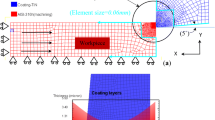
Abstract
With the feed rate decreasing to the dimension of grain size and tool edge radius, cutting process is often carried out in the grain interior and grain boundary. In this paper, the orthogonal cutting process of hot-rolled AISI1045 steel is studied and its metallographic microstructure is analyzed for the establishment of microstructure-based models which incorporate the effect of ferrite and pearlite grains. In order to discover the contribution of microstructure and edge radius to the cutting process, three contrast simulation models including equivalent homogeneous material model with rounded-edge cutting insert (model I), rectangular grain model with sharp edge cutting insert (model II), and rectangular grain model with rounded-edge cutting insert (model III) are built up for the orthogonal cutting processes of hot-rolled AISI1045. Then Voronoi grain model (model IV) and real grain model (model V) are also developed to compare with model III to study the effect of grain shape on the cutting process. The simulation models are compared with the experiments in terms of chip morphology, cutting force, and specific cutting force. And the examination on the stress distribution shows that the real grain model with tool edge radius discovers more details about the mechanics in primary shear zone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu K, Melkote SN (2007) Finite element analysis of the influence of tool edge radius on size effect in orthogonal micro-cutting process. Int J Mech Sci 49(5):650–660. doi:10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2006.09.012
Larsen-Basse J, Oxley PLB (1973) Effect of strain rate sensitivity on scale phenomena in chip formation. In Proceedings of 13th International Machine Tool Design and Research Conference 209–216
Liu K, Melkote SN (2006) Material strengthening mechanisms and their contribution to size effect in micro-cutting. J Manuf Sci Eng 128(3):730–738. doi:10.1115/1.2193548
Liu K, Li XP, Rahman M, Neo KS, Liu XD (2007) A study of the effect of tool cutting edge radius on ductile cutting of silicon wafers. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 32(7–8):631–637. doi:10.1007/s00170-005-0364-7
Özel T, Hsu TK, Zeren E (2005) Effects of cutting edge geometry, workpiece hardness, feed rate and cutting speed on surface roughness and forces in finish turning of hardened AISI H13 steel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25(3–4):262–269. doi:10.1007/s00170-003-1878-5
Yang K, Liang YC, Zheng KN, Bai QS, Chen WQ (2011) Tool edge radius effect on cutting temperature in micro-end-milling process. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 52(9–12):905–912. doi:10.1007/s00170-010-2795-z
Mian AJ, Driver N, Mativenga PT (2010) A comparative study of material phase effects on micro-machinability of multiphase materials. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 50(1–4):163–174. doi:10.1007/s00170-009-2506-9
Waldorf DJ (1996) Shearing, ploughing, and wear in orthogonal machining. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Fang F, Xu F, Lai M (2015) Size effect in material removal by cutting at nano scale. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 1–8. doi:10.1007/s00170-015-7032-3
Astakhov VP (1998) Metal cutting mechanics. CRC press
Ozel T (2007) Numerical modelling of meso-scale finish machining with finite edge radius tools. Int J Mach Mach Mater 2(3–4):451–468. doi:10.1504/IJMMM.2007.015476
Moronuki N, Liang Y, Furukawa Y (1994) Experiments on the effect of material properties on microcutting processes. Precision Eng 16(2):124–131. doi:10.1016/0141-6359(94)90197-X
Simoneau A, Ng E, Elbestawi MA (2006) Chip formation during microscale cutting of a medium carbon steel. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 46(5):467–481. doi:10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.07.019
Chuzhoy L, DeVor RE, Kapoor SG, Beaudoin AJ, Bammann DJ (2003) Machining simulation of ductile iron and its constituents, part 1: estimation of material model parameters and their validation. J Manuf Sci Eng 125(2):181–191. doi:10.1115/1.1557294
Chuzhoy L, DeVor RE, Kapoor SG (2003) Machining simulation of ductile iron and its constituents, part 2: numerical simulation and experimental validation of machining. J Manuf Sci Eng 125(2):192–201. doi:10.1115/1.1557295
Chuzhoy L, DeVor RE, Kapoor SG, Bammann DJ (2002) Microstructure-level modeling of ductile iron machining. J Manuf Sci Eng 124(2):162–169. doi:10.1115/1.1455642
Hill R (1963) Elastic properties of reinforced solids, some theoretical principles. J Mech Phys Solids 11:357–372. doi:10.1016/0022-5096(63)90036-X
Ghosh S, Moorthy S (2004) Three dimensional Voronoi cell finite element model for microstructures with ellipsoidal heterogeneities. Comput Mech 34:510–531. doi:10.1007/s00466-004-0598-5
Abouridouane M, Klocke F, Lung D (2013) Microstructure-based 3D finite element model for micro drilling carbon steels. Procedia CIRP 8:94–99. doi:10.1016/j.procir.2013.06.071
Langer SA, Fuller ER Jr, Carter WC (2001) OOF: image-based finite-element analysis of material microstructures. Comput Sci Eng 3(3):15–23. doi:10.1109/5992.919261
Dong Y, Bhattacharyya D (2010) Morphological-image analysis based numerical modelling of organoclay filled nanocomposites. Mech Adv Mater Struct 17(7):534–541. doi:10.1080/15376490903399746
Johnson GR, Cook WH (1983) A constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Ballistics 21:541–547
Abouridouane M, Klocke F, Lung D, Adams O (2012) A new 3D multiphase FE model for micro cutting ferritic–pearlitic carbon steels. CIRP Ann-Manuf Technol 61(1):71–74. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2012.03.075
Abaqus 6.11 Documentation, Abaqus/CAE user’s manual, 2011
Zorev NN(1963). Inter-relationship between shear processes occurring along tool face and shear plane in metal cutting. International Research in Production Engineering 49
Childs THC, Maekawa K (1990) Computer-aided simulation and experimental studies of chip flow and tool wear in the turning of low alloy steels by cemented carbide tools. Wear 139(2):235–250. doi:10.1016/0043-1648(90)90048-F
Zhang X, Wu S, Wang H, Liu CR (2011) Predicting the effects of cutting parameters and tool geometry on hard turning process using finite element method. J Manuf Sci Eng 133(4):041010. doi:10.1115/1.4004611
Rech J, Claudin C, D’Eramo E (2009) Identification of a friction model—application to the context of dry cutting of an AISI 1045 annealed steel with a TiN-coated carbide tool. Tribol Int 42(5):738–744. doi:10.1016/j.triboint.2008.10.007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, L., Shang, T., Chen, X. et al. Comparative investigation on microstructure-based modelling for the orthogonal cutting of AISI1045. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 88, 603–611 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8717-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-016-8717-y