Abstract
Purpose
Well balanced knees with good alignment are essential for a well-functioning TKA with long survival of its implants. This prospective randomized study comparing navigation-assisted TKA and conventional TKA reported the clinical and radiological outcomes at a follow-up of 9 years. The purpose of this study was to compare the clinical and radiological outcomes for patients who underwent navigation-assisted TKA or conventional TKA after long-term follow-up.
Methods
A total of 80 patients (88 knees) were available for physical and radiological examination 9 years after TKA. Clinical outcomes were evaluated using HSS, WOMAC, and KS function and pain scores. And radiological outcomes of the component loosening and its survivorship during 9-year follow-up were also evaluated.
Results
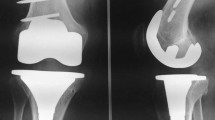
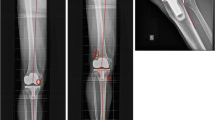
There were no significant differences in the field of clinical outcomes between the two groups. In terms of radiological outcomes, the navigation group had fewer alignment outliers (7.3 vs 20 %, p = 0.006). Although the clinical outcomes showed no differences between the two groups, the survival rate was slightly better in the navigation group than in the conventional group without statistical significance (best-case scenario 100 vs 95.3 %, n.s., worst-case scenario 95.6 vs 88.4 %, n.s.).
Conclusion
Navigation-assisted TKA produced better alignment outcomes and better survival rates than conventional instruments although some of the differences were not statistically significant.
Level of evidence
I.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babazadeh S, Dowsey MM, Bingham RJ, Ek ET, Stoney JD, Choong PF (2013) The long leg radiograph is a reliable method of assessing alignment when compared to computer-assisted navigation and computer tomography. Knee 20(4):242–249
Bauwens K, Matthes G, Wich M, Gebhard F, Hanson B, Ekkernkamp A, Stengel D (2007) Navigated total knee replacement. A meta-analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(2):261–269
Boonen B, Schotanus MG, Kernes B, Van der Weegen W, Van Drumpt RA, Kort NP (2013) Intra-operative results and radiological outcome of conventional and patient-specific surgery in total knee arthroplasty: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(10):2206–2212
Chauhan SK, Scott RG, Breidahl W, Beaver RJ (2004) Computer assisted knee arthroplasty versus a conventional jig based technique: a randomised prospective trial. J Bone Joint Surgery Br 86(3):372–377
Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD (2009) Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 24(4):560–569
Cip J, Widemschek M, Lueqmair M, Sheinkop MB, Benesch T, Martin A (2014) Conventional versus computer-assisted technique for total knee arthroplasty: a minimum of 5-year follow-up of 200 patients in a prospective randomized comparative trial. J Arthroplasty 29(9):1795–1802
Clemens U, Miehlke RK (2005) Advanced navigation planning including soft tissue management. Orthopaedics 28(10 suppl):s1259–s1262
Eckhoff DG, Piatt BE, Gnadinger CA, Blaschke RC (1995) Assessing rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 318:176–181
Ewald FC (1989) The knee society total knee arthroplasty roentgenographic evaluation and scoring system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:9–12
Fehring TK, Odum S, Griffin WL, Mason JB, Nadaud M (2001) Early failures in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:315–318
Han SB, Nha KW, Yoon JR, Lee DH, Chae IJ (2008) The reliability of navigation-guided gap technique in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopaedics 31(10 suppl 1):300–302
Harvie P, Sloan K, Beaver RJ (2012) Computer navigation vs conventional total knee arthroplasty five-year functional results of a prospective randomized trial. J Arthroplasty 27(5):667–672
Huang TW, Peng KT, Huang KC, Lee MS, Hsu RW (2014) Differences in component and limb alignment between computer-assisted and conventional surgery total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22(12):2954–2961
Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Tsumura N, Kubo S, Kitagawa A, Chin T, Iquchi T, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2011) Mid-term outcomes of computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(7):1107–1112
Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA (1991) Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 73(5):709–714
Kim YH, Park JW, Kim JS (2012) Computer-navigated versus conventional total knee arthroplasty a prospective randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(22):2017–2024
Lin SY, Chen CH, Fu YC et al (2013) Comparison of the clinical and radiological outcomes of three minimally invasive techniques for total knee replacement at two years. Bone Joint J 95B(7):906–910
Longstaff LM, Sloan K, Stamp K, Scaddan M, Beaver R (2009) Good alignment after total knee arthroplasty leads to faster rehabilitation and better function. J Arthroplasty 24(4):570–578
Lutzner J, Dexel J, Kirschner S (2013) No difference between computer-assisted and conventional total knee arthroplasty: five-year results of a prospective randomised study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(10):2241–2247
Marques CJ, Daniel S, Sufi-Siavach A, Lampe F (2015) No differences in clinical outcomes between fixed- and mobile-bearing computer-assisted total knee arthroplasties and no correlations between navigation data and clinical scores. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(6):1660–1668
Mason JB, Fehring TK, Estok R, Banel D, Fahrbach K (2007) Meta-analysis of alignment outcomes in computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty surgery. J Arthroplasty 22(8):1097–1106
Miller MC, Berger RA, Petrella AJ, Karmas A, Rubash HE (2001) Optimizing femoral component rotation in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 392:38–45
Molfetta L, Caldo D (2008) Computer navigation versus conventional implantation for varus knee total arthroplasty: a case–control study at 5 years follow-up. Knee 15(2):75–79
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement. Its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:153–156
Seon JK, Song EK (2006) Navigation-assisted less invasive total knee arthroplasty compared with conventional total knee arthroplasty: a randomized prospective trial. J Arthroplasty 21:777–782
Seon JK, Song EK, Yoon TR, Park SJ, Bae BH, Cho SG (2007) Comparison of functional results with navigation-assisted minimally invasive and conventional techniques in bilateral total knee arthroplasty. Comput Aided Surg 12(3):189–193
Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH, Shastri S, Jacoby SM (2002) Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop Relat Res 404:7–13
Sikorski JM (2008) Alignment in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(9):1121–1127
Spencer JM, Chauhan SK, Sloan K, Taylor A, Beaver RJ (2007) Computer navigation versus conventional total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 89(4):477–480
Victor J, Hoste D (2004) Image-based computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty leads to lower variability in coronal alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:131–139
Wasiliewski RC, Galante JO, Leighty RM, Natarajan RN, Rosenberg AG (1994) Wear patterns on retrieval polyethylene inserts and their relationship to technical considerations during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:31–43
Zhang GQ, Chen JY, Chai W, Liu M, Wang Y (2011) Comparison between computer-assisted-navigation and conventional total knee arthroplasties in patients undergoing simultaneous bilateral procedures: a randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93(13):1190–1196
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2014R1A1A2059147).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, E.K., Agrawal, P.R., Kim, S.K. et al. A randomized controlled clinical and radiological trial about outcomes of navigation-assisted TKA compared to conventional TKA: long-term follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24, 3381–3386 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-3996-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-3996-2