Abstract
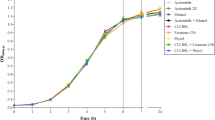
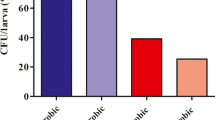
Quorum sensing regulates a variety of phenotypes in bacteria including the production of virulence factors. Salmonella spp. have quorum sensing systems mediated by three autoinducers (AI-1, AI-2, and AI-3). The AI-1-mediated system is incomplete in that the bacterium relies on the synthesis of signaling molecules by other microorganisms. This study aimed to evaluate the influence of the AI-1 N-dodecanoyl-DL-homoserine lactone (C12-HSL) on the growth, motility, adhesion, and biofilm formation of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis PT4 578 on a polystyrene surface. Experiments were conducted at 37 °C in anaerobic tryptone soy broth supplemented with C12-HSL and/or a mixture of four synthetic furanones, at the concentration of 50 nM each. The planktonic growth, adhesion, swarming, and twitching motility were not altered in the presence of C12-HSL and/or furanones under anaerobic conditions. However, C12-HSL induced biofilm formation after 36 h of cultivation as determined by quantification of biofilm formation, by enumeration of adhered cells to polystyrene coupons, and finally by imaging the presence of multilayered cells on an epifluorescence microscope. When furanones were present in the medium, an antagonistic effect against C12-HSL on the biofilm development was observed. The results demonstrate an induction of biofilm formation in Salmonella Enteritidis by AI-1 under anaerobic conditions. Considering that Salmonella does not produce AI-1 but respond to it, C12-HSL synthesized by other bacterial species could trigger biofilm formation by this pathogen in conditions that are relevant for its pathogenesis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida FA, Pinto UM, Vanetti MCD (2016) Novel insights from molecular docking of SdiA from Salmonella Enteritidis and Escherichia coli with quorum sensing and quorum quenching molecules. Microb Pathog 99:178–190. doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2016.08.024
Burmølle M, Thomsen TR, Fazli M, Dige I, Christensen L, Homøe P et al (2010) Biofilms in chronic infections—a matter of opportunity—monospecies biofilms in multispecies infections. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 59(3):324–336. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2010.00714.x
Campos-Galvão MEM, Leite TDS, Ribon AOB, Araújo EF, Vanetti MCD (2015a) A new repertoire of informations about the quorum sensing system in Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis PT4. Genet Mol Res 14(2):4068–4084. doi:10.4238/2015.April.27.22
Campos-Galvão MEM, Ribon AOB, Araújo EF, Vanetti MCD (2015b) Changes in the Salmonella enterica Enteritidis phenotypes in presence of acyl homoserine lactone quorum sensing signals. J Basic Microbiol 55:1–9. doi:10.1002/jobm.201500471
Chironna M, Tafuri S, Gallone MS, Sallustio A, Martinelli D, Prato R et al (2014) Outbreak of Salmonella infantis gastroenteritis among people who had eaten at a hash house in southern Italy. Public Health 128(5):438–443. doi:10.1016/j.puhe.2014.02.002
Choi J, Shin D, Ryu S (2007) Implication of quorum sensing in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium virulence: the luxS gene is necessary for expression of genes in pathogenicity island 1. Infect Immun 75(10):4885–4890. doi:10.1128/IAI.01942-06
Chorianopoulos NG, Giaouris ED, Kourkoutas Y, Nychas GJE (2010) Inhibition of the early stage of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis biofilm development on stainless steel by cell-free supernatant of a Hafnia alvei culture. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(6):2018–2022. doi:10.1128/AEM.02093-09
Dourou D, Ammor MS, Skandamis PN, Nychas GJE (2011) Growth of Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Typhimurium in the presence of quorum sensing signalling compounds produced by spoilage and pathogenic bacteria. Food Microbiol 28(5):1011–1018. doi:10.1016/j.fm.2011.02.004
Dyszel JL, Smith JN, Lucas DE, Soares JA, Swearingen MC, Vross MA et al (2010a) Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium can detect acyl homoserine lactone production by Yersinia enterocolitica in mice. J Bacteriol 192(1):29–37. doi:10.1128/JB.01139-09
Dyszel JL, Soares JA, Swearingen MC, Lindsay A, Smith JN, Ahmer BM (2010b) E. coli K-12 and EHEC genes regulated by SdiA. PLoS ONE 5:e8946. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008946
Ferreira DF (2011) SISVAR: a computer statistical analysis system. Cienc e Agrotecnol 35(6):1039–1042. doi:10.1590/s1413-70542011000600001
Finstad S, O’Bryan CA, Marcy JA, Crandall PG, Ricke SC (2012) Salmonella and broiler processing in the United States: relationship to foodborne salmonellosis. Food Res Int 45(2):789–794. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2011.03.057
Fuqua WC, Winans SC, Greenberg EP (1994) Quorum sensing in bacteria: the LuxR-LuxI family of cell density- responsive transcriptional regulators. J Bacteriol 176(2):269–275
Fuqua C, Winans SC, Greenberg EP (1996) Census and consensus in bacterial ecosystems: the LuxR-LuxI family of quorum-sensing transcriptional regulators. Annu Rev Microbiol 50:727–751. doi:10.1146/annurev.micro.50.1.727
Fuqua C, Parsek MR, Greenberg EP (2001) Regulation of gene expression by cell-to-cell communication: acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing. Annu Rev Genet 35:439–468. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.35.102401.090913
Guerrieri E, de Niederhäusern S, Messi P, Sabia C, Iseppi R, Anacarso I et al (2009) Use of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) biofilms for the control of Listeria monocytogenes in a small-scale model. Food Control 20(9):861–865. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2008.11.001
Hayward MR, Jansen VAA, Woodward MJ (2013) Comparative genomics of Salmonella enterica serovars Derby and Mbandaka, two prevalent serovars associated with different livestock species in the UK. BMC Genom 14(1):365. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-365
Hensel M (2004) Evolution of pathogenicity islands of Salmonella enterica. Int J Med Microbiol 294(2–3):95–102. doi:10.1016/j.ijmm.2004.06.025
Hentzer M, Riedel K, Rasmussen TB, Heydorn A, Andersen JB, Parsek MR et al (2002) Inhibition of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm bacteria by a halogenated furanone compound. Microbiology 148(1):87–102. doi:10.1099/00221287-148-1-87
Hentzer M, Wu H, Andersen JB, Riedel K, Rasmussen TB, Bagge N et al (2003) Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by quorum sensing inhibitors. EMBO J 22:3803–3815. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg366
Høiby N, Bjarnsholt T, Givskov M, Molin S, Ciofu O (2010) Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int J Antimicrob Agents 35(4):322–332. doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.12.011
Huber B, Riedel K, Hentzer M, Heydorn A, Gotschlich A, Givskov M et al (2001) The cep quorum-sensing system of Burkholderia cepacia H111 controls biofilm formation and swarming motility. Microbiology 147(9):2517–2528. doi:10.1099/00221287-147-9-2517
Hughes DT, Sperandio V (2008) Inter-kingdom signalling: communication between bacteria and their hosts. Nat Rev Microbiol 6(2):111–120. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1836
Humphrey TJ, Williams A, McAlpine K, Lever MS, Guard-Petter J, Cox JM (1996) Isolates of Salmonella enterica Enteritidis PT4 with enhanced heat and acid tolerance are more virulent in mice and more invasive in chickens. Epidemiol Infect 117(1):79–88. doi:10.1017/S0950268800001151
Humphrey TJ, Williams A, McAlpine K, Jørgensen F, O’Byrne C (1998) Pathogenicity in isolates of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis PT4 which differ in RpoS expression: effects of growth phase and low temperature. Epidemiol Infect 121(2):295–301. doi:10.1017/S0950268898001162
Irino K, Fernandes SA, Tavechio AT, Neves BC, Dias AMG (1996) Progression of Salmonella Enteritidis phage type 4 strains in São Paulo state, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 38(3):193–196. doi:10.1590/S0036-46651996000300005
Janssens JCA, Steenackers H, Robijns S, Gellens E, Levin J, Zhao H et al (2008) Brominated furanones inhibit biofilm formation by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(21):6639–6648. doi:10.1128/AEM.01262-08
Jensen PO, Givskov M, Bjarnsholt T, Moser C (2010) The immune system vs. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 59(3):292–305. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2010.00706.x
Kalai Chelvam K, Chai LC, Thong KL (2014) Variations in motility and biofilm formation of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Gut Pathog 6(1):2. doi:10.1186/1757-4749-6-2
Kearns DB (2010) A field guide to bacterial swarming motility. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(9):634–644. doi:10.1038/nrmicro2405
Keller L, Surette MG (2006) Communication in bacteria: an ecological and evolutionary perspective. Nat Rev Microbiol 4(4):249–258. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1383
Lamas A, Miranda JM, Vázquez B, Cepeda A, Franco CM (2016) Biofilm formation, phenotypic production of cellulose and gene expression in Salmonella enterica decrease under anaerobic conditions. Int J Food Microbiol 238:63–67. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.08.043
LaSarre B, Federle MJ (2013) Exploiting quorum sensing to confuse bacterial pathogens. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77:73–111. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00046-12
Lima JR, Ribon ADOB, Russell JB, Mantovani HC (2009) Bovicin HC5 inhibits wasteful amino acid degradation by mixed ruminal bacteria in vitro. FEMS Microbiol Lett 292(1):78–84. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.2008.01474.x
Liu Z, Que F, Liao L, Zhou M, You L, Zhao Q et al (2014) Study on the promotion of bacterial biofilm formation by a Salmonella conjugative plasmid and the underlying mechanism. PLoS ONE 9(10):e109808. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0109808
Lynch MJ, Swift S, Kirke DF, Keevil CW, Dodd CER, Williams P (2002) The regulation of biofilm development by quorum sensing in Aeromonas hydrophila. Environ Microbiol 4(1):18–28. doi:10.1046/j.1462-2920.2002.00264.x
Manefield M, Rasmussen TB, Henzter M, Andersen JB, Steinberg P, Kjelleberg S et al (2002) Halogenated furanones inhibit quorum sensing through accelerated LuxR turnover. Microbiology 148(4):1119–1127. doi:10.1099/00221287-148-4-1119
Michael B, Smith JN, Swift S, Heffron F, Ahmer BM (2001) SdiA of Salmonella enterica is a LuxR homolog that detects mixed microbial communities. J Bacteriol 183:5733–5742. doi:10.1128/JB.183.19.5733-5742.2001
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harb. Lab. Press, Cold Spring Harbour
Moreira CG, Weinshenker D, Sperandio V (2010) QseC mediates Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium virulence in vitro and in vivo. Infect Immun 78(3):914–926. doi:10.1128/IAI.01038-09
Nguyen Y, Nguyen NX, Rogers JL, Liao J, MacMillan JB, Jiang Y et al (2015) Structural and mechanistic roles of novel chemical ligands on the SdiA quorum-sensing transcription regulator. mBio 6(2):1–10. doi:10.1128/mBio.02429-14
Nunes IA, Helmuth R, Schroeter A, Mead GC, Santos MAA, Solari CA et al (2003) Phage typing of Salmonella Enteritidis from different sources in Brazil. J Food Prot 66(2):324–327
Nunes MM, Mota ALAA, Caldas ED (2013) Investigation of food and water microbiological conditions and foodborne disease outbreaks in the Federal District, Brazil. Food Control 34(1):235–240. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.04.034
Ong SY, Ng FL, Badai SS, Yuryev A, Alam M (2010) Analysis and construction of pathogenicity island regulatory pathways in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. J Integr Bioinform. doi:10.2390/biecoll-jib-2010-145
Papenfort K, Bassler BL (2016) Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:576–588. doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2016.89
Parker CT, Sperandio V (2009) Cell-to-cell signalling during pathogenesis. Cell Microbiol 11:363–369. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01272.x
Parsek MR, Greenberg EP (2000) Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: a signaling mechanism involved in associations with higher organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(16):8789–8793. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.16.8789
Pimentel-Filho NDJ, Martins MCDF, Nogueira GB, Mantovani HC, Vanetti MCD (2014) Bovicin HC5 and nisin reduce Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to polystyrene and change the hydrophobicity profile and Gibbs free energy of adhesion. Int J Food Microbiol 190:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.08.004
Prouty AM, Schwesinger WH, Gunn JS (2002) Biofilm formation and interaction with the surfaces of gallstones by Salmonella spp. Infect Immun 70(5):2640–2649. doi:10.1128/IAI.70.5.2640-2649.2002
Rasmussen TB, Manefield M, Andersen JB, Eberl L, Anthoni U, Christophersen C et al (2000) How Delisea pulchra furanones affect quorum sensing and swarming motility in Serratia liquefaciens MG1. Microbiology 146:3237–3244. doi:10.1099/00221287-146-12-3237
Reimmann C, Ginet N, Michel L, Keel C, Michaux P, Krishnapillai V et al (2002) Genetically programmed autoinducer destruction reduces virulence gene expression and swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microbiology 148(4):923–932. doi:10.1099/00221287-148-4-923
Ryall B, Lee X, Zlosnik JEA, Hoshino S, Williams HD (2008) Bacteria of the Burkholderia cepacia complex are cyanogenic under biofilm and colonial growth conditions. BMC Microbiol 8:108. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-8-108
Sabag-Daigle A, Soares JA, Smith JN, Elmasry ME, Ahmer BMM (2012) The acyl homoserine lactone receptor, SdiA, of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium does not respond to indole. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(15):5424–5431. doi:10.1128/AEM.00046-12
Santos LR, Nascimento VP, Oliveira SD, Rodrigues DP, Reis EMF, Seki LM et al (2003) Phage types of Salmonella Enteritidis isolated from clinical and food samples, and from broiler carcasses in southern Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 45(1):1–4. doi:10.1590/S0036-46652003000100001
Smith JN, Ahmer BMM (2003) Detection of other microbial species by Salmonella: expression of the SdiA regulon. J Bacteriol 185(4):1357–1366. doi:10.1128/JB.185.4.1357-1366.2003
Smith JN, Dyszel JL, Soares JA, Ellermeier CD, Altier C, Lawhon SD et al (2008) SdiA, an N-acylhomoserine lactone receptor, becomes active during the transit of Salmonella enterica through the gastrointestinal tract of turtles. PLoS ONE 3(7):e2826. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002826
Sperandio V, Torres AG, Kaper JB (2002) Quorum sensing Escherichia coli regulators B and C (QseBC): a novel two-component regulatory system involved in the regulation of flagella and motility by quorum sensing in E. coli. Mol Microbiol 43(3):809–821. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.02803.x
Srey S, Jahid IK, Ha S-D (2013) Biofilm formation in food industries: a food safety concern. Food Control 31(2):572–585. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2012.12.001
Steenackers H, Hermans K, Vanderleyden J, De Keersmaecker SCJ (2012) Salmonella biofilms: an overview on occurrence, structure, regulation and eradication. Food Res Int 45(2):502–531. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2011.01.038
Stepanović S, Ćirković I, Mijač V, Švabić-Vlahović M (2003) Influence of the incubation temperature, atmosphere and dynamic conditions on biofilm formation by Salmonella spp. Food Microbiol 20:339–343. doi:10.1016/S0740-0020(02)00123-5
Vestby LK, Johannesen KCS, Witsø IL, Habimana O, Scheie AA, Urdahl AM et al (2013) Synthetic brominated furanone F202 prevents biofilm formation by potentially human pathogenic Escherichia coli O103: H2 and Salmonella ser. Agona on abiotic surfaces. J Appl Microbiol 116(2):258–268. doi:10.1111/jam.12355
Viana ES, Campos MEM, Ponce AR, Mantovani HC, Vanetti MCD (2009) Biofilm formation and acyl homoserine lactone production in Hafnia alvei isolated from raw milk. Biol Res 42(4):427–436. doi:10.4067/S0716-97602009000400004
Walters M, Sperandio V (2006) Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Int J Med Microbiol. doi:10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.01.041
Wang HH, Ye KP, Zhang QQ, Dong Y, Xu XL, Zhou GH (2013) Biofilm formation of meat-borne Salmonella enterica and inhibition by the cell-free supernatant from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Food Control 32(2):650–658. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.01.047
Wei Y, Lee JM, Smulski DR, LaRossa RA (2001) Global impact of sdiA amplification revealed by comprehensive gene expression profiling of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 183(7):2265–2272. doi:10.1128/JB.183.7.2265-2272.2001
Widmer KW, Jesudhasan PR, Dowd SE, Pillai SD (2007) Differential expression of virulence-related genes in a Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium luxS mutant in response to autoinducer AI-2 and poultry meat-derived AI-2 inhibitor. Foodborne Pathog Dis 4(1):5–15. doi:10.1089/fpd.2006.40
Xavier KB, Bassler BL (2005) Regulation of uptake and processing of the quorum-sensing autoinducer AI-2 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187(1):238–248. doi:10.1128/JB.187.1.238-248.2005
CLC Drug Discovery Workbench 2.5. http://www.clcbio.com/products/clc-drug-discovery-workbench/
Zhu J, Winans SC (2001) The quorum-sensing transcriptional regulator TraR requires its cognate signaling ligand for protein folding, protease resistance, and dimerization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(4):1507–1512. doi:10.1073/pnas.98.4.1507
Acknowledgements
Felipe Alves de Almeida was supported by a fellowship from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), and this research has been supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), Brazil and by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). UMP acknowledges funding from CNPq for his research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jorge Membrillo-Hernández.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Fig. S1
Molecular docking of SdiA protein of Salmonella Enteritidis PT4 578 to ligands such as C12-HSL (A), C6-HSL (B), 3-methyl-2(5H)-furanone (C), 2(5H)-furanone (D), 2-methyltetrahydro-3-furanone (E), and 2,2-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone (F). The white arrows indicate the residues of the SdiA protein that bind to ligands. W67 = Tryptophan 67, Y63 = Tyrosine 63, D80 = Aspartate 80. (JPEG 120 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almeida, F.A., Pimentel-Filho, N.J., Pinto, U.M. et al. Acyl homoserine lactone-based quorum sensing stimulates biofilm formation by Salmonella Enteritidis in anaerobic conditions. Arch Microbiol 199, 475–486 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1313-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1313-6