Abstract
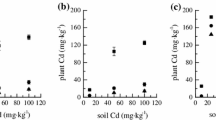
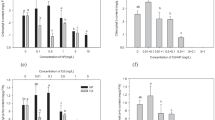
The effects of Cd and HCHs with single and combined forms on Cd and HCHs phytoavailability of Allium sativum L. were investigated. The results indicated that the coexistence of Cd and HCHs presented antagonistic interactions mostly, which might be partly due to the formation of Cd–HCHs complex, compared with single stress. The bioaccumulation of Cd and HCHs in plants depended largely on their concentrations applied in pot soils, and the phytoavailability of HCH isomers was in the sequence: δ- > γ- ≥ β- > α-HCH.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abhilash PC, Jamila S, Singh V, Singh A, Singh N, Srivastava SC (2008) Occurrence and distribution of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers in vegetation samples from a contaminated area. Chemosphere 72(1):79–86
Binet P, Portal JM, Leyval C (2000) Fate of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) in the rhizosphere and mycorrhizosphere of ryegrass. Plant Soil 227(1–2):207–213
Calvelo Pereira R, Camps-Arbestain M, Rodriguez Garrido B, Macias F, Monterroso C (2006) Behaviour of alpha-, beta-, gamma-, and delta-hexachlorocyclohexane in the soil-plant system of a contaminated site. Environ Pollut 144(1):210–217
European Commission (2006) Maximum levels of contaminants in foods. Heavy metals, vol 1881/2006. European Commission
Gao F, Jia JY, Wang XM (2008) Occurrence and ordination of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and hexachlorocyclohexane in agricultural soils from Guangzhou. Ch Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 54(2):155–166
Gong ZM, Xu FL, Dawson R, Cao J, Liu WX, Li BG, Shen WR, Zhang WJ, Qin BP, Sun R, Tao S (2004) Residues of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers and their distribution characteristics in soils in the Tianjin area. Ch Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46(4):432–437
Haugen JE, Wania F, Ritter N, Schlabach M (1998) Hexachlorocyclohexanes in air in southern Norway. Temporal variation, source allocation, and temperature dependence. Environ Sci Technol 32(2):217–224
Jiang YN, Feng BM, Zhang HY, Ma M (2005) Improving heavy metal tolerance of yeast by transferring a phytochelatin synthase gene from garlic. Acta Phytoecol Sin 29(4):659–664
Li BG, Cao J, Liu WX, Shen WR, Wang XJ, Tao S (2006) Geostatistical analysis and kriging of hexachlorocyclohexane residues in topsoil from Tianjin. Ch Environ Pollut 142(3):567–575
Lin AJ, Zhu YG, Tong YP, Geng CN (2005) Evaluation of genotoxicity of combined pollution by cadmium and atrazine. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 74(3):589–596
Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China (2005) Maximum levels of contaminants in foods. In GB 2762-2005. Chinese Standard Publish Company, Beijing, p 1
Pereira RC, Monterroso C, Macias F, Camps-Arbestain M (2008) Distribution pathways of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers in a soil-plant-air system. A case study with Cynara scolymus L. and Erica sp. plants grown in a contaminated site. Environ Pollut 155(2):350–358
Shi Y, Meng F, Guo F, Lu Y, Wang T, Zhang H (2005) Residues of organic chlorinated pesticides in agricultural soils of Beijing. Ch Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 49(1):37–44
Su YH, Zhu YG (2008) Uptake of selected PAHs from contaminated soils by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa) and influence of rhizosphere on PAH distribution. Environ Pollut 155(2):359–365
Tao S, Xu FL, Wang XJ, Liu WX, Gong ZM, Fang JY, Zhu LZ, Luo YM (2005) Organochlorine pesticides in agricultural soil and vegetables from Tianjin. Ch Environ Sci Technol 39(8):2494–2499
Wieczorek JK, Wieczorek ZJ (2007) Phytotoxicity and accumulation of anthracene applied to the foliage and sandy substrate in lettuce and radish plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 66(3):369–377
Wu Q, Yang J, Zhang J, Jiang H, Hou Y (2007) Effects of cadmium and bensulfur on methyl co-contamination on some biological characteristics of rice. J Agro-Environ Sci 26(5):1789–1796
Wu D, Zhang T, Liu S, Wan H, Hou M (2009) Pollution characteristics of organochlorinated pesticides in the soils of vegetable fields in typical area of Pearl River Delta: a case study of Dongguan. Eco Environ Sci 18(4):1261–1265
Yin X, Sun L, Pan C (2004) Bioaccumulation of HCHs and DDT in antarctic tundra plant-soil system. Prog Nat Sci 14(7):822–825
Zhang HY, Jiang YN, He ZY, Ma M (2005) Cadmium accumulation and oxidative burst in garlic (Allium sativum). J Plant Physiol 162(9):977–984
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Ministry of Land and Resources’ Special Funds for Scientific Research on Public Benefit(No.201011006-1)and the National Key Basic Research and Development (973) Program of China (Grant No. 2007CB407302). In addition, we thank the participating institutes, as well as the anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments regarding the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Zhao, Y., Guo, T. et al. Accumulation and Phytoavailability of Hexachlorocyclohexane Isomers and Cadmium in Allium sativum L. Under the Stress of Hexachlorocyclohexane and Cadmium. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 90, 182–187 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0882-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0882-6