Abstract
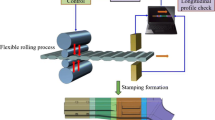
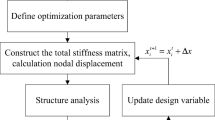
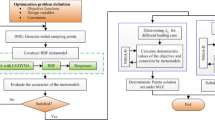
Lightweight and crashworthiness design have been two main challenges in the vehicle industry. These two performances often conflict with each other. To not sacrifice vehicle crashworthiness performance when performing vehicle lightweight design, a novel inner part of front longitudinal beam (FLB-inner) structure with a tailor rolled blank (TRB) concept is proposed in this work, and the corresponding design method is also proposed to minimize the weight of FLB-inner. Firstly, a full-scale vehicle finite element model is adopted and experimentally verified. Secondly, the conventional uniform thickness FLB-inner panel is replaced with a TRB structure, herein, the FLB-inner is divided into four segments with different thickness according to the crashworthiness requirements of frontal impact. Then the material constitutive model and finite element modeling for TRB is established. Thirdly, the optimal Latin hypercube sampling (OLHS) technique is used to generate sampling points and the objective and constraints function values are calculated using commercial software LS-DYNA. Based on the simulation results, the ε-SVR surrogate models are constructed. Finally, the artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm is applied to obtain the optimal thickness distribution of FLB-inner. The results indicated that the weight of the FLB-inner is reduced by 15.21 %, while the crashworthiness is mproved in comparison with the baseline design.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TRB:
-
Tailor rolled blank
- TWB:
-
Tailor welded blank
- CTZ:
-
Constant thickness zone
- TTZ:
-
Thickness transition zone
- FLB:
-
Front longitudinal beam
- CLB:
-
Center longitudinal beam
- FLB-inner:
-
Inner part of the front longitudinal beam
- FLB-TRB:
-
Front longitudinal beam with TRB
- TRB FLB-inner:
-
Inner part of front longitudinal beam with TRB
- EA:
-
Energy absorption
- UHSS:
-
Ultra high strength steel
- AHSS:
-
Advanced high strength steel
- OLHS:
-
Optimal Latin hypercube sampling
- ABC:
-
Artificial bee colony
- FSV:
-
Future Steel Vehicle
- MDO:
-
Multidisciplinary design optimization
- BIW:
-
Body-in-white
- RSM:
-
Response surface models
- RBF:
-
Radial basis functions
- MARS:
-
Multivariate adaptive regression splines
- KG:
-
Kriging
- SVR:
-
Support vector regression
- ε-SVR:
-
ε-support vector regression
- ν-SVR:
-
ν-support vector regression
References
Akay B, Karaboga D (2012) Artificial bee colony algorithm for large-scale problems and engineering design optimization. J Intell Manuf 23(4):1001–1014
Allen DM (1974) The relationship between variable selection and data augmentation and a method for prediction. Technometrics 16(1):125–127
Beiter P, Groche P (2011) On the development of novel light weight profiles for automotive industries by roll forming of tailor rolled blanks. Key Eng Mater 473:45–52
Browne MW (2000) Cross-validation methods. J Math Psychol 44(1):108–132
Chen VCP, Tsui KL, Barton RR, Meckesheimer M (2006) A review on design, modeling and applications of computer experiments. IIE Trans 38(4):273–291
Cherkassky V, Mulier F (1998) Learning from data: concepts, theory. Wiley, New York
Chuang CH, Yang RJ, Li G, Mallela K, Pothuraju P (2008) Multidisciplinary design optimization on vehicle tailor rolled blank design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 35(6):551–560
Clarke SM, Griebsch JH, Simpson TW (2005) Analysis of support vector regression for approximation of complex engineering analyses. J Mech Des 127(6):1077–1087
Cristianni N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines and other Kernel-based learning methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Dyn N, Levin D, Rippa S (1986) Numerical procedures for surface fitting of scattered data by radial basis functions. SIAM J Sci Stat Comput 7(2):639–659
Engelund WC, Douglas OS, Lepsch RA, McMillian MM, Unal R (1993) Aerodynamic configuration design using response surface methodology analysis. AIAA, Aircraft Design, Systems and Operations Meeting, Monterey, CA, Aug. 11–13
Friedman JH (1991) Multivariate adaptive regression splines. Ann Stat 19(1):1–141
Future Steel Vehicle - Final Engineering Report, www.worldautosteel.org (5/17/2011)
Goede M, Stehlin M, Rafflenbeul L, Kopp G, Beeh E (2009) Super light car-lightweight construction thanks to a multi-material design and function integration. Eur Transp Res Rev 1(1):15–20
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Addison-Wisely, MA
Gu GX, Sun GY, Li GY, Mao LC, Li Q (2013) A Comparative study on multiobjective reliable and robust optimization for crashworthiness design of vehicle structure. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48:669–684
Halquist J (2007) LS-DYNA keyword user’s manual version 971. Livermore Software Technology Corporation, Livermore
Hardy RL (1971) Multiquadratic equations of topography and other irregular surfaces. J Geophys Res 76:1905–1915
Hirt G, Dávalos-Julca DH (2012) Tailored profiles made of tailor rolled strips by roll forming - part 1 of 2. Steel Res Int 83(1):100–105
Hou SJ, Li Q, Long SY, Yang XJ, Li W (2008) Multiobjective optimization of multi-cell sections for the crashworthiness design. Int J Impact Eng 35(12):1355–1367
Jeon SJ, Lee MY, Kim BM (2011) Development of automotive door inner panel using AA 5J32 tailor rolled blank. Trans Mater Process 20(7):512–517
Jin R, Chen W, Simpson TW (2001) Comparative studies of metamodeling techniques under multiple modeling criteria. Struct Multidiscip Optim 23(1):1–13
Karaboga D, Akay B (2009) A comparative study of artificial bee colony algorithm. Appl Math Comput 214(1):108–132
Karaboga D, Basturk B (2007) A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J Glob Optim 39(3):459–471
Karaboga D, Basturk B (2008) On the performance of artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. Appl Soft Comput 8(1):687–697
Kennedy J, Eberhart RC (1995) Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 1995 I.E. International Conference on Neural Networks (4): 1942–1948
Kleijnen JP (2009) Kriging metamodeling in simulation: a review. Eur J Oper Res 192(3):707–716
Kohavi R (1995) A study of cross-validation and bootstrap for accuracy estimation and model selection. In: International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 1137–1143
Kopp R, Wiedner C, Meyer A (2005a) Flexibly rolled sheet metal and its use in sheet metal forming. Adv Mater Res 6–8:81–92
Kopp R, Wiedner C, Meyar A (2005b) Flexible rolling for load-adapted blanks. Int Sheet Metal Rev 7(4):20–24
Li Y, Lin Z, Jiang A, Chen G (2003) Use of high strength steel sheet for lightweight and crashworthy car body. Mater Des 24(3):177–182
Li GY, Xu FX, Huang XD, Sun GY (2015a) Topology optimization of an automotive tailor-welded blank door. J Mech Des 137(5):055001
Li GY, Xu FX, Sun GY, Li Q (2015b) A comparative study on thin-walled structures with functionally graded thickness (FGT) and tapered tubes withstanding oblique impact loading. Int J Impact Eng 77:68–83
Liao XT, Li Q, Yang XJ, Zhang WG, Li W (2008) Multi-objective optimization for crash safety design of vehicles using stepwise regression model. Struct Multidiscip Optim 35(6):561–569
Matheron G (1963) Principles of geostatistics. Econ Geol 58(8):1246–1266
Meyer A, Wietbrock B, Hirt G (2008) Increasing of the drawing depth using tailor rolled blanks-numerical and experimental analysis. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48(5):522–531
Muhr und Bender KG (2013) http://www.mubea.com (10.06.13)
Myers RH, Montgomery DC (1995) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. Wiley & Sons, New York
Pan F, Zhu P (2011) Lightweight design of vehicle front end structure: contributions of multiple surrogates. Int J Veh Des 57(2–3):124–147
Pan F, Zhu P, Zhang Y (2010) Metamodel-based lightweight design of B-pillar with TWB structure via support vector regression. Comput Struct 88(1–2):36–44
Park JS (1994) Optimal Latin-hypercube designs for computer experiments. J Stat Plan Infer 39(1):95–111
Poli R, Kennedy J, Blackwell T (2007) Particle swarm optimization. Swarm Intell 1(1):33–57
Ryabkov N, Jackel F, Van Putten K, Hirt G (2008) Production of blanks with thickness transitions in longitudinal and lateral direction through 3D-strip profile rolling. Int J Mater Form Suppl 1(1):391–394
Sacks J, Welch WJ, Mitchell TJ, Wynn HP (1989) Design and analysis of computer experiments. Stat Sci 4(4):409–435
Schölkopf B, Smola AJ (2002) Learning with Kernels: support vector machines, regularization, optimization, and beyond. MIT Press, Cambridge
Schölkopf B, Smola AJ, Williamson RC, Bartlett PL (2002) New support vector algorithms. Neural Comput 12(5):1207–1245
Shi YL, Zhu P, Shen LB, Lin ZQ (2007) Lightweight design of automotive front side rails with TWB concept. Thin-Walled Struct 45(7):8–14
Singh A (2009) An artificial bee colony algorithm for the leaf-constrained minimum spanning tree problem. Appl Soft Comput 9(2):625–631
Song XG, Sun GY, Li GY, Zhao W, Li Q (2013) Crashworthiness optimization of foam-filled tapered thin-walled structure using multiple surrogate models. Struct Multidiscip Optim 47(2):221–231
Srinivasan D, Seow TH (2003) Evolutionary computation, CEC’03, 8–12 Dec. 4, Canberra, Australia, pp 2292–2297
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution-a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Glob Optim 11(4):341–359
Sun GY, Li GY, Li Q (2012) Variable fidelity design based surrogate and artificial bee colony algorithm for sheet metal forming process. Finite Elem Anal Des 59:76–90
Sun GY, Xu FX, Li GY, Li Q (2014) Crashing analysis and multiobjective optimization for thin-walled structures with functionally graded thickness. Int J Impact Eng 64:62–67
Sun GY, Tian XY, Fang JG, Xu FX, Li GY, Huang XD (2015) Dynamical bending analysis and optimization design for functionally graded thickness (FGT) tube. Int J Impact Eng 78:128–137
Vapnik V (1995) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, Berlin
Vapnik V (1998) Statistical learning theory. Wiley, New York
Varma S, Simon R (2006) Bias in error estimation when using cross-validation for model selection. BMC Bioinf 791
Viana FAC, Haftka RT, Steffen V (2009) Multiple surrogates: how cross-validation errors can help us to obtain the best predictor. Struct Multidiscip Optim 39:439–457
Wu SR, Zhang XT, Lenk P (2001) Step function-a measure for frontal crash pulse and its applications. Int J Veh Des 26(4):385–394
Xiao Z, Fang JG, Sun GY, Li Q (2015) Crashworthiness design for functionally graded foam-filled bumper beam. Adv Eng Softw 85:81–95
Zhang Y, Lai XM, Zhu P, Wang WR (2006) Lightweight design of automobile component using high strength steel based on dent resistance. Mater Des 27(1):64–68
Zhang Y, Zhu P, Chen GL (2007) Lightweight design of automotive front side rail based on robust optimization. Thin-Walled Struct 45(7–8):670–676
Zhang HW, Liu LZ, Hu P, Liu XH (2012a) Numerical simulation and experimental investigation of springback in U-channel forming of tailor rolled blank. Int J Iron Steel Res 19(9):8–12
Zhang HW, Liu LZ, Hu P, Liu XH (2012b) Springback characteristics in U-channel forming of tailor rolled blank. Acta Metall Sin English Lett 25(3):207–213
Zhu P, Zhang Y, Chen GL (2009) Metamodel-based lightweight design of automotive front body structure using robust optimization. Proc Inst Mech Eng D J Automob Eng 223(9):1133–1147
Acknowledgments
This work was supported from The Key Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (61232014) and the Program of NSFC of China (11202072), The Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (20120161120005), The Open Fund Program of the State Key Laboratory of Vehicle Light-weight Design, P. R. China (20130303) and the Hunan Provincial Science Foundation of China (13JJ4036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, L., Sun, G., Cui, J. et al. Crashworthiness design of vehicle structure with tailor rolled blank. Struct Multidisc Optim 53, 321–338 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1315-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1315-z