Roberts IS, Kopp JB, ten Dijke P, Mundel P, Bottinger EP (2001) Apoptosis in podocytes induced by TGF-beta and Smad7. J Clin Invest 108(6):807–816. doi:10.1172/JCI12367
Song MJ, Hwang SW, Whang D (2010) Non-enzymatic electrochemical CuO nanoflowers sensor for hydrogen peroxide detection. Talanta 80(5):1648–1652. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2009.09.061
Susztak K, Raff AC, Schiffer M, Bottinger EP (2006) Glucose-induced reactive oxygen species cause apoptosis of podocytes and podocyte depletion at the onset of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 55(1):225–233
Termini J (2000) Hydroperoxide-induced DNA damage and mutations. Mutat Res 450(1–2):107–124
Thill A, Zeyons O, Spalla O, Chauvat F, Rose J, Auffan M, Flank AM (2006) Cytotoxicity of CeO2 nanoparticles for Escherichia coli. Physico-chemical insight of the cytotoxicity mechanism. Environ Sci Technol 40(19):6151–6156
Tsutsui H (2006) Mitochondrial oxidative stress and heart failure. Intern Med 45(13):809–813
Wang Y, Aker WG, Hwang HM, Yedjou CG, Yu H, Tchounwou PB (2011) A study of the mechanism of in vitro cytotoxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles using catfish primary hepatocytes and human HepG2 cells. Sci Total Environ 409(22):4753–4762. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.07.039
Xia T, Kovochich M, Brant J, Hotze M, Sempf J, Oberley T, Sioutas C, Yeh JI, Wiesner MR, Nel AE (2006) Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett 6(8):1794–1807. doi:10.1021/nl061025k
Xu LJ, Zhao JX, Zhang T, Ren GG, Yang Z (2009) In vitro study on influence of nano particles of CuO on CA1 pyramidal neurons of rat hippocampus potassium currents. Environ Toxicol 24(3):211–217. doi:10.1002/tox.20418
Yu M, Mo Y, Wan R, Chien S, Zhang X, Zhang Q (2010) Regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in endothelial cells with exposure to metal nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 195(1):82–89. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.02.010
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant from the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB944003) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31070890). The authors gratefully acknowledge the kind gift of nanoparticles and the suggestions of Dr. GG Ren.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, J., Li, Z., Xu, P. et al. Nanosized copper oxide induces apoptosis through oxidative stress in podocytes. Arch Toxicol 87, 1067–1073 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0925-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0925-0