Abstract
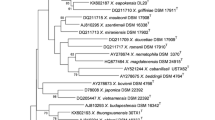
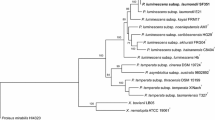
The relationships between six bacterial symbionts of the entomopathogenic nematodes Heterorhabditis bacteriophora and Heterorhabditis megidis from Poland to species and subspecies of the genus Photorhabdus were evaluated. This study was based on phylogenetic analysis of sequence data of five genes: 16S rRNA, gyrB, recA, gltX, and dnaN. The bacteria were also characterized phenotypically by biochemical and physiological tests. Our results have revealed that the Photorhabdus strains isolated from H. megidis belong to P. temperata, subsp. temperata and subsp. cinerea. Isolates from H. bacteriophora represent P. luminescens subs. kayaii and P. temperata subs. cinerea. This study for the first time provides evidence for H. bacteriophora and P. temperata subsp. cinerea symbiotic association. In addition, we tested whether the microsymbionts of the Polish H. bacteriophora and H. megidis isolates support the development of non-native nematode host population and colonization of their infective juveniles. It has been shown that the studied Photorhabdus strains can readily swap their nematode host, both at intra- and interspecies level. It supports the hypothesis of different symbiotic associations in the Heterorhabditis–Photorhabdus lineage.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IJ (s):
-
Infective juvenile (s)
- EPN (s):
-
Entomopathogenic nematode (s)
- w/v:
-
Weight per volume
- LBA:
-
Luria–Bertani agar
- LB:
-
Luria–Bertani broth
- NA:
-
Nutrient agar
References
Adams BJ, Fodor A, Koppenhöfer HS, Stackebrandt E, Stock PS, Klein MG (2006) Reprint of “Biodiversity and systematics of nematode–bacterium entomopathogens” [Biol. Control 37 (2006) 32–49]. Biol Control 38(1):4–21. doi:10.1016/S1049-9644(06)00126-5
Akhurst RJ (1980) Morphological and functional dimorphism in Xenorhabdus spp., bacteria symbiotically associated with the insect pathogenic nematodes Neoaplectana and Heterorhabditis. Microbiol 121(2):303–309. doi:10.1099/00221287-121-2-303
Akhurst RJ, Bedding RA (1975) A simple technique for the detection of insect parasitic rhabditid nematodes in soil. Nematologica 21(1):109–110. doi:10.1163/187529275X00419
Akhurst RJ, Boemare NE (1988) A numerical taxonomic study of the genus Xenorhabdus (Enterobacteriaceae) and proposed elevation of the subspecies of X. nematophilus to species. J Gen Microbiol 134(7):1835–1845. doi:10.1099/00221287-134-7-1835
Akhurst RJ, Mourant RG, Baud L, Boemare NE (1996) Phenotypic and DNA relatedness between nematode symbionts and clinical strains of the genus Photorhabdus (Enterobacteriaceae). Int J Syst Bacteriol 46(4):1034–1041. doi:10.1099/00207713-46-4-1034
Akhurst RJ, Boemare NE, Janssen PH, Peel MM, Alfredson DA, Beard CE (2004) Taxonomy of Australian clinical isolates of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of Photorhabdus asymbiotica subsp. asymbiotica subsp. nov. and P. asymbiotica subsp. australis subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54(4):1301–1310. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.03005-0
An R, Grewal PS (2010) Photorhabdus temperata subsp. stackebrandtii subsp. nov. (Enterobacteriales: Enterobacteriaceae). Curr Microbiol 61(4):291–297. doi:10.1007/s00284-010-9610-9
An R, Grewal PS (2011) Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. kleinii subsp. nov. (Enterobacteriales: Enterobacteriaceae). Curr Microbiol 62(2):539–543. doi:10.1007/s00284-010-9741-z
Boemare NE, Akhurst RJ (1988) Biochemical and physiological characterization of colony form variants in Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae). Microbiol 134(3):751–761. doi:10.1099/00221287-134-3-751
Boemare NE, Akhurst RJ, Mourant RG (1993) DNA relatedness between Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae), symbiotic bacteria of entomopathogenic nematodes, and a proposal to transfer Xenorhabdus luminescens to a new genus, Photorhabdus gen. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43(2):249–255. doi:10.1099/00207713-43-2-249
Chapuis E, Emelianoff V, Paulmier V, Le Brun N, Pages S, Sicard M, Ferdy J-B (2009) Manifold aspects of specificity in a nematode-bacterium mutualism. J Evol Biol 22(10):2104–2117. doi:10.1111/j.1420-9101.2009.01829.x
Ehlers R-U, Han RC (1998) Cultivation of axenic Heterorhabditis spp. dauer juveniles and their response to non-specific Photorhabdus luminescens food signals. Nematologica 44(4):425–435. doi:10.1163/005525998X00089
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on pylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evol Int J org Evolution 39(4):783–791. doi:10.2307/2408678
Ferreira T, van Reenen CA, Pages S, Tailliez P, Malan AP, Dicks LMT (2013) Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. noenieputensis subsp. nov., a symbiotic bacterium associated with a novel Heterorhabditis species related to Heterorhabditis indica. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63(5):1853–1858. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.044388-0
Ferreira T, van Reenen CA, Endo A, Tailliez P, Pages S, Sproer C, Malan AP, Dicks LMT (2014) Photorhabdus heterorhabditis sp. nov., a symbiont of the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis zealandica. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64(5):1540–1545. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.059840-0
Fischer-Le Saux M, Viallard V, Brunel B, Normand P, Boemare NE (1999) Polyphasic classification of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of new taxa: P. luminescens subsp. luminescens subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. akhurstii subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. laumondii subsp. nov., P. temperata sp. nov., P. temperata subsp. temperata subsp. nov. and P. asymbiotica sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49(4):1645–1656. doi:10.1099/00207713-49-4-1645
Gerritsen LJM, Smits PH (1993) Variation in pathogenicity of recombinations of Heterorhabditis and Xenorhabdus luminescens strains. Fund Appl Nematol 16(4):367–373
Gerritsen LJM, Wiegers GL, Smits PH (1998) Pathogenicity of new combinations of Heterorhabditis spp. and Photorhabdus luminescens against Galleria mellonella and Tipula oleracea. Biol Control 13(1):9–15. doi:10.1006/bcon.1998.0640
Grewal PS, Selvan S, Gaugler R (1994) Thermal adaptation of entomopathogenic nematodes. Niche breadth for infection, establishment, and reproduction. J Therm Biol 19(4):245–253. doi:10.1016/0306-4565(94)90047-7
Han R, Wouts WM, Li L (1991) Development and virulence of Heterorhabditis spp. strains associated with different Xenorhabdus luminescens isolates. J Invertebr Pathol 58(1):27–32. doi:10.1016/0022-2011(91)90158-M
Hazir S, Stackebrandt E, Lang E, Schumann P, Ehlers R-U, Keskin N (2004) Two new subspecies of Photorhabdus luminescens, isolated from Heterorhabditis bacteriophora (Nematoda: Heterorhabditidae): Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. kayaii subsp. nov. and Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. thracensis subsp. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 27(1):36–42. doi:10.1078/0723-2020-00255
Hominick WM (2002) Biogeography. In: Gaugler R (ed) Entomopathogenic nematology. CABI Publishing, New York, pp 115–143. doi:10.1079/9780851995670.0115
Janda JM, Abbott SL (2007) 16S rRNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification in the diagnostic laboratory: pluses, perils, and pitfalls. J Clin Microbiol 45(9):2761–2764. doi:10.1128/JCM.01228-07
Kazimierczak W, Sajnaga E, Skowronek M, Kreft AM, Skrzypek HW, Wiater A (2016) Molecular and phenotypic characterization of Xenorhabdus bovienii symbiotically associated with Steinernema silvaticum. Arch Microbiol 198(10):995–1003. doi:10.1007/s00203-016-1261-1
Koppenhöfer HS (2007) Bacterial symbionts of Steinernema and Heterorhabditis. In: Nguyen KB, Hunt DJ (eds) Entomopathogenic nematodes: systematics, phylogeny and bacterial symbionts. Brill Academic Publishers (Nematology Monographs and Perspectives, 5), Leiden-Boston, pp 735–808
Lerat E, Daubin V, Moran NA (2003) From gene trees to organismal phylogeny in prokaryotes: the case of the γ-Proteobacteria. PLoS Biol 1(1):e19. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0000019
Maher AMD, Asaiyah MAM, Brophy C, Griffin CT (2016) An entomopathogenic nematode extends its niche by associating with different symbionts. Microb Ecol 73(1):211–223. doi:10.1007/s00248-016-0829-2
Maneesakorn P, An R, Daneshvar H, Taylor K, Bai X, Adams BJ, Grewal PS, Chandrapatya A (2011) Phylogenetic and cophylogenetic relationships of entomopathogenic nematodes (Heterorhabditis: Rhabditida) and their symbiotic bacteria (Photorhabdus: Enterobacteriaceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 59(2):271–280. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2011.02.012
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Hahnke RL, Petersen J, Scheuner C, Michael V, Fiebig A, Rohde C, Rohde M, Fartmann B, Goodwin L, Chertkov O, Reddy TBK, Pati A, Ivanova NN, Markowitz V, Kyrpides NC, Woyke T, Göker M, Klenk H-P (2014). Complete genome sequence of DSM 30083T, the type strain (U5/41T) of Escherichia coli, and a proposal for delineating subspecies in microbial taxonomy. Stand Genomic Sci 8(9):e2. doi:10.1186/1944-3277-9-2
Orozco RA, Hill T, Stock SP (2013) Characterization and phylogenetic relationships of Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. sonorensis (γ-Proteobacteria: Enterobacteriaceae), the bacterial symbiont of the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis sonorensis (Nematoda: Heterorhabditidae). Curr Microbiol 66(1):30–39. doi:10.1007/s00284-012-0220-6
Peat SM, ffrench-Constant RH, Waterfield NR, Marokhazi J, Fodor A, Adams BJ (2010) A robust phylogenetic framework for the bacterial genus Photorhabdus and its use in studying the evolution and maintenance of bioluminescence: a case for 16 S, gyrB, and glnA. Mol Phylogenet Evol 57(2):728–740. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2010.08.012
Peel MM, Alfredson DA, Gerrard JG, Davis JM, Robson JM, McDougall RJ, Scullie BL, Akhurst RJ (1999) Isolation, identification, and molecular characterization of strains of Photorhabdus luminescens from infected humans in Australia. J Clin Microbiol 37(11):3647–3653
Peters A (1996) The natural host range of Steinernema and Heterorhabditis spp. and their impact on insect populations. Biocontrol Sci Technol 6(3):389–402. doi:10.1080/09583159631361
Rajendhran J, Gunasekaran P (2011) Microbial phylogeny and diversity: small subunit ribosomal RNA sequence analysis and beyond. Microbiol Res 166(2):99–110. doi:10.1016/j.micres.2010.02.003
Rossi-Tamisier M, Benamar S, Raoult D, Fournier P-E (2015) Cautionary tale of using 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity values in identification of human-associated bacterial species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1929–1934. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.000161
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425
Sergeant M, Baxter L, Jarrett P, Shaw E, Ousley M, Winstanley C, Morgan J, Alun W (2006) Identification, typing, and insecticidal activity of Xenorhabdus isolates from entomopathogenic nematodes in United Kingdom soil and characterization of the xpt toxin loci. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(9):5895–5907. doi:10.1128/AEM.00217-06
Sicard M, Ferdy J-B, Pages S, Le Brun N, Godelle B, Boemare N, Moulia C (2004) When mutualists are pathogens: an experimental study of the symbioses between Steinernema (entomopathogenic nematodes) and Xenorhabdus (bacteria). J Evol Biol 17(5):985–993. doi:10.1111/j.1420-9101.2004.00748.x
Sicard M, Hinsinger J, Le Brun N, Pages S, Boemare N, Moulia C (2006) Interspecific competition between entomopathogenic nematodes (Steinernema) is modified by their bacterial symbionts (Xenorhabdus). BMC Evol Biol 6:e68. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-6-68
Skrzypek HW, Kazimierczak WS, Kreft AM, Mráček Z (2011) Location of the phasmids in first generation males of Steinernema arenarium (Artyukhovsky), S. carpocapsae (Weiser) and S. feltiae (Filipjev). Nematology 13(3):365–367. doi:10.1163/138855410X526822
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today 33:152–155
Stackebrandt E, Frederiksen W, Garrity GM, Grimont PAD, Kämpfer PM, Maiden MC, Nesme X, Roselló-Mora R, Swings J, Trüper HG, Vauterin L, Ward AC, Whitman WB (2002) Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52(3):1043–1047. doi:10.1099/00207713-52-3-1043
Stock SP, Goodrich-Blair H (2012) Nematode parasites, pathogens and associates of insects and invertebrates of economic importance. In: Lacey LA (ed) Manual of techniques in invertebrate pathology. Elsevier, New York, pp 373–426. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-386899-2.00012-9
Tailliez P, Laroui C, Ginibre N, Paule A, Pages S, Boemare N (2010) Phylogeny of Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus based on universally conserved protein-coding sequences and implications for the taxonomy of these two genera. Proposal of new taxa: X. vietnamensis sp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. caribbeanensis subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. hainanensis subsp. nov., P. temperata subsp. khanii subsp. nov., P. temperata subsp. tasmaniensis subsp. nov., and the reclassification of P. luminescens subsp. thracensis as P. temperata subsp. thracensis comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60(8):1921–1937. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.014308-0
Tailliez P, Pages S, Edgington S, Tymo LM, Buddie AG (2012) Description of Xenorhabdus magdalenensis sp. nov., the symbiotic bacterium associated with Steinernema australe. Int J Syst Evol Micr 62(8):1761–1765. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.034322-0
Tamura K, Nei M, Kumar S (2004) Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(30):11030–11035. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404206101
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197
Thomas GM, Poinar GO (1979) Xenorhabdus gen. nov., a genus of entomopathogenic, nematophilic bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Int J Syst Bacteriol 29(4):352–360. doi:10.1099/00207713-29-4-352
Tindall BJ, Roselló-Móra R, Busse HJ, Ludwig W, Kämpfer P (2010) Notes on the characterization of prokaryote strains for taxonomic purposes. Int J Syst Microbiol 60:249–266. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.016949-0
Tóth T, Lakatos T (2008) Photorhabdus temperata subsp. cinerea subsp. nov., isolated from Heterorhabditis nematodes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58(11):2579–2581. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.2008/000273-0
Wouts WM (1981) Mass production of the entomogenous nematode Heterorhabditis heliothidis (Nematoda: Heterorhabditidae) on artificial media. J Nematol 13(4):467–469
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Polish Ministry of Science and Higher Education grant for statutory activity.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazimierczak, W., Skrzypek, H., Sajnaga, E. et al. Strains of Photorhabdus spp. associated with polish Heterorhabditis isolates: their molecular and phenotypic characterization and symbiont exchange. Arch Microbiol 199, 979–989 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1368-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1368-z