Abstract
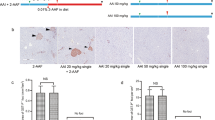
Some renal carcinogens can induce karyomegaly, which reflects aberrant cell division in the renal tubules, from the early stages of exposure. To clarify the cell cycle-related changes during the early stages of renal carcinogenesis, we performed immunohistochemical analysis of tubular cells in male F344 rats treated with carcinogenic doses of representative renal carcinogens for 28 days. For this purpose, the karyomegaly-inducing carcinogens ochratoxin A (OTA), ferric nitrilotriacetic acid, and monuron, and the non-karyomegaly-inducing carcinogens tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate and potassium bromate were examined. For comparison, a karyomegaly-inducing non-carcinogen, p-nitrobenzoic acid, and a non-carcinogenic non-karyomegaly-inducing renal toxicant, acetaminophen, were also examined. The outer stripe of the outer medulla (OSOM) and the cortex + OSOM were subjected to morphometric analysis of immunoreactive proximal tubular cells. Renal carcinogens, irrespective of their karyomegaly-inducing potential, increased proximal tubular cell proliferation accompanied by an increase in topoisomerase IIα−immunoreactive cells, suggesting a reflection of cell proliferation. Karyomegaly-inducing carcinogens increased nuclear Cdc2-, γH2AX-, and phosphorylated Chk2-immunoreactive cells in both areas, the former two acting in response to DNA damage and the latter one suggestive of sustained G2. OTA, an OSOM-targeting carcinogen, could easily be distinguished from untreated controls and non-carcinogens by evaluation of molecules responding to DNA damage and G2/M transition in the OSOM. Thus, all renal carcinogens examined facilitated proximal tubular proliferation by repeated short-term treatment. Among these, karyomegaly-inducing carcinogens may cause DNA damage and G2 arrest in the target tubular cells.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APAP:
-
Acetaminophen
- Fe-NTA:
-
Ferric nitrilotriacetic acid
- KBrO3 :
-
Potassium bromate
- MON:
-
Monuron
- OSOM:
-
The outer stripe of the outer medulla
- OTA:
-
Ochratoxin A
- p-Chk2:
-
Phosphorylated Chk2
- p-Histone H3:
-
Phosphorylated-Histone H3
- PNBA:
-
p-Nitrobenzoic acid
- Topo IIα:
-
Topoisomerase IIα
- TRCP:
-
Tris(2-chloroethyl) phosphate
References
Adler M, Müller K, Rached E, Dekant W, Mally A (2009) Modulation of key regulators of mitosis linked to chromosomal instability is an early event in ochratoxin A carcinogenicity. Carcinogenesis 30:711–719
Allen DG, Pearse G, Haseman JK, Maronpot RR (2004) Prediction of rodent carcinogenesis: an evaluation of prechronic liver lesions as forecasters of liver tumors in NTP carcinogenicity studies. Toxicol Pathol 32:393–401
Ashby J (1992) Use of short-term tests in determining the genotoxicity or nongenotoxicity of chemicals. IARC Sci Publ 116:135–164
Boorman GA, McDonald MR, Imoto S, Persing R (1992) Renal lesions induced by ochratoxin A exposure in the F344 rat. Toxicol Pathol 20:236–245
Bower JJ, Karaca GF, Zhou Y, Simpson DA, Cordeiro-Stone M, Kaufmann WK (2010) Topoisomerase IIα maintains genomic stability through decatenation G2 checkpoint signaling. Oncogene 29:4787–4799
Brizova H, Kalinova M, Krskova L, Mrhalova M, Kodet R (2010) A novel quantitative PCR of proliferation markers (Ki-67, topoisomerase IIα, and TPX2): an immunohistochemical correlation, testing, and optimizing for mantle cell lymphoma. Virchows Arch 456:671–679
Brown AL, Odell EW, Mantle PG (2007) DNA ploidy distribution in renal tumours induced in male rats by dietary ochratoxin A. Exp Toxicol Pathol 59:85–95
Chan TA, Hermeking H, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1999) 14–3-3σ is required to prevent mitotic catastrophe after DNA damage. Nature 401:616–620
Clawson GA, Blankenship LJ, Rhame JG, Wilkinson DS (1992) Nuclear enlargement induced by hepatocarcinogens alters ploidy. Cancer Res 52:1304–1308
Doi AM, Hill G, Seely J, Hailey JR, Kissling G, Bucher JR (2007) α2u-globulin nephropathy and renal tumors in national toxicology program studies. Toxicol Sci 35:533–540
Eastin WC (1998) The U.S. National toxicology program evaluation of transgenic mice as predictive models for identifying carcinogens. Environ Health Perspect 106:81–84
Halicka HD, Huang X, Traganos F, King MA, Dai W, Darzynkiewicz Z (2005) Histone H2AX phosphorylation after cell irradiation with UV-B. Cell Cycle 4:339–345
Hard GC, Boorman GA, Wolf DC (2000) Re-evaluation of the 2-year chloroform drinking water carcinogenicity bioassay in Osborne-Mendel rats supports chronic renal tubule injury as the mode of action underlying the renal tumor response. Toxicol Sci 53:327–344
Hibi D, Suzuki Y, Ishii Y, Jin M, Watanabe M, Sugita-Konishi Y, Yanai T, Nohmi T, Nishikawa A, Umemura T (2011) Site-specific in vivo mutagenicity in the kidney of gpt delta rats given a carcinogenic dose of ochratoxin A. Toxicol Sci 122:406–414
Hirota T, Lipp JL, Tof BH, Peters JM (2005) Histone H3 serine 10 phosphorylation by Aurora B causes HP1 dissociation from heterochromatin. Nature 438:1176–1180
Hu ML, Chuang CH, Sio HM, Yeh SL (2002) Simple cryoprotection and cell dissociation techniques for application of the comet assay to fresh and frozen rat tissues. Free Radic Res 36:203–209
Inoue K, Shibutani M, Masutomi N, Toyoda K, Takagi H, Uneyama C, Nishikawa A, Hirose M (2008) A 13-week subchronic toxicity study of madder color in F344 rats. Food Chem Toxicol 46:241–252
Inoue K, Yoshida M, Takahashi M, Shibutani M, Takagi H, Hirose M, Nishikawa A (2009a) Induction of kidney and liver cancers by the natural food additive madder color in a two-year rat carcinogenicity study. Food Chem Toxicol 47:184–191
Inoue K, Yoshida M, Takahashi M, Fujimoto H, Ohnishi K, Nakashima K, Shibutani M, Hirose M, Nishikawa A (2009b) Possible contribution of rubiadin, a metabolite of madder color, to renal carcinogenesis in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 47:752–759
Kobayashi J, Iwabuchi K, Miyagawa K, Sonoda E, Suzuki K, Takata M, Tauchi H (2008) Current topics in DNA double-strand break repair. J Radiat Res 49:93–103
Kumada K, Amano R, Ichinoe M, Uchiyama S (1980) Culture conditions and purification method for large-scale production of ochratoxins by Aspergillus ochraceus. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi 21:171–176
Kurokawa Y, Maekawa A, Takahashi M, Hayashi Y (1990) Toxicity and carcinogenicity of potassium bromate—a new renal carcinogen. Environ Health Perspect 87:309–335
Li JL, Okada S, Hamazaki S, Ebina Y, Midorikawa O (1987) Subacute nephrotoxicity and induction of renal cell carcinoma in mice treated with ferric nitrilotriacetate. Cancer Res 47:1867–1869
Lock EA, Hard GC (2004) Chemically induced renal tubule tumors in the laboratory rat and mouse: review of the NCI/NTP database and categorization of renal carcinogens based on mechanistic information. Crit Rev Toxicol 34:211–299
Luo K, Yuan J, Chen J, Lou Z (2009) Topoisomerase IIα controls the decatenation checkpoint. Nat Cell Biol 11:204–210
Mattila R, Alanen K, Syrjänen S (2007) Immunohistochemical study on topoisomerase IIα, Ki-67 and cytokeratin-19 in oral lichen planus lesions. Arch Dermatol Res 298:381–388
Niida H, Nakanishi M (2006) DNA damage checkpoints in mammals. Mutagenesis 21:3–9
Nishiyama L, Suwa H, Okamoto K, Fukumoto M, Hiai H, Toyokuni S (1995) Low incidence of point mutations in H-, K- and N-ras oncogenes and p53 tumor suppressor gene in renal cell carcinoma and peritoneal mesothelioma of Wistar rats induced by ferric nitrilotriacetate. Jpn J Cancer Res 86:1150–1158
NTP (1988) Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of Monuron (CAS No. 150–68-5) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (FEED STUDIES). Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser 266:1–166
NTP (1989) Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Ochratoxin A (CAS No. 303–47-9) in F344/N rats (gavage studies). Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser 358:1–142
NTP (1991) Toxicology and carcinogenesis studies of Tris (2-chloroethyl) phosphate (CAS No. 115–96-8) in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice (gavage studies). Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser 391:1–233
NTP (1993) NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of Acetaminophen (CAS No. 103–90-2) in F344 Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Feed Studies). Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser 394:1–274
NTP (1994) NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of p-Nitrobenzoic Acid (CAS No. 62–23-7) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Feed Studies). Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser 442:1–306
NTP (1996) NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of 1-Amino-2,4-Dibromoanthraquinone (CAS No. 81–49-2) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Feed Studies). Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser 383:1–370
Parodi S, Malacarne D, Taningher M (1992) Non-genotoxic factors in the carcinogenic process: problems of detection and hazard evaluation. Toxicol Lett 64–65:621–630
Pentheroudakis G, Goussia A, Voulgaris E, Nikolaidis K, Ioannidou E, Papoudou-Bai A, Grepi K, Kanavaros P, Pavlidis N, Bai M (2010) High levels of topoisomerase IIα protein expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma are associated with high proliferation, germinal center immunophenotype, and response to treatment. Leuk Lymphoma 51:1260–1268
Pérez de Castro I, de Cάrcer G, Malumbres M (2007) A census of mitotic cancer genes: new insights into cell biology and cancer therapy. Carcinogenesis 28:899–912
Rached E, Hard GC, Blumbach K, Weber K, Draheim R, Luts WK, Özden S, Steger U, Dekant W, Mally A (2007) Ochratoxin A: 13-week oral toxicity and cell proliferation in male F344/N rats. Toxicol Sci 97:288–298
Ruchaud S, Carmena M, Earnshaw WC (2007) Chromosomal passengers: conducting cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:798–812
Scholzen T, Gerdes J (2000) The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 182:311–322
Seely JC, Hard GC (2008) Chronic progressive nephropathy (CPN) in the rat: review of pathology and relationship to renal tumorigenesis. J Toxicol Pathol 21:199–205
Sherr CJ (1995) D-type cyclins. Trends Biochem Sci 20:187–190
Snyderwine EG (1999) Mammary gland carcinogenesis by 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine in rats: possible mechanisms. Cancer Lett 143:211–215
Sugita-Konishi Y, Tanaka T, Nakajima M, Fujita K, Norizuki H, Mochizuki N, Takatori K (2006) The comparison of two clean-up procedures, multifunctional column and immunoaffinity column, for HPLC determination of ochratoxin A in cereals, raisins and green coffee beans. Talanta 69:650–655
Tamano S (2010) Carcinogenesis risk assessment of chemicals using medium-term carcinogenesis bioassays. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev 11:4–5
Tanaka T, Kohno H, Murakami M, Shimada R, Kagami S (2000) Colitis-related rat colon carcinogenesis induced by 1-hydroxy-anthraquinone and methylazoxymethanol acetate. Oncol Rep 7:501–508
Toyokuni S, Uchida K, Okamoto K, Nakakuki YH, Hiai H, Stadtman ER (1994) Formation of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified proteins in the renal proximal tubules of rats treated with a renal carcinogen, ferric nitrilotriacetate. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91:2616–2620
Uhlmann F (2004) The mechanism of sister chromatid cohesion. Exp Cell Ress 296:80–85
Umemura T, Kanki K, Kuroiwa Y, Ishii Y, Okano K, Nohmi T, Nishikawa A, Hirose M (2006) In vivo mutagenicity and initiation following oxidative DNA lesion in the kidneys of rats given potassium bromate. Cancer Sci 97:829–835
Vogestseder A, Picard N, Gaspert A, Walch M, Kaissling B, Le Hir M (2008) Proliferation capacity of the renal proximal tubule involves the bulk of differentiated epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 294:22–28
Wang Y, Azuma Y, Moore D, Osheroff N, Neufeld KL (2008) Interaction between tumor suppressor adenomatous polyposis coli and topoisomerase IIα: implication for the G2/M transition. Mol Biol Cell 19:4076–4085
Williams GM, Iatropoulos MJ, Jeffrey AM, Shirai T (2002) Protective effect of acetaminophen against colon cancer initiation effects of 3,2′-dimethyl-4-aminobiphenyl in rats. Eur J Cancer Prev 11:39–48
Wilson DW, Lamé MW, Dunston SK, Segall HJ (2000) DNA damage cell checkpoint activities are altered in monocrotaline pyrrole-induced cell cycle arrest in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 166:69–80
Woo RA, Poon RYC (2003) Cyclin-dependent kinases and s phase control in mammalian cells. Cell Cycle 2:316–324
Yoshida K, Yamaguchi T, Shinagawa H, Taira N, Nakayama KI, Miki Y (2006) Protein kinase c delta activates topoisomerase IIα to induce apoptotic cell death in response to DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol 26:3414–3431
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs. Shigeko Suzuki for her technical assistance in preparing the histological specimens. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. Eriko Taniai is a Research Fellow of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
Conflict of interest
All authors disclose that there are no conflicts of interest that could inappropriately influence the outcome of the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taniai, E., Hayashi, H., Yafune, A. et al. Cellular distribution of cell cycle-related molecules in the renal tubules of rats treated with renal carcinogens for 28 days: relationship between cell cycle aberration and carcinogenesis. Arch Toxicol 86, 1453–1464 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0829-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0829-z