Abstract
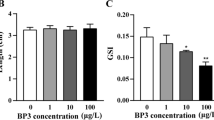
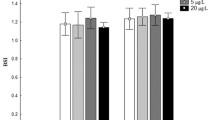
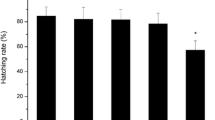
Adult zebrafish pairs were exposed to sub-lethal concentrations of BaCl2 for 21 days, and the effects on reproduction, sex steroid hormones, and transcription of the genes belonging to the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonad (HPG) axis were investigated. The adverse effects on performances of F1 generation were further examined with or without subsequent exposure to BaCl2. Egg production was significantly decreased, and parental exposure to BaCl2 resulted in lesser rates of hatching. In males, exposure to BaCl2 resulted in greater concentrations of E2 along with greater mRNA expression of cyp19a. The results demonstrated that BaCl2 could modulate gene transcriptions and hormone production of the HPG axis in a sex-dependent way, which could cause adverse effects on reproduction and the development of offspring.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjerselius R, Lundstedt-Enkel K, Olsén H, Mayer I, Dimberg K (2001) Male goldfish reproductive behaviour and physiology are severely affected by exogenous exposure to 17β-estradiol. Aquat Toxicol 53:139–152
Cosmetic Ingredient Review (2014) Safety assessment of barium sulfate as used in cosmetics
Devlin RH, Nagahama Y (2002) Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: an overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 208:191–364
Fenske M, Segner H (2004) Aromatase modulation alters gonadal differentiation in developing zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 67:105–126
Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) (2014) http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/. Accessed 16 Jun 2014
Hutchinson TH, Ankley GI, Segner H, Tyler CR (2006) Screening and testing for endocrine disruption in fish-biomarkers as “signposts”, not “traffic lights”, in risk assessment. Environ Health Perspect 114:106–114
Ji K, Liu X, Lee S, Kang S, Kho Y, Giesy JP, Choi K (2013) Effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on hormones and genes of the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonad axis, and reproduction of zebrafish. J Hazard Mater 254–255:242–251
Kang IJ, Yokata H, Oshima Y, Tsuruda Y, Hano T, Maeda M, Imada N, Tadokoro H, Honjo T (2003) Effects of 4-nonylphenol on reproduction of Japanese medaka, Oryzias latipes. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2438–2445
Kinnberg K, Korsgaard B, Bjerregaard P, Jespersen AS (2000) Effects of nonylphenol and 17β-estradiol on vitellogenin synthesis and testis morphology in male platyfish Xiphophorus maculates. J Exp Biol 203:171–181
Korea Consumer Agency (2013) Children’s face paint found to be toxic. http://www.kca.go.kr/brd/m_32/view.do?seq=1428&multi_itm_seq=8. Accessed 02 Jun 2015
Liu X, Ji K, Jo A, Moon HB, Choi K (2013) Effects of TDCPP or TPP on gene transcriptions and hormones of HPG axis, and their consequences on reproduction in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquat Toxicol 134–135:104–111
Ma Y, Han J, Guo Y, Lam PKS, Wu RSS, Giesy JP, Zhang X, Zhou B (2012) Disruption of endocrine function in in vitro H295R cell-based and in in vivo assay in zebrafish by 2,4-dichlorophenol. Aquat Toxicol 106–107:173–181
Miles-Richardson SR, Pierens SL, Nichols KM, Kramer VJ, Snyder SA, Render JA, Fitzgerald SD, Giesy JP (1999) Effects of waterborne exposure to 4-nonylphenol and nonylphenol ethoxylate on secondary sex characteristics and gonads of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Environ Res 80:S122–S137
Nagahama Y, Yamashita M (2008) Regulation of oocyte maturation in fish. Dev Growth Differ 50:S195–S219
OECD (2009) OECD guideline for testing of chemicals, test no. 229: fish short term reproduction assay. Paris, France
Sofikitis N, Giotitsas N, Tsounapi P, Baltogiannis D, Giannakis D, Pardalidis N (2008) Hormonal regulation of spermatogenesis and spermiogenesis. Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 109:323–330
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF; Project No. 2013R1A1A1061684).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, B., Ha, N., Jung, J. et al. Effects of Barium Chloride Exposure on Hormones and Genes of the Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonad Axis, and Reproduction of Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96, 341–346 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1731-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1731-9