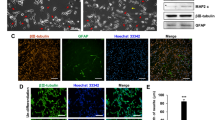
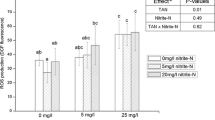
Abstract
In this study, extracellular polymeric substances of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae (EPS-A) were investigated in order to explore their effect on astrocytes of zebrafish and potential risk for environment. Astrocytes were treated with varying concentrations of EPS-A, the results showed that EPS-A inhibited astrocytes growth in a dose-and time-dependent manner. With the concentrations of EPS-A increasing, the adherent ability of astrocytes decreased and the number of astrocytes floating in the culture medium increased. When treated with 2.35 µg/mL EPS-A, EPS-A induced cell cycle arrest and made the collapse of mitochondrial membrane potential and then led to astrocytes apoptosis. The results suggested that EPS-A could pose a threat to zebrafish and represent risk for environment, so regularly monitoring the presence of EPS-A was very important in nutrient-rich freshwaters when A. flos-aquae blooms broke out.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Challouf R, Trabelsi L, Ben Dhieb R, El Abed O, Yahia A, Ghozzi K, Ben Ammar J, Omran H, Ben Ouada H (2011) Evaluation of cytotoxicity and biological activities in extracellular polysaccharides released by cyanobacterium Arthrospira platensis. Braz Arch Biol Technol 54:831–838
Chorus I, Bartram J (1999) Toxic cyanobacteria in water: a guide to their public health consequences, monitoring and management. Spon Press, London
Farina C, Aloisi F, Meinl E (2007) Astrocytes are active players in cerebral innate immunity. Trends Immunol 28:138–145. doi:10.1016/j.it.2007.01.005
Gavrilović BR, Despotović SG, Gavrić JP, Borković-Mitić SS, Ognjanović BI, Pavlović SZ, Saičić ZS (2014) Changes in antioxidant enzyme activities in the livers and gills of three cyprinids after exposure to a cyanobacterial bloom in the Gruža Reservoir, Serbia. Ecol Ind 38:141–148
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Hindawi PC (2014) Assessment of morphology, activity, and infiltration of astrocytes on marine EPS-imbedded electrospun PCL nanofiber. J Nanomater 11:713–723
Hou R, Zhou QL, Wang BX, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T (2004) Diosgenin induces apoptosis in HeLa cells via activation of caspase pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25:1077–1082
Hu C, Liu Y, Paulsen BS, Petersen D, Klaveness D (2003) Extracellular carbohydrate polymers from five desert soil algae with different cohesion in the stabilization of fine sand grain. Carbohydr Polym 54:33–42
Kist LW, Fritsch RS, Yunes JS, Bonan CD, Bogo MR (2012) Microcystin-LR acute exposure does not alter in vitro and in vivo ATP, ADP and AMP hydrolysis in adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) brain membranes. J Xenobiot 2:e9
Lemasters JJ, Nieminen AL, Qian T, Trost LC, Elmore SP, Nishimura Y, Crowe RA, Cascio WE, Bradham CA, Brenner DA, Herman B (1998) The mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death: a common mechanism in necrosis, apoptosis and autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1366:177–196
Ma S, Shan LQ, Xiao YH, Li F, Huang L, Shen L, Chen JH (2011) The cytotoxicity of methacryloxylethyl cetyl ammonium chloride, a cationic antibacterial monomer, is related to oxidative stress and the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res 44:1125–1133
Miura T, Sano D, Suenaga A, Yoshimura T, Fuzawa M, Nakagomi T, Nakagomi O, Okabe S (2013) Histo-blood group antigen-like substances of human enteric bacteria as specific adsorbents for human noroviruses. J Virol 87:9441–9451. doi:10.1128/JVI.01060-13
Park HS, Hwang HJ, Kim GY, Cha HJ, Kim WJ, Kim ND, Yoo YH, Choi YH (2013) Induction of apoptosis by fucoidan in human leukemia U937 cells through activation of p38 MAPK and modulation of Bcl-2 family. Mar Drugs 11:2347–2364. doi:10.3390/md11072347
Vermeiren C, Najimi M, Maloteaux JM, Hermans E (2005) Molecular and functional characterisation of glutamate transporters in rat cortical astrocytes exposed to a defined combination of growth factors during in vitro differentiation. Neurochem Int 46:137–147. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2004.08.004
Xu H, Yu G, Jiang H (2013) Investigation on extracellular polymeric substances from mucilaginous cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic freshwater lakes. Chemosphere 93:75–81. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.04.077
Xue X, Lv Y, Liu Q, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Zhang L, Xu S (2015) Extracellular polymeric substance from Aphanizomenon flos-aquae induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway in A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells. Exp Ther Med 10:927–932. doi:10.3892/etm.2015.2644
Yang L, Wang P, Wang H, Li Q, Teng H, Liu Z, Yang W, Hou L, Zou X (2013) Fucoidan derived from Undaria pinnatifida induces apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells via the ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Mar Drugs 11:1961–1976. doi:10.3390/md11061961
Zanchett G, Oliveira-Filho EC (2013) Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins: from impacts on aquatic ecosystems and human health to anticarcinogenic effects. Toxins (Basel) 5:1896–1917. doi:10.3390/toxins5101896
Zhang X, Chen W, Guillermo R, Chandrasekher G, Kaushik RS, Young A, Fahmy H, Dwivedi C (2010) Alpha-santalol, a chemopreventive agent against skin cancer, causes G2/M cell cycle arrest in both p53-mutated human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells and p53 wild-type human melanoma UACC-62 cells. BMC Res Notes 3:220. doi:10.1186/1756-0500-3-220
Zhang D, Hu C, Wang G, Li D, Li G, Liu Y (2013a) Zebrafish neurotoxicity from aphantoxins–cyanobacterial paralytic shellfish poisons (PSPs) from Aphanizomenon flos-aquae DC-1. Environ Toxicol 28:239–254. doi:10.1002/tox.20714
Zhang D, Hu C, Wang G, Li D, Li G, Liu Y (2013b) Zebrafish neurotoxicity from aphantoxins–cyanobacterial paralytic shellfish poisons (PSPs) from Aphanizomenon flos-aquae DC-1. Environ Toxicol 28:239–254. doi:10.1002/tox.20714
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT0966) and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31560234).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Y., Xue, X., Tao, L. et al. Extracellular Polymeric Substances of Aphanizomenon flos-aquae (EPS-A) Induced Apoptosis in Astrocytes of Zebrafish. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96, 320–325 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1729-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1729-3