Abstract
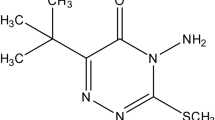
Persistence and dissipation of quinalphos residues in/on cauliflower was studied after giving spray applications at 2 concentrations, i.e. recommended dose of 500 g a.i. ha−1 and double the recommended dose of 1,000 g a.i. ha−1. Residue analysis of cauliflower curds was carried out after the third spray over a period of 15 days. Initial residues of quinalphos on cauliflower from the two treatments were 1.19 and 1.842 mg kg−1. The residues persisted up to 15 days from both the treatments. The residues of quinalphos dissipated from both treatments with the half-life of 4.8 and 5.3 days. Based on the persistence study and maximum residue limit value of 0.05 mg kg−1 the safe pre-harvest interval was worked out as 17 and 22 days from treatment at the recommended and double the recommended dose, respectively. Analysis of soil samples was carried out on the 15th day of sampling and residues were found to be 0.013 and 0.044 mg kg−1.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aktar MW, Sengupta D, Chowdhury A (2008) Degradation dynamics and persistence of quinalphos and methomyl in/on okra (Ablemoschus esculentus) fruits and cropped soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:74–77
Aktar MW, Sengupta D, Purkait S, Chowdhury A (2010) Risk assessment and decontamination of quinalphos under different culinary processes in/on cabbage. Environ Monit Assess 163(1–4):369–377
Bhanti M, Taneia A (2007) Contamination of vegetables of different seasons with organophosphorous pesticides and related health risk assessment in Northern India. Chemosphere 69(1):63–68
Boriss H, Brunke H, Kreith M (2006) Commodity profile: cauliflower agricultural issue centre. University of California, USA
Gupta YC, Kauntey RPS (2007) Efficacy of some insecticides against brinjal shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee. Proc Zool Soc India 6(2):31–38
Hoskins WM (1961) Mathematical treatment of loss of pesticide residues. Plant Protec Bull (FAO) 9:163–168
Kabir KH, Rahman MA, Ahmed MS, Prodhan MDH, Akon MW (2008) Determination of residue of diazinon and carbosulfan in brinjal and quinalphos in yard long bean under supervised field trial. Bangladesh J Agric Res 33(3):503–513
Kumar GVS, Sannaveerappanavar VT (2004) Evaluation of bio-efficacy of insecticide and seed oil combinations against Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae) on cabbage. Mysore J Agric Sci 38(3):302–305
Mohan M, Gujar GT (2003) Local variation in susceptibility of diamond back moth to insecticides and role of detoxification enzymes. J Crop Protec 22:495–504
Ramzan M, Singh D (1980) Chemical control of the tobacco caterpillar, Spodoptera litura Fabr. on cauliflower. J Res Punjab Agric Univ India 17(2):236–239
Sengupta D, Aktar MW, Purkait S, Ganguly M (2009) Impact of quinalphos on microbial biomass and activities in tropical clay loam soil. Electron J Environ Agric Food Chem 8(11):1127–1135
Suvardhan K, Kumar SK, Chiranjeevi P (2005) Extractive spectrofluorometric determination of quinalphos using fluorescein in environmental samples. Environ Monit Asses 108:217–227
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Director, I.I.H.R., Bangalore for providing the required facilities and ICAR, New Delhi for providing funds for carrying out the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohapatra, S., Deepa, M. Persistence and Dissipation of Quinalphos in/on Cauliflower and Soil Under the Semi Arid Climatic Conditions of Karnataka, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90, 489–493 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0937-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0937-8