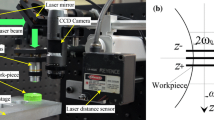
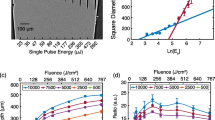
Abstract
The machining of micro-geometries requires a corresponding micro-cutting tool. Up to now, industry primarily fabricates such tools by grinding or electrical discharge machining. In this paper, an overview of the direct laser fabrication of micro-cutting tool-related geometries on polycrystalline diamond composites and single crystal diamond is presented. This is made possible using picosecond laser pulses operating at second harmonics and a micro-scanning deflection system exhibiting a high-numerical aperture. The generated geometries are inspected using scanning electron microscopy while quality of the cutting edge radius and graphitisation is investigated. The laser ablation process is further enhanced by demonstrating the feasibility of a sequential roughing and finishing strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klotzbach A, Hauser M, Beyer E (2011) Laser cutting of carbon fiber reinforced polymers using highly brilliant laser beam sources. Phys Procedia 12:572–577. doi:10.1016/j.phpro.2011.03.072
Ancona A, Röser F, Rademaker K, Limpert J, Nolte S, Tünnermann A (2008) High speed laser drilling of metals using a high repetition rate, high average power ultrafast fiber CPA system. Opt Express 16:8958–8968. doi:10.1364/OE.16.008958
Huo D, Cheng K (2013) Overview of micro cutting. In: Cheng K, Huo D (eds) Micro-cutting: fundamentals and applications, 1st edn. Wiley, West Sussex, pp 10–14
Harrison P, Henry M, Brownell M (2006) Laser processing of polycrystalline diamond, tungsten carbide and a related composite material. J Laser Appl 18:117–126. doi:10.2351/1.2164472
Everson C, Molian P (2009) Fabrication of polycrystalline diamond microtool using a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 45:521–530. doi:10.1007/s00170-009-1999-6
Dold C, Henerichs M, Gilgen P, Wegener K (2013) Laser processing of coarse grain polycrystalline diamond (PCD) cutting tool inserts using picosecond laser pulses. Phys Procedia 41:610–616. doi:10.1016/j.phpro.2013.03.123
Eberle G, Jefimovs K, Wegener K (2014) Characterisation of thermal influences after laser processing polycrystalline diamond composites using long to ultrashort pulse durations. Precis Eng 39:16–24. doi:10.1016/j.precisioneng.2014.06.008
Weikert M, Dausinger F (2004) Cutting of diamond. In: Dausinger F, Lubatschowski H, Lichtner F (eds) Femtosecond technology for technical and medical applications. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 155–165
Joswig A, Risse S, Eberhardt R, Tünnermann A (2010) Laser generated and structured prototypes of diamond tool tips for microoptics fabrication. In: 25th Annual Meeting of the American Society for Precision Engineering: Proceedings 31, Atlanta, USA, pp 53–56
Dumitru G, Lüscher B, Krack M, Bruneau S, Hermann J, Gerbig Y (2005) Laser processing of hardmetals: physical basics and applications. Int J Refract Met Hard 23:278–286. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2005.04.020
Miyazawa H, Takeuchi S, Miyake S, Murakawa M (1996) Sintered diamond cutting inserts with chip breaker prepared by laser technique. Surf Coat Technol 86–87:797–802. doi:10.1016/S0257-8972(96)03068-X
Gottmann J, Horstmann-Jungemann M, Hermans M, Beckmann D (2009) High speed and high precision fs-laser writing using a scanner with large numerical aperture. J Laser Micro/Nanoeng 4:192–196. doi:10.2961/jlmn.2009.03.0009
Dold C (2013) Picosecond laser processing of diamond cutting edges. VDI-Verlag, Düsseldorf
Pinto F, Vargas G, Wegener K (2008) Simulation for optimizing grain pattern on engineered grinding tools. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 57:353–356. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2008.03.069
Wyen C, Wegener K (2010) Influence of cutting edge radius on cutting forces in machining titanium. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 59:93–96. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2010.03.056
Henerichs M, Voss R, Kuster F, Wegener K (2014) Charakterisierung der Schneidkantengeometrie für Standzeitoptimierung beim Bohren von CFK. Diam Bus 4:42–47
Yuan Z, Zhou M, Dong S (1996) Effect of diamond tool sharpness on minimum cutting thickness and cutting surface integrity in ultraprecision machining. J Mater Process Technol 62:327–330. doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(96)02429-6
Choi J, Lee S (2001) Efficient chip breaker design by predicting the chip breaking performance. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 17:489–497. doi:10.1007/PL00003947
Jawahir I, Fang X (1995) A knowledge-based approach for designing effective grooved chip breakers—2D and 3D chip flow, chip curl and chip breaking. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 10:225–239. doi:10.1007/BF01186875
Eberle G, Dold C, Wegener K (2015) Picosecond laser fabrication of micro cutting tool geometries on polycrystalline diamond composites using a high-numerical aperture micro scanning system. Proc SPIE:9351. doi: 10.1117/12.2075420
Li T, Lou Q, Dong J, Wei Y, Liu J (2001) Ablation of cobalt with pulsed UV laser radiation. Appl Surf Sci 172:356–365. doi:10.1016/S0169-4332(00)00883-7
Ageev P, Builov L, Konov I, Kuzmichev V, Pimenov M (1988) Interaction of laser radiation with diamond films. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 303:598–601
Kuznetsov V, Butenko Y (2012) Diamond phase transitions at nanoscale. In: Shenderova O, Gruen D (eds) Ultrananocrystalline diamond, 2nd edn. William Andrew, Waltham/Oxford, pp 181–244
Corbari C, Champion A, Gecevicius M, Beresna M, Bellouard Y, Kazansky P (2013) Femtosecond versus picosecond laser machining of nano-gratings and micro-channels in silica glass. Opt Express 21:3946–3958. doi:10.1364/OE.21.003946
Zong W, Zhang J, Liu Y, Sun T (2014) Achieving ultra-hard surface of mechanically polished diamond crystal by thermo-chemical refinement. Appl Surf Sci 316:617–624. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.057
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eberle, G., Dold, C. & Wegener, K. Laser fabrication of diamond micro-cutting tool-related geometries using a high-numerical aperture micro-scanning system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 81, 1117–1125 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7240-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7240-x