Abstract
Purpose
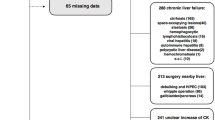
Hypoxic hepatitis (HH) is a frequent cause of acute hepatocellular damage at the intensive care unit. Although mortality is reported to be high, risk factors for mortality in this population are unknown.
Methods
One-hundred and seventeen consecutive patients with HH were studied prospectively at three medical intensive care units of a university hospital.
Results
The main causes of hypoxic hepatitis were low cardiac output and septic shock, and most patients (74%) had more than one underlying factor. Peak aspartate transaminase (P = 0.02), lactate dehydrogenase (P = 0.03), INR (P < 0.001) and lactate (P < 0.01) were higher in non-survivors. Prolonged duration of HH caused higher overall mortality rate (P = 0.03). INR > 2 (P = 0.02), septic shock (P = 0.01) and SOFA score >10 (P = 0.04) were risk factors of mortality in the regression model.
Conclusions
Hypoxic hepatitis is the consequence of multiorgan injury. Outcome is influenced by the severity of liver impairment and the etiology and severity of the basic disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HH:
-
Hypoxic hepatitis
- ICU:
-
Intensive care unit
- AST:
-
Serum aspartate transaminase level
- ALT:
-
Serum alanine transaminase level
- LDH:
-
Lactate dehydrogenase level
- INR:
-
International normalized ratio
- SAPS:
-
Simplified acute physiology score
- SOFA:
-
Sequential organ failure assessment
- IQR:
-
Interquartile range
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
References
Kramer L, Jordan B, Druml W, Bauer P, Metnitz PG (2007) Incidence and prognosis of early hepatic function in critically ill patients—a prospective multicenter study. Crit Care Med 35:1099–1104
Fuhrmann V, Madl C, Mueller C, Holzinger U, Kitzberger R, Funk G, Schenk P (2006) Hepatopulmonary syndrome in patients with hypoxic hepatitis. Gastroenterology 131:69–75
American Gastroenterological Association (2002) American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement: evaluation of liver chemistry tests. Gastroenterology 123:1364–1366
Henrion J, Schapira M, Luwaert R, Colin L, Delannoy A, Heller FR (2003) Hypoxic hepatitis. Clinical and hemodynamic study in 142 consecutive cases. Medicine (Baltimore) 82:392–406
Whitehead MW, Hawkes ND, Hainsworth I, Kingham JG (1999) A prospective study of the causes of notably raised aspartate aminotransferase of liver origin. Gut 45:129–133
Johnson RD, O′Connor C, Kerr RM (1995) Extreme serum elevations of aspartate aminotransferase. Am J Gastroenterol 90:1244–1245
Gibson PR, Dudely F (1984) Ischemic hepatitis: clinical features, diagnosis and prognosis. Aust N Z J Med 14:822–825
Fuchs S, Bogomolski-Yahalom V, Paltiel O, Ackerman Z (1998) Ischemic hepatitis. Clinical and laboratory observations of 34 patients. J Clin Gastroenterol 26:183–186
Birrer R, Takuda Y, Takara T (2007) Hypoxic hepatopathy: pathophysiology and prognosis. Intern Med 46:1063–1070
Seeto RK, Fenn B, Rockey DC (2000) Ischemic hepatitis: clinical presentation and pathogenesis. Am J Med 109:109–113
Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, Peterson E, Tomlanovich M, Early Goal-Directed Therapy Collaborative Group (2001) Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med 345:1368–1377
Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood KE, Light B, Parillo JE, Sharma S, Suppes S, Feinstein D, Zanotti S, Taiberg L, Gurka D, Kumar A, Cheang M (2006) Duration of hypotension prior to initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit Care Med 34:1589–1596
Topalian S, Ginsberg F, Parrillo JE (2008) Cardiogenic shock. Crit Care Med 36(Suppl):S66–S74
Schneeweiss B, Pammer J, Ratheiser K, Schneider B, Madl C, Kramer L, Kranz A, Ferenci P, Druml W, Grimm G (1993) Energy metabolism in acute hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 105:1515–1521
Hickman PE, Potter J (1990) Mortality associated with ischemic hepatitis. Aust N Z J Med 20:32–34
Goldberg RJ, Samad N, Yarzebski J, Gurwitz J, Bigelow C, Gore JM (1999) Temporal trends in cardiogenic shock complicating acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 340:1162–1168
Califf RM, Bengtson J (1994) Cardiogenic shock. N Engl J Med 330:1724–1730
American College of Chest Physicians (Society of Critical Care Medicine Consensus Conference) (1992) Definition of sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Crit Care Med 20:864–874
Van den Berghe G, Wouters P, Weekers F, Verwaest C, Bruyninckx F, Schetz M, Vlasselaers D, Ferdinande P, Lauwers P, Bouillon R (2001) Intensive insulin therapy in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 345:1359–1367
Brunkhorst FM, Engel C, Bloos F, Meier-Hellmann A, Ragaller M, Weiler N, Moerer O, Gruendling M, Oppert M, Grond S, Olthoff D, Jaschinski U, John S, Rossaint R, Welte T, Schaefer M, Kern P, Kuhnt E, Kiehntopf M, Hartog C, Natanson C, Loeffler M, Reinhart K, German Competence Network Sepsis (SepNet) (2008) Intensive insulin therapy and pentastarch resuscitation in severe sepsis. N Engl J Med 358:125–139
Henrion J, Minette P, Colin L, Schapira M, Delannoy A, Heller FR (1999) Hypoxic hepatitis caused by acute exacerbation of chronic respiratory failure: A case-controlled, hemodynamic study of 17 consecutive cases. Hepatology 29:427–433
Malinchoc M, Kamath P, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC (2000) A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology 31:864–871
Polson J, Lee WM, American Association for the Study of Liver disease (2005) AASLD position paper: the management of acute liver failure. Hepatology 41:1179–1197
Peralta C, Perales J, Bartrons R, Mitchell C, Gilgenkrantz H, Xaus C, Prats N, Fernandez N, Gelpi E, Panes J, Rosello-Catafau J (2002) The combination of ischemic preconditioning and liver Bcl-2 over expression is a suitable strategy to prevent liver and lung damage after hepatic ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Pathol 160:2111–2122
Nielsen VG, Tan S, Baird MS, Samuelson PN, McCammon AT, Parks DA (1997) Xanthine oxidase mediates myocardial injury after hepatoenteric ischemia-reperfusion. Crit Care Med 25:1044–1050
Van den Berghe G, Wilmer A, Hermans G, Meersseman W, Wouters PJ, Milants I, Van Wijngaerden E, Bobbaers H, Bouillon R (2006) Intensive insulin therapy in the medical ICU. N Engl J Med 354:449–461
Stravitz RT, Kramer A, Davern T, Shaikh O, Caldwell SH, Mehta RL, Blei AT, Fontana RJ, McGuire BM, Rossaro L, Smith AD, Lee WM, Acute Liver Failure Study Group (2007) Intensive care of patients with acute liver failure: Recommendations of the U.S. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Crit Care Med 35:2498–2508
Dunn G, Hayes P, Breen KJ (1973) The liver in congestive heart failure: a review. Am J Med Sci 265:174–189
Henrion J, Descamps O, Luwaert R, Schapira M, Parfonry A, Heller F (1994) Hypoxic hepatitis in patients with cardiac failure: incidence in a coronary care unit and measurement of hepatic blood flow. J Hepatol 21:696–703
Myers R, Cerini R, Sayegh R, Moreau R, Degott C, Lebrec D, Lee SS (2003) Cardiac hepatopathy: clinical, hemodynamic, and histologic characteristics and correlations. Hepatology 37:393–400
Sakka S, von Hout N (2006) Relation between indocyanine green clearance (ICG) plasma disappearance rate and ICG blood clearance in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 32:766–769
Sakka S, Koeck H, Meier-Hellmann A (2004) Measurement of indocyanine green plasma disappearance rate by two different dosages. Intensive Care Med 30:506–509
Sakka S, Reinhart K, Meier-Hellmann A (2000) Comparison of invasive and noninvasive measurements of indocyanine green plasma disappearance rate in critically ill patients with mechanical ventilation and stable hemodynamics. Intensive Care Med 26:1553–1556
Kneidinger N, Fuhrmann V, Kitzberger R, Warszawska J, Holzinger U, Lindner G, Schenk P, Locker G, Heinz G, Madl C (2007) Intensive Care Med 33(2):0188
Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendoca A, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG (1996) The SOFA (sepsis-related organ assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. Intensive Care Med 22:707–710
Aninat C, Seguin P, Descheemaeker P-N, Morel F, Malledant Y, Guillouzo A (2008) Catecholamines induce an inflammatory response in human hepatocytes. Crit Care Med 36:848–854
Carvalho F, Remiao F, Soares ME, Catarino R, Queiroz G, Bastos ML (1997) d-Amphetamine-induced hepatotoxicity: possible contribution of catecholamines and hyperthermia to the effect studied in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch Toxicol 71:429–436
Acknowledgments
There was no financial support for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was performed at the intensive care units 13H1, 13H3 and 13I2 of the Medical University of Vienna.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuhrmann, V., Kneidinger, N., Herkner, H. et al. Hypoxic hepatitis: underlying conditions and risk factors for mortality in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 35, 1397–1405 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-009-1508-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-009-1508-2