Abstract
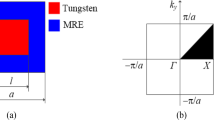
Self-collimating phononic crystals (PCs) are periodic structures that enable self-collimation of waves. While various design parameters such as material property, period, lattice symmetry, and material distribution in a unit cell affect wave scattering inside a PC, this work aims to find an optimal material distribution in a unit cell that exhibits the desired self-collimation properties. While earlier studies were mainly focused on the arrangement of self-collimating PCs or shape changes of inclusions in a unit cell having a specific topological layout, we present a topology optimization formulation to find a desired material distribution. Specifically, a finite element based formulation is set up to find the matrix and inclusion material distribution that can make elastic shear-horizontal bulk waves propagate along a desired target direction. The proposed topology optimization formulation newly employs the geometric properties of equi-frequency contours (EFCs) in the wave vector space as essential elements in forming objective and constraint functions. The sensitivities of these functions with respect to design variables are explicitly derived to utilize a gradient-based optimizer. To show the effectiveness of the formulation, several case studies are considered.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2003) Topology optimization: theory, methods and applications. Springer, Berlin
Bucay J, Roussel E, Vasseur J, Deymier P, Hladky-Hennion A, Pennec Y, Muralidharan K, Djafari-Rouhani B, Dubus B (2009) Positive, negative, zero refraction, and beam splitting in a solid/air phononic crystal: theoretical and experimental study. Phys Rev B 79(21):214305
Cao Y, Hou Z, Liu Y (2004) Finite difference time domain method for band-structure calculations of two-dimensional phononic crystals. Solid State Commun 132(8):539–543
Chiang C-Y, Luan P-G (2010) Imaging off-plane shear waves with a two-dimensional phononic crystal lens. J Phys Condens Matter 22(5):055405
Choi KK, Kim NH (2005) Structural sensitivity analysis and optimization I: linear systems, vol 1. Springer, Berlin
Cicek A, Kaya OA, Ulug B (2011) Wide-band all-angle acoustic self-collimation by rectangular sonic crystals with elliptical bases. J Phys D Appl Phys 44(20):205104
Cicek A, Kaya OA, Ulug B (2012a) Impacts of uniaxial elongation on the bandstructures of two-dimensional sonic crystals and associated applications. Appl Acoust 73(1):28–36
Cicek A, Kaya OA, Ulug B (2012b) Refraction-type sonic crystal junction diode. Appl Phys Lett 100(11):111905
Diaz A, Haddow A, Ma L (2005) Design of band-gap grid structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 29(6):418–431
Economou EN, Sigalas M (1994) Stop bands for elastic waves in periodic composite materials. J Acoust Soc Am 95(4):1734–1740
Fornberg B (1988) Generation of finite difference formulas on arbitrarily spaced grids. Math Comput 51(184):699–706
Frei WR, Tortorelli DA, Johnson HT (2005) Topology optimization of a photonic crystal waveguide termination to maximize directional emission. Appl Phys Lett 86(11):111114
Gao D, Zhou Z, Citrin DS (2008) Self-collimated waveguide bends and partial bandgap reflection of photonic crystals with parallelogram lattice. J Opt Soc Am A 25(3):791–795
Guest JK, Prévost J, Belytschko T (2004) Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(2):238–254
Halkjær S, Sigmund O, Jensen JS (2006) Maximizing band gaps in plate structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 32(4):263–275
Huang Y, Liu S, Zhao J (2013) Optimal design of two-dimensional band-gap materials for uni-directional wave propagation. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(3):487–499
Hussein MI (2009) Reduced Bloch mode expansion for periodic media band structure calculations. Proc Royal Soc A: Math, Physi Eng Sci 465(2109):2825–2848
Hussein MI, Hamza K, Hulbert GM, Saitou K (2007) Optimal synthesis of 2D phononic crystals for broadband frequency isolation. Waves Random Complex Media 17(4):491–510
Jensen JS, Sigmund O (2005) Topology optimization of photonic crystal structures: a high-bandwidth low-loss T-junction waveguide. J Opt Soc Am B 22(6):1191–1198
Kaya OA, Cicek A, Ulug B (2012) Self-collimated slow sound in sonic crystals. J Phys D Appl Phys 45(36):365101
Kobayashi F, Biwa S, Ohno N (2004) Wave transmission characteristics in periodic media of finite length: multilayers and fiber arrays. Int J Solids Struct 41(26):7361–7375
Kosaka H, Kawashima T, Tomita A, Notomi M, Tamamura T, Sato T, Kawakami S (1998) Superprism phenomena in photonic crystals. Phys Rev B 58(16):R10096–R10099
Kosaka H, Kawashima T, Tomita A, Notomi M, Tamamura T, Sato T, Kawakami S (1999) Self-collimating phenomena in photonic crystals. Appl Phys Lett 74(9):1212–1214
Kushwaha M, Halevi P, Martinez G, Dobrzynski L, Djafari-Rouhani B (1994) Theory of acoustic band structure of periodic elastic composites. Phys Rev B 49(4):2313–2322
Langlet P, Hladky‐Hennion AC, Decarpigny JN (1995) Analysis of the propagation of plane acoustic waves in passive periodic materials using the finite element method. J Acoust Soc Am 98:2792–2800
Liang WY, Wang TB, Yin CP, Dong JW, Leng FC, Wang HZ (2010) Super-broadband non-diffraction guiding modes in photonic crystals with elliptical rods. J Phys D Appl Phys 43(7):075103
Pérez-Arjona I, Sánchez-Morcillo VJ, Redondo J, Espinosa V, Staliunas K (2007) Theoretical prediction of the nondiffractive propagation of sonic waves through periodic acoustic media. Phys Rev B 75(1):014304
Prather DW, Shi S, Murakowski J, Schneider GJ, Sharkawy A, Chen C, Miao B, Martin R (2007) Self-collimation in photonic crystal structures: a new paradigm for applications and device development. J Phys D Appl Phys 40(9):2635–2651
Rupp CJ, Evgrafov A, Maute K, Dunn ML (2007) Design of phononic materials/structures for surface wave devices using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 34(2):111–121
Shi J, Lin S-CS, Huang TJ (2008) Wide-band acoustic collimating by phononic crystal composites. Appl Phys Lett 92(11):111901
Sigmund O, Jensen JS (2003) Systematic design of phononic band–gap materials and structures by topology optimization. Philos Trans Royal Soc A: Math Phys Eng Sci 361(1806):1001–1019
Stainko R, Sigmund O (2007) Tailoring dispersion properties of photonic crystal waveguides by topology optimization. Waves Random Complex Media 17(4):477–489
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24(2):359–373
Tang D, Chen L, Ding W (2006) Efficient beaming from photonic crystal waveguides via self-collimation effect. Appl Phys Lett 89(13):131120
Wang F, Jensen JS, Sigmund O (2011) Robust topology optimization of photonic crystal waveguides with tailored dispersion properties. J Opt Soc Am B 28(3):387–397
Wu L-Y, Chen L-W, Wu M-L (2008) The nondiffractive wave propagation in the sonic crystal consisting of rectangular rods with a slit. J Phys Condens Matter 20(29):295229
Yablonovitch E (1987) Inhibited spontaneous emission in solid-state physics and electronics. Phys Rev Lett 58(20):2059–2062
Zhang X, Liu Z (2004) Negative refraction of acoustic waves in two-dimensional phononic crystals. Appl Phys Lett 85(2):341–343
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant (No: 2014–021950) funded by the Korean Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MEST), Basic Science Research Program through NRF funded by the Korean Ministry of Education (No: 2014–048162), contracted through Institute of Advanced Machinery and Design at Seoul National University and the Global Frontier R&D Program on Center for Wave Energy Control based on Metamaterials funded by the NRF under the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning, Korea (No: 2014–063711).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The main idea of this work was first presented at WCSMO10 (May 19–24, 2013, Orlando, Florida, USA) under the title of “Topology Optimization of Phononic Crystals for Self-collimation of Elastic Waves” by the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.H., Ma, P.S. & Kim, Y.Y. Design of phononic crystals for self-collimation of elastic waves using topology optimization method. Struct Multidisc Optim 51, 1199–1209 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-014-1206-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-014-1206-8