Abstract
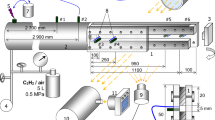
An experimental study is presented of the influence of detonation wave parameters and detonation product composition upstream of a perforated plate on the onset of detonation downstream. Experiments were performed in detonation tube 106 mm in diameter, separated into two sections by a perforated plate combined with a diaphragm. The tube was equipped with pressure sensors and a semi-cylindrical smoked foil. Hydrogen–air mixtures with different hydrogen concentrations were used upstream and downstream of the perforated plate. It is shown for mixtures containing 25 and 34 % of hydrogen in air that the onset of detonation downstream depends on detonation parameters upstream of the perforated plate. An increase in the initial pressure upstream of the plate leads to detonation initiation immediately downstream. The variation of mixture composition upstream of a perforated plate does not affect on detonation initiation downstream under the present experimental conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soloukhin, R.I.: Ignition and detonation processes in the interaction of shock waves with perforated plates. Acta Astronautica 1, 249–258 (1974)
Medvedev, S.P., Khomik, S.V., Olivier, H., et al.: Hydrogen detonation and fast deflaglation triggered by a turbulent jet of combustion products. Shock Waves 14(3), 193–203 (2005)
Chao, J., Lee, J.H.S.: An investigation of the conditions for detonation initiation at a 1D turbulent mixing interface. In: Proceedings of 20 ICDERS on CD-ROM, Montreal (2005)
Medvedev, S.P., Khomik, S.V., Gelfand, B.E.: Recovery and suppression of the detonation of hydrogen–air mixtures at an obstacle with orifices. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 3(6), 963–970 (2009)
Khomik, S.V., Veyssiere, B., Medvedev, S.P., et al.: Concentration limits of detonation re-initiation behind the multi-orifice plate. Shock Waves 12(3), 199–205 (2012)
Carnasciali, F., Lee, J.H.S., Knystautas, R.: Turbulent jet initiation of detonation. Comb. Flame 84, 170–180 (1991)
Gavrikov, A.I., Efimenko, A.A., Dorofeev, S.B.: A model for detonation cell size prediction from chemical kinetics. Comb. Flame 120(1), 19–33 (2000)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by CNRS (France).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Dorofeev.
This paper is based on work that was presented at the 23rd International Colloquium on the Dynamics of Explosions and Reactive Systems, Irvine, CA, USA, 24–29 July 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khomik, S.V., Veyssiere, B., Medvedev, S.P. et al. On some conditions for detonation initiation downstream of a perforated plate. Shock Waves 23, 207–211 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-012-0409-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-012-0409-4