Abstract
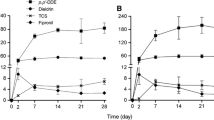
We assessed chronic effects of fipronil and metabolite contaminated sediments from non-vegetated and Thallia dealbata vegetated wetland microcosms on Hyalella azteca during wet and dry exposures. Mean sediment concentrations (ng g−1) ranged from 0.72–1.26, 0.01–0.69, 0.07–0.23, and 0.49–7.87 for fipronil, fipronil-sulfide, fipronil-sulfone, and fipronil-desulfinyl, respectively. No significant differences in animal survival or growth were observed between non-vegetated and vegetated microcosms during wet or dry exposures. Mean animal body residue concentrations (ng g−1) ranged from 28.4–77.6, 0–30.7, and 8.3–43.8 for fipronil, fipronil-sulfide, and fipronil-sulfone. Fipronil-desulfinyl was not detected in any animal samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Bennett ER, Moore MT, Cooper CM, Smith S (2000) Method for the simultaneous extraction and analysis of two current use pesticides, atrazine and lambda-cyhalothrin, in sediment and aquatic plants. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 64:825–833. doi:10.1007/s001280000077
Biever RC, Hoberg JR, Jacobsen B, Dionne E, Sulaiman M, McCahon P (2003) ICON® rice seed treatment toxicity to crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) in experimental rice paddies. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:167–174. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2003)022<0167:IRSTTT>2.0.CO;2
Chaton PF, Ravanel P, Tissut M, Meyran JC (2002) Toxicity and bioaccumulation of fipronil in the nontarget arthropodan fauna associated with subalpine mosquito breeding sites. Ecotox Environ Saf 52:8–12. doi:10.1006/eesa.2002.2166
Deaver E, Rodgers JH Jr (1996) Measuring bioavailable copper using anodic stripping voltammetry. Environ Toxicol Chem 15:1925–1930. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1996)015<1925:MBCUAS>2.3.CO;2
de March BGE (1981) Hyalella azteca (Saussure). In: Lawrence SG (ed) Manual for the culture of selected freshwater invertebrates. Can Spec Publ Fish Aquat Sci 54:61–77
Gunasekara AS, Truong T, Goh KS, Spurlock F, Tjeerdema RS (2007) Environmental fate and toxicology of fipronil. J Pest Sci 32:189–199. doi:10.1584/jpestics.R07-02
Knight SS, Lizotte RE Jr, Smith S Jr, Bryant CT (2007) Distribution and spatial variation in surface sediment pesticides of Mississippi alluvial plain. J Int Environmental Application & Science 2:40–50
Kröger R, Moore MT (2008) Utilization of common ditch vegetation in the reduction of fipronil and its sulfone metabolite. Pest Manag Sci. doi:10.1002/ps.1619
Lin K, Haver D, Oki L, Gan J (2008) Transformation and sorption of fipronil in urban stream sediments. J Agric Food Chem. doi:10.1021/jf8018886
Maul JD, Brennan AA, Harwood AD, Lydy MJ (2008) Effect of sediment associated pyrethroids, fipronil, and metabolites on Chironomus tentans growth rate, body mass, condition index, immobilization, and survival. Environ Toxicol Chem. doi:10.1897/08-185.1
Smith S, Lizotte RE, Knight SS (2007) Pesticide body residues of Hyalella azteca exposed to Mississippi delta sediments. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 78:26–29. doi:10.1007/s00128-007-9020-2
Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), Inc. (1997) SigmaStat for windows version 2.03. SPSS, Chicago
US Department of Agriculture (USDA) National Agricultural Statistical Service (NASS) (2008) Agricultural chemical use database. http://www.pestmanagment.info/nass/
US Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (1994) Methods for measuring the toxicity and bioaccumulation of sediment-associated contaminants with freshwater invertebrates. EPA 600/R-94/024. US Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Acknowledgments
Appreciation is extended to J. Renee Russell, Lisa Brooks, Dan McChesney, and Sam Testa for sample collection and analytical assistance. Mention of equipment, software or a pesticide does not constitute an endorsement for use by the US Department of Agriculture nor does it imply pesticide registration under FIFRA as amended. All programs and services of the USDA are offered on a nondiscriminatory basis without regard to race, color, national origin, religion, sex, marital status, or handicap.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kröger, R., Lizotte, R.E. & Moore, M.T. Survival, Growth, and Body Residues of Hyalella azteca (Saussure) Exposed to Fipronil Contaminated Sediments from Non-Vegetated and Vegetated Microcosms. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83, 369–373 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9759-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9759-8