Abstract
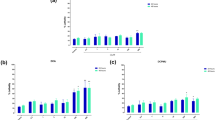
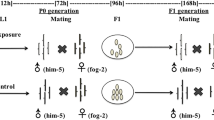
The effects of acetochlor on the mortality, growth and reproduction of two nematode species were assessed. The LC50 values for Caenorhabditis elegans and Pristionchus pacificus were 1,296 and 210.7 mg/L at 24 h, and 540.0 and 126.4 mg/L at 48 h exposure, respectively. In three succession generations, reproductive capacity was more sensitive in P. pacificus than in C. elegans. Moreover, the sublethal test endpoint of final length was more sensitive with P. pacificus. This study suggested that acetochlor had no long-term effects on C. elegans at lower concentrations. The higher concentrations of acetochlor (from 40 to 160 mg/L) revealed sublethal toxicity to the two tested species, with P. pacificus being more sensitive than C. elegans.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boyd WA, Williams PL (2003) Comparison of the sensitivity of three nematode species to copper and their utility in aquatic and soil toxicity tests. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2768–2774
Brenner SJ (1974) The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 77:71–94
Calabrese EJ, Baldwin LA (2003) The hormetic dose-response model is more common than the threshold model in toxicology. Toxicol Sci 71:246–250
Frantzios G, Paptsiki K, Sidiropoulou B, Lazaridis I, Theophilidis G, Mavragani-Tsipidou P (2008) Evaluation of insecticidal and genotoxic effects of imidacloprid and acetochlor in Drosophila melanogaster. J Appl Entomol 132:583–590
Kammenga JE, Riksen JAG (1996) Comparing differences in species sensitivity to toxicants: Phenotypic plasticity versus concentration-response relationships. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1649–1653
Lengyel Z, Földényi R (2003) Acetochlor as a soil pollutant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 10:13–18
Michalski AI, Johson TE, Cypser JR, Yashin AI (2001) Heating stress patterns in Caenorhabditis elegans longevity and survivorship. Biogerontology 2:35–44
Rajini PS, Melstrom P, Williams PL (2008) A comparative study on the relationship between various toxicological endpoints in Caenorhabditis elegans exposed to organophosphorus insecticides. J Toxicol Environ Health 71:1043–1050
Wang H, Wick RL, Xing B (2009) Toxicity of nanoparticulate and bulk ZnO, Al2O3 and TiO2 to the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Pollut 157:1171–1177
Williams PL, Dusenbery DB (1990) Aquatic toxicology testing using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Toxicol Chem 9:1285–1290
Xiao NW, Jing BB, Ge F, Liu XH (2006) The fate of herbicide acetochlor and its toxicity to Eisenia fetida under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 62:1366–1373
Ye C (2003) Environmental behavior of the herbicide acetochlor in soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 71:919–923
Zhang JN, Li Q, Liang WJ (2010) Effect of acetochlor and carbofuran on soil nematode communities in a Chinese soybean field. Afr J Agric Res 5:2787–2794
Zhou QX, Zhang QR, Liang JD (2006) Toxic effects of acetochlor and methamidophos on earthworm Eisenia fetida in phaiozem, northeast China. J Environ Sci-China 18:741–745
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Science and Technology Project of Liaoning Province (No. 2009403053) and the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Project No. KZCX2-YW-QN403).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Liang, W., Wu, X. et al. Toxic Effects of Acetochlor on Mortality, Reproduction and Growth of Caenorhabditis elegans and Pristionchus pacificus . Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90, 364–368 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0915-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0915-1