Abstract
Purpose
The range of motion of the knee is a critical element of clinical assessment. The tested hypothesis was that the measurement of the knee flexion angle measured with two specific smartphone applications using either inclinometer or camera technology was different from the reference measurement with a navigation system designed for total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
Methods
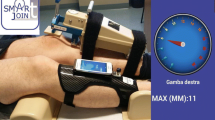
Ten consecutive patients were selected for navigation-assisted TKA. Five navigated, five inclinometer and five camera measurements of knee flexion angle were obtained for each patient throughout the complete range of motion. The difference, the correlation and the coherence between all measurements and all paired sub-groups were analysed.
Results
There was a strong correlation and a good coherence between the three techniques of measurements, but the knee flexion angle reported by the inclinometer differed substantially from the camera- and navigation-based measurements. The camera-based measurement was clinically identical to the navigated data, with a mean difference of <1° and only 1/50 difference >3°.
Conclusion
Camera-based smartphone measurement of the knee range of motion is fit for purpose in a routine clinical setting. The accuracy may be higher than other conventional measurement techniques, allowing a more precise rating of the clinical outcomes after TKA.
Level of evidence
II.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlbäck S (1968) Osteoarthrosis of the knee. A radiographic investigation. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) Suppl. 277:1–72
Austin MS, Ghanem E, Joshi A, Trappler R, Parvizi J, Hozack WJ (2008) The assessment of intraoperative prosthetic knee range of motion using two methods. J Arthroplast 23:515–521
Bennett D, Hanratty B, Thompson N, Beverland D (2009) Measurement of knee joint motion using digital imaging. Int Orthop 33:1627–1631
Cleffken B, van Breukelen G, Brink P, van Mameren H, Damink SO (2007) Digital goniometric measurement of knee joint motion. Evaluation of usefulness for research settings and clinical practice. Knee 14:385–389
Edwards JZ, Greene KA, Davis RS, Kovacik MW, Noe DA, Askew MJ (2004) Measuring flexion in knee arthroplasty patients. J Arthroplast 19:369–372
Favre J, Jolles BM, Aissaoui R, Aminian K (2008) Ambulatory measurement of 3D knee joint angle. J Biomech 41:1029–1035
Ferriero G, Vercelli S, Sartorio F, Lasa SM, Ilieva E, Brigatti E, Ruella C, Foti C (2013) Reliability of a smartphone-based goniometer for knee joint goniometry. Int J Rehabil Res 36:146–151
Hefti F, Müller W, Jakob RP, Stäubli HU (1993) Evaluation of knee ligament injuries with the IKDC form. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 1:226–234
Huddleston J, Alaiti A, Goldvasser D, Scarborough D, Freiberg A, Rubash H, Malchau H, Harris W, Krebs D (2006) Ambulatory measurement of knee motion and physical activity: preliminary evaluation of a smart activity monitor. J Neuroeng Rehabil 3:21
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN (1989) Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 248:13–14
Jenny JY, Clemens U, Kohler S, Kiefer H, Konermann W, Miehlke RK (2005) Consistency of implantation of a total knee arthroplasty with a non-image-based navigation system: a case-control study of 235 cases compared with 235 conventionally implanted prostheses. J Arthroplasty 20:832–839
Jenny JY (2013) Measurement of the knee flexion angle with a Smartphone-application is precise and accurate. J Arthroplast 28:784–787
Lavernia C, D’Apuzzo M, Rossi MD, Lee D (2008) Accuracy of knee range of motion assessment after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 23(Suppl 1):85–91
Lenssen AF, van Dam EM, Crijns YH, Verhey M, Geesink RJ, van den Brandt PA, de Bie RA (2007) Reproducibility of goniometric measurement of the knee in the in-hospital phase following total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 8:83
Naylor JM, Ko V, Adie S, Gaskin C, Walker R, Harris IA, Mittal R (2011) Validity and reliability of using photography for measuring knee range of motion: a methodological study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 12:77
Russell TG, Jull GA, Wootton R (2003) Can the Internet be used as a medium to evaluate knee angle? Man Ther 8:242–246
Yaikwawongs N, Limpaphayom N, Wilairatana V (2009) Reliability of digital compass goniometer in knee joint range of motion measurement. J Med Assoc Thai 92:517–522
Acknowledgments
The authors thank gratefully Prof. Justin Cobb for having reviewed the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenny, JY., Bureggah, A. & Diesinger, Y. Measurement of the knee flexion angle with smartphone applications: Which technology is better?. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24, 2874–2877 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3537-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3537-4