Abstract
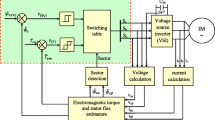
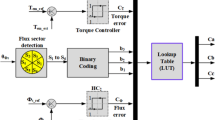
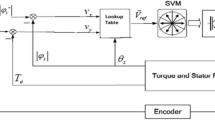
This paper presents an effective scheme to minimize the torque ripples for direct torque control (DTC) of induction motor drives. The switching strategy compares the torque error from a PI torque controller with two triangular waveforms, and then produces a constant switching frequency, which is determined by the frequency of the triangular waveforms and is almost independent of the speed. The gains of PI torque controller are designed based on root-locus plot to guarantee a good convergence of the torque error. In order to examine the performance of the proposed DTC scheme for an induction motor drive, a complete simulation model is developed using MATLAB/Simulink and validated under a wide speed range. The proposed DTC drive is also implemented and tested in real-time using a DSP-DS1102 control board for a prototype 1 KW induction motor. Simulation and experimental results show that the proposed DTC drive exhibits a good dynamic and steady state performances with low torque ripples over a wide speed control range.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Takahashi I, Noguchi T (1986) A new quick-response and high-efficiency control strategy of an induction motor. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 22:820–827
Depenbrock M (1988) Direct self-control (DSC) of inverter-fed induction machine. IEEE Trans Power Electron 3:420–429
Casadei D, Profumo F, Serra G, Tani A (2002) FOC and DTC: two viable schemes for induction motors torque control. IEEE Trans Power Electron 17(5):779–787
Casadei D, Grandi G, Serra G, Tani A (1994) Effects of flux and torque hysteresis band amplitude in direct torque control of induction machines. In: Proceedings of the IECON’94, Bologna, Italy, Sept 5–9, 1994, pp 299–304
Kang JK, Sul SK (2001) Analysis and prediction of inverter switching frequency in direct torque control of induction machine based on hysteresis bands and machine parameters. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 48(3):545–553
Purcell A, Acarnley PP (2001) Enhanced inverter switching for fast response direct torque control. IEEE Trans Power Electron 16(3):382–389
Kang JK, Sul SK (1999) New direct torque control of induction motor for minimum torque ripple and constant switching frequency. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 35(5):1076–1082
Shyu K, Lin JK, Pham V, Yang M, Wang T (2010) Global minimum torque ripple design for direct torque control of induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(9):3148–3156
Beerten J, Verveckken J, Driesen J (2010) Predictive direct torque control for flux and torque ripple reduction. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(1):404–412
Kaboli S, Zolghadri MR, Vahdati-Khajeh E (2007) A fast flux search controller for DTC-based induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 54(5):2407–2416
Zhang Y, Zhu J, Zhao Z, Xu W, Dorrell DG (2012) An improved direct torque control for three-level inverter-fed induction motor sensorless drive. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(3):1502–1513
Singh B, Jain S, Dwivedi S (2013) Torque ripple reduction technique with improved flux response for a direct torque control induction motor drive. IET Power Electron 6(2):326–342
Metidji B, Taib N, Baghli L, Rekioua T, Bacha S (2012) Low-cost direct torque control algorithm for induction motor without AC phase current sensors. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(9):4132–4139
El Badsi B, Bouzidi B, Masmoudi A (2013) DTC scheme for a four-switch inverter-fed induction motor emulating the six-switch inverter operation. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28(7):3528–3538
Lai YS, Chen JH (2001) A new approach to direct torque control of induction motor drives for constant inverter switching frequency and torque ripple reduction. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 16(3):220–227
Casadei D, Serra G, Tani A (2000) Implementation of a direct torque control algorithm for induction motors based on discrete space vector modulation. IEEE Trans Power Electron 15(4):769–777
Zhang Z, Tang R, Bai B, Xie D (2010) Novel direct torque control based on space vector modulation with adaptive stator flux observer for induction motors. IEEE Trans Magn 46(8):3133–3136
Casadei D, Serra G, Stefani A, Tani A, Zarri L (2007) DTC drives for wide speed range applications using a robust flux-weakening algorithm. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 54(5):2451–2461
Kaboli S, Zolghadri MR, Khajeh EV (2007) A fast flux search controller for DTC-based induction motor drives. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 54(5):2407–2416
Romeral L, Arias A, Aldabas E, Jayne MG (2003) Novel direct torque control (DTC) scheme with fuzzy adaptive torque-ripple reduction. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 50(3):487–492
Uddin MN, Hafeez M (2012) FLC-based DTC scheme to improve the dynamic performance of an IM drive. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 48(2):823–831
Grcar B, Stumberger G, Hofer A, Cafuta P (2014) IM torque control schemes based on stator current vector. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 61(1):126–138
Sutikno T, Idris NR, Jidin A, Cirstea MN (2013) An improved FPGA implementation of direct torque control for induction machines. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 9(3):1280–1290
Lascu C, Boldea I, Blaabjerg F (2000) A modified direct torque control for induction motor sensorless drive. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 36(1):122–130
Lee KB, Song JH, Choy I, Yoo JY (2001) Improvement of low-speed operation performance of DTC for three-level inverter-fed induction motors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 48(5):1006–1014
Toh CL, Idris NRN, Yatim AHM (2005) Constant and high switching frequency torque controller for DTC drives. IEEE Power Electron Lett 3(2):76–80
Idris N, Yatim AM (2004) Direct torque control of induction machines with constant switching frequency and reduced torque ripple. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 51(4):758–767
Hajian M, Soltani J, Markadeh GA, Hosseinnia S (2010) Adaptive nonlinear direct torque control of sensorless IM drives with efficiency optimization. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 57(3):975–985
Xiao D, Rahman MF (2013) Sensorless direct torque and flux controlled IPM synchronous machine fed by matrix converter over a wide speed range. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 9(4):1855–1867
Lascu C, Boldea I, Blaabjerg F (2005) Very-low-speed variable-structure control of sensorless induction machine drives without signal injection. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 41(2):591–598
Buja G, Menis R (2008) Steady-state performance degradation of a DTC IM drive under parameter and transduction errors. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 55(4):1749–1760
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaky, M.S. High performance DTC of induction motor drives over a wide speed range. Electr Eng 97, 139–154 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-014-0321-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-014-0321-2