Abstract
Purpose
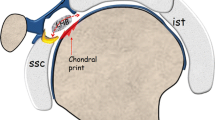
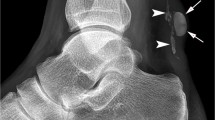
Calcifying tendinitis is a common condition of the shoulder. In many cases, arthroscopic reduction in the deposit is indicated. The localization of the deposit is sometimes challenging and time-consuming. Pre-operative ultrasound (US)-guided needle placement in the deposit and pre-operative US marking of the deposit at the skin with a ballpoint are described and recommended methods to alleviate the procedure without using ionizing radiation by fluoroscopy.
Methods
Intra-operative sonography of the shoulder is introduced as a new method to localize the calcific deposit with high accuracy. After standard arthroscopic buresectomy, the surgeon performs an ultrasound examination under sterile conditions to localize the deposits. A ventral longitudinal US section is recommended, and the upper arm is rotated until the deposit is visible. Subsequently, perpendicular to the skin at the position of the transducer, a needle is introduced under arthroscopic and ultrasound visualization to puncture the deposit.
Results
The presence of snow-white crystals at the tip of the needle proves the exact localization. Consecutively, the curettage can be accomplished. Another intra-operative sonography evaluates possible calcific remnants and the tendon structure.
Conclusion
This new technique may alleviate arthroscopic calcific deposit curettage by visualizing the deposit without using ionizing radiation. Additionally, soft tissue damage due to decreased number of punctures to detect the deposit may be achieved. Both factors may contribute to reduced operation time.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lorbach O, Kusma M, Pape D, Kohn D, Dienst M (2008) Influence of deposit stage and failed ESWT on the surgical results of arthroscopic treatment of calcifying tendonitis of the shoulder. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 16:516–521
Bethune R, Bull AM, Dickinson RJ, Emery RJ (2007) Removal of calcific deposits of the rotator cuff tendon using an intra-articular ultrasound probe. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15:289–291
Franceschi F, Longo UG, Ruzzini L, Rizzello G, Denaro V (2007) Arthroscopic management of calcific tendinitis of the subscapularis tendon. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15:1482–1485
Ifesanya A, Scheibel M (2007) Arthroscopic treatment of calcifying tendonitis of subscapularis and supraspinatus tendon: a case report. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15:1473–1477
Seil R, Litzenburger H, Kohn D, Rupp S (2006) Arthroscopic treatment of chronically painful calcifying tendinitis of the supraspinatus tendon. Arthroscopy 22:521–527
Seyahi A, Demirhan M (2009) Arthroscopic removal of intraosseous and intratendinous deposits in calcifying tendinitis of the rotator cuff. Arthroscopy 25:590–596
Yoo JC, Park WH, Koh KH, Kim SM (2010) Arthroscopic treatment of chronic calcific tendinitis with complete removal and rotator cuff tendon repair. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-010-1067-7
Kayser R, Hampf S, Seeber E, Heyde CE (2007) Value of preoperative ultrasound marking of calcium deposits in patients who require surgical treatment of calcific tendinitis of the shoulder. Arthroscopy 23:43–50
Sørensen L, Teichert G, Skjødt T, Dichmann OL (2004) Preoperative ultrasonographic-guided marking of calcium deposits in the rotator cuff facilitates localization during arthroscopic surgery. Arthroscopy 20:103–104
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabeti-Aschraf, M., Gonano, C., Nemecek, E. et al. Intra-operative ultrasound facilitates the localization of the calcific deposit during arthroscopic treatment of calcifying tendinitis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18, 1792–1794 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1227-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1227-9