Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to quantitatively describe the locations of the syndesmotic ligaments and the tibiofibular articulating cartilage surfaces on standard radiographic views using reproducible radiographic landmarks and reference axes.
Methods
Twelve non-paired ankles were dissected to identify the anterior–inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL), posterior–inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL), interosseous tibiofibular ligament (ITFL), and the cartilage surfaces of the syndesmosis. Structures were marked with 2-mm radiopaque spheres prior to obtaining lateral and mortise radiographs. Measurements were performed by two independent raters to assess intra- and interobserver reliability via intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs).
Results
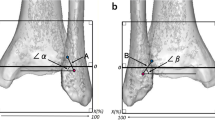
Measurements demonstrated excellent agreement between observers and across trials (all ICCs ≥ 0.960). On the lateral view, the AITFL tibial origin was 9.6 ± 1.5 mm superior and posterior to the anterior tibial plafond. Its fibular insertion was 4.4 ± 1.7 mm superior and posterior to the anterior fibular tubercle. The centre of the tibial cartilage facet of the tibiofibular contact zone was 8.4 ± 2.1 mm posterior and superior to the anterior plafond. The proximal and distal aspects of the ITFL tibial attachment were 45.9 ± 7.9 and 12.4 ± 3.4 mm proximal to the central plafond, respectively. The superficial and deep PITFL coursed anterior and distally from the posterior tibia to fibula. On the mortise view, the AITFL tibial attachment centre was 5.6 ± 2.4 mm lateral and superior to the lateral extent of the plafond (4.3 mm lateral, 3.3 mm superior), and its fibular insertion was 21.2 ± 2.1 mm superior and medial to the inferior tip of the lateral malleolus.
Conclusions
Quantitative radiographic guidelines describing the locations of the primary syndesmotic structures demonstrated excellent reliability and reproducibility. Defined guidelines provide additional clinically relevant information regarding the radiographic anatomy of the syndesmosis and may assist with preoperative planning, augment intraoperative navigation, and provide additional means for objective postoperative assessment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartonícek J (2003) Anatomy of the tibiofibular syndesmosis and its clinical relevance. Surg Radiol Anat 25(5–6):379–386
Bassett FH III, Gates HS III, Billys JB, Morris HB, Nikolaou PK (1990) Talar impingement by the anteroinferior tibiofibular ligament. A cause of chronic pain in the ankle after inversion sprain. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72(1):55–59
Bava E, Charlton T, Thordarson D (2010) Ankle fracture syndesmosis fixation and management: the current practice of orthopedic surgeons. Am J Orthop 39(5):242–246
Beumer A, Heijboer RP, Fontijne WP, Swierstra BA (2000) Late reconstruction of the anterior distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: good outcome in 9 patients. Acta Orthop Scand 71(5):519–521
Beumer A, van Hemert WL, Niesing R, Entius CA, Ginai AZ, Mulder PG, Swierstra BA (2004) Radiographic measurement of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis has limited use. Clin Orthop Relat Res 423:227–234
Bonnin JG (1970) Injuries to the ankle. Hafner Pub. Co., Darien
Boytim MJ, Fischer DA, Neumann L (1991) Syndesmotic ankle sprains. Am J Sports Med 19(3):294–298
Candal-Couto JJ, Burrow D, Bromage S, Briggs PJ (2004) Instability of the tibio-fibular syndesmosis: have we been pulling in the wrong direction? Injury 35(8):814–818
Davidovitch RI, Weil Y, Karia R, Forman J, Looze C, Liebergall M, Egol K (2013) Intraoperative syndesmotic reduction: three-dimensional versus standard fluoroscopic imaging. J Bone Joint Surg Am 95(20):1838–1843
Ebraheim NA, Taser F, Shafiq Q, Yeasting RA (2006) Anatomical evaluation and clinical importance of the tibiofibular syndesmosis ligaments. Surg Radiol Anat 28(2):142–149
Ebraheim NA, Lu J, Yang H, Mekhail AO, Yeasting RA (1997) Radiographic and CT evaluation of tibiofibular syndesmotic diastasis: a cadaver study. Foot Ankle Int 18(11):693–698
Gardner MJ, Demetrakopoulos D, Briggs SM, Helfet DL, Lorich DG (2006) Malreduction of the tibiofibular syndesmosis in ankle fractures. Foot Ankle Int 27(10):788–792
Gerber JP, Williams GN, Scoville CR, Arciero RA, Taylor DC (1998) Persistent disability associated with ankle sprains: a prospective examination of an athletic population. Foot Ankle Int 19(10):653–660
Grass R, Rammelt S, Biewener A, Zwipp H (2003) Peroneus longus ligamentoplasty for chronic instability of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Foot Ankle Int 24(5):392–397
Hamid N, Loeffler BJ, Braddy W, Kellam JF, Cohen BE, Bosse MJ (2009) Outcome after fixation of ankle fractures with an injury to the syndesmosis: the effect of the syndesmosis screw. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91(8):1069–1073
Haytmanek CT, Williams BT, James EW, Campbell KJ, Wijdicks CA, LaPrade RF, Clanton TO (2015) Radiographic identification of the primary lateral ankle structures. Am J Sports Med 43(1):79–87
Hopkinson WJ, St Pierre P, Ryan JB, Wheeler JH (1990) Syndesmosis sprains of the ankle. Foot Ankle 10(6):325–330
Hsu AR, Gross CE, Lee S (2013) Intraoperative O-arm computed tomography evaluation of syndesmotic reduction: case report. Foot Ankle Int 34(5):753–759
Hunt KJ, George E, Harris AH, Dragoo JL (2013) Epidemiology of syndesmosis injuries in intercollegiate football: incidence and risk factors from National Collegiate Athletic Association injury surveillance system data from 2004–2005 to 2008–2009. Clin J Sports Med 23(4):278–282
Johannsen AM, Anderson CJ, Wijdicks CA, Engebretsen L, LaPrade RF (2013) Radiographic landmarks for tunnel positioning in posterior cruciate ligament reconstructions. Am J Sports Med 41(1):35–42
Lui TH (2010) Tri-ligamentous reconstruction of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: a minimally invasive approach. J Foot Ankle Surg 49(5):495–500
Manjoo A, Sanders DW, Tieszer C, MacLeod MD (2010) Functional and radiographic results of patients with syndesmotic screw fixation: implications for screw removal. J Orthop Trauma 24(1):2–6
Marmor M, Hansen E, Han HK, Buckley J, Matityahu A (2011) Limitations of standard fluoroscopy in detecting rotational malreduction of the syndesmosis in an ankle fracture model. Foot Ankle Int 32(6):616–622
McBryde A, Chiasson B, Wilhelm A, Donovan F, Ray T, Bacilla P (1997) Syndesmotic screw placement: a biomechanical analysis. Foot Ankle Int 18(5):262–266
Miller AN, Barei DP, Iaquinto JM, Ledoux WR, Beingessner DM (2013) Iatrogenic syndesmosis malreduction via clamp and screw placement. J Orthop Trauma 27(2):100–106
Miller RS, Weinhold PS, Dahners LE (1999) Comparison of tricortical screw fixation versus a modified suture construct for fixation of ankle syndesmosis injury: a biomechanical study. J Orthop Trauma 13(1):39–42
Montagne J, Chevrot A, Galmiche JM, Chafetz N (eds) (1983) Atlas of foot radiology. Mason Publishing, New York
Morris MW, Rice P, Schneider TE (2009) Distal tibiofibular syndesmosis reconstruction using a free hamstring autograft. Foot Ankle Int 30(6):506–511
Mukhopadhyay S, Metcalfe A, Guha AR, Mohanty K, Hemmadi S, Lyons K, O’Doherty D (2011) Malreduction of syndesmosis—are we considering the anatomical variation? Injury 42(10):1073–1076
Naqvi GA, Cunningham P, Lynch B, Galvin R, Awan N (2012) Fixation of ankle syndesmotic injuries: comparison of tightrope fixation and syndesmotic screw fixation for accuracy of syndesmotic reduction. Am J Sports Med 40(12):2828–2835
Nielson JH, Gardner MJ, Peterson MG, Sallis JG, Potter HG, Helfet DL, Lorich DG (2005) Radiographic measurements do not predict syndesmotic injury in ankle fractures: an MRI study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:216–221
Phisitkul P, Ebinger T, Goetz J, Vaseenon T, Marsh JL (2012) Forceps reduction of the syndesmosis in rotational ankle fractures: a cadaveric study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(24):2256–2261
Pietrini SD, LaPrade RF, Griffith CJ, Wijdicks CA, Ziegler CG (2009) Radiographic identification of the primary posterolateral knee structures. Am J Sports Med 37(3):542–551
Pietrini SD, Ziegler CG, Anderson CJ, Wijdicks CA, Westerhaus BD, Johansen S, Engebretsen L, LaPrade RF (2011) Radiographic landmarks for tunnel positioning in double-bundle ACL reconstructions. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(5):792–800
Rammelt S, Zwipp H, Grass R (2008) Injuries to the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis: an evidence-based approach to acute and chronic lesions. Foot Ankle Clin 13(4):611–633
Ramsey PL, Hamilton W (1976) Changes in tibiotalar area of contact caused by lateral talar shift. J Bone Joint Surg Am 58(3):356–357
Sagi HC, Shah AR, Sanders RW (2012) The functional consequence of syndesmotic joint malreduction at a minimum 2-year follow-up. J Orthop Trauma 26(7):439–443
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL (1979) Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 86(2):420–428
Sikka RS, Fetzer GB, Sugarman E, Wright RW, Fritts H, Boyd JL, Fischer DA (2012) Correlating MRI findings with disability in syndesmotic sprains of NFL players. Foot Ankle Int 33(5):371–378
Song DJ, Lanzi JT, Groth AT, Drake M, Orchowski JR, Shaha SH, Lindell KK (2014) The effect of syndesmosis screw removal on the reduction of the distal tibiofibular joint: a prospective radiographic study. Foot Ankle Int 35(6):543–548
Thordarson DB, Motamed S, Hedman T, Ebramzadeh E, Bakshian S (1997) The effect of fibular malreduction on contact pressures in an ankle fracture malunion model. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79(12):1809–1815
Westermann RW, Rungprai C, Goetz JE, Femino J, Amendola A, Phisitkul P (2014) The effect of suture-button fixation on simulated syndesmotic malreduction: a cadaveric study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96(20):1732–1738
Wijdicks CA, Griffith CJ, LaPrade RF, Johansen S, Sunderland A, Arendt EA, Engebretsen L (2009) Radiographic identification of the primary medial knee structures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91(3):521–529
Williams BT, Ahrberg AB, Goldsmith MT, Campbell KJ, Shirley L, Wijdicks CA, LaPrade RF, Clanton TO (2015) Ankle syndesmosis: a qualitative and quantitative anatomic analysis. Am J Sports Med 43(1):88–97
Yasui Y, Takao M, Miyamoto W, Innami K, Matsushita T (2011) Anatomical reconstruction of the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament for chronic disruption of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(4):691–695
Zalavras C, Thordarson D (2007) Ankle syndesmotic injury. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 15(6):330–339
Zamzami MM, Zamzam MM (2009) Chronic isolated distal tibiofibular syndesmotic disruption: diagnosis and management. Foot Ankle Surg 15(1):14–19
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, B.T., James, E.W., Jisa, K.A. et al. Radiographic identification of the primary structures of the ankle syndesmosis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24, 1187–1199 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3743-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3743-0