Abstract
Purpose
This study was performed to compare the efficacy of treatment in three groups of patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA) given an intra-articular injection of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), hyaluronic acid (HA) or ozone gas.
Methods
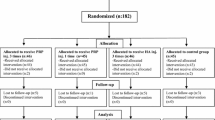
A total of 102 patients with mild–moderate and moderate knee OA who presented at the polyclinic with at least a 1-year history of knee pain and VAS score ≥4 were randomly separated into three groups. Group 1 (PRP group) received intra-articular injection of PRP × 2 doses, Group 2 (HA group) received a single dose of HA, and Group 3 (Ozone group) received ozone × four doses. Weight-bearing anteroposterior–lateral and Merchant’s radiographs of both knees were evaluated. WOMAC and VAS scores were applied to all patients on first presentation and at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months.
Results
At the end of the 1st month after injection, significant improvements were seen in all groups. In the 3rd month, the improvements in WOMAC and VAS scores were similar in Groups 1 and 2, while those in Group 3 were lower (p < 0.001). At the 6th month, while the clinical efficacies of PRP and HA were similar and continued, the clinical effect of ozone had disappeared (p < 0.001). At the end of the 12th month, PRP was determined to be both statistically and clinically superior to HA (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In the treatment of mild–moderate knee OA, PRP was more successful than HA and ozone injections, as the application alone was sufficient to provide at least 12 months of pain-free daily living activities.
Level of evidence
Therapeutic study, Level I.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abate M, Verna S, Schiavone C, Di Gregorio P, Salini V (2015) Efficacy and safety profile of a compound composed of platelet-rich plasma and hyaluronic acid in the treatment for knee osteoarthritis (preliminary results. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 25(8):1321–1326
Adams ME, Atkinson MH, Lussier AJ et al (1995) The role of viscosupplementation with hylan G-F 20 in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a Canadian multicenter trial comparing hylan G-F 20 alone, hylan G-F 20 with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and NSAIDs alone. Osteoarthr Cartil 3(4):213–225
Al-Jaziri AA, Mahmoodi SM (2008) Painkilling effect of ozone-oxygen injection on spine and joint osteoarthritis. Saudi Med J 29(4):553–557
Anitua E, Sánchez M, Orive G (2010) Potential of endogenous regenerative technology for in situ regenerative medicine. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62(7–8):741–752
Balazs EA, Denlinger JL (1993) Viscosupplementation: a new concept in the treatment of osteoarthritis. J Rhematol Suppl 39:3–9
Balazs EA (2003) Analgesic effect of elastoviscous hyaluronan solutions and the treatment of arthritic pain. Cells Tissues Organs 174(1–2):49–62
Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH et al (1988) Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol 15:1833–1840
Bellamy N, Campbell J, Robinson V et al (2006) Viscosupplementation for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cochrane Libr 19(2):CD005321
Bernstein J, Hou SM, Wang CT (2004) Therapeutic effects of hyaluronic acid on osteoarthritis of the knee. S.-M. Hou and C.-T. Wang reply. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86:2567
Bocci V, Valacci G, Gorradeschi F et al (1998) Studies on the biological effects of ozone. Effects of the total antioxidant status and on interlukin-8 production. Mediat Inflamm 7:313–317
Busija L, Bridgett L, Williams SR et al (2010) Osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 24:757–768
Cardoso CC et al (2000) Action of ozonized water in preclinical inflammatory models. Pharmacol Res 42(1):51–54
Cerza F, Carnì S, Carcangiu A et al (2012) Comparison between hyaluronic acid and platelet-rich plasma, intra-articular infiltration in the treatment of gonarthrosis. Am J Sports Med 40:2822–2827
Chang KV, Hung CY, Aliwarga F et al (2014) Comparative effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injections for treating knee joint cartilage degenerative pathology: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 95(3):562–575
Filardo G, Kon E, Buda R et al (2011) Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular knee injections for the treatment of degenerative cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19:528–535
Filardo G, Kon E, Di Martino A et al (2012) Platelet-rich plasma vs hyaluronic acid to treat knee degenerative pathology: study design and preliminary results of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 23(13):229
Filardo G, Di Matteo B, Di Martino A et al (2015) Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular knee injections show no superiority versus viscosupplementation: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 43(7):1575–1582
Filardo G et al (2015) Platelet-rich plasma: why intra-articular? A systematic review of preclinical studies and clinical evidence on PRP for joint degeneration. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(9):2459–2474
Gobbi A, Lad D, Karnatzikos G (2015) The effects of repeated intra-articular PRP injections on clinical outcomes of early osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(8):2170–2177
Görmeli G, Görmeli CA, Ataoglu B et al (2015) Multiple PRP injections are more effective than single injections and hyaluronic acid in knees with early osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-015-3705-6
Hammesfahr JF, Knopf AB, Stitik T (2003) Safety of intra-articular hyaluronates for pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee. Am J Orthop 32(6):277–283
Kanchanatawan W, Arirachakaran A, Chaijenkij K et al (2015) Short-term outcomes of platelet-rich plasma injection for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-015-3784-4
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1957) Radiological assessment of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheumatol Dis 16:494–502
Kon E, Mandelbaum B, Buda R, Filardo G et al (2011) Plateletrich plasma intra-articular injection versus hyaluronic acid viscosupplementation as treatments for cartilage pathology: from early degeneration to osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy 27:1490–1501
Mishra SK, Pramanik R, Das P et al (2011) Role of intra-articular ozone in osteo-arthritis of knee for functional and symptomatic improvement. Ind J Phys Med Rehabilit 22(2):65–69
Nakazawa F, Matsuno H, Yudoh K et al (2002) Corticosteroid treatment induces chondrocyte apoptosis in an experimental arthritis model and in chondrocyte cultures. Clin Exp Rheumatol 20:773–781
Neustadt DH (2006) Intra-articular injections for osteoarthritis of the knee. Clevel Clin J Med 73(10):897–898
Nurden AT, Nurden P, Sanchez M et al (2008) Platelets and wound healing. Front Biosci 13:3532–3548
Ornetti P, Nourissat G, Berenbaum F et al (2016) Does platelet-rich plasma have a role in the treatment of osteoarthritis? Joint Bone Spine 83(1):31–36
Patel S, Dhillon MS, Aggarwal S et al (2013) Treatment with platelet-rich plasma is more effective than placebo for knee osteoarthritis: a prospective, double-blind, randomized trial. Am J Sports Med 41:356–364
Riva Sanseverino E (1989) Knee-joint disorders treated by oxygen-ozone therapy. Eur Med Phys 25(3):163–170
Samposon S, Gerhardt M, Mandelaum B (2008) Platelet rich plasma injection grafts for musculoskeletal injuries: a review. Curr Rew Musculoskelet Med 1(3–4):165–174
Smyth NA, Murawski CD, Fortier LA et al (2013) Platelet-rich plasma in the pathologic processes of cartilage: review of basic science evidence. Arthroscopy 29(8):1399–1409
Sundman EA, Cole BJ, Karas V et al (2014) The anti-inflammatory and matrix restorative mechanisms of platelet-rich plasma in osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med 42(1):35–41
Wearing SC, Henning EM, Byrne NM et al (2006) Musculoskeletal disorders associated with obesity: a biomechanical perspective. Obes Rev 7(3):239–250
Zhang W, Moskowitz RW, Nuki G et al (2008) OARSI recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis, Part II: OARSI evidence-based, expert consensus guidelines. Osteoarthr Cartil 16:137–162
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duymus, T.M., Mutlu, S., Dernek, B. et al. Choice of intra-articular injection in treatment of knee osteoarthritis: platelet-rich plasma, hyaluronic acid or ozone options. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25, 485–492 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4110-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4110-5