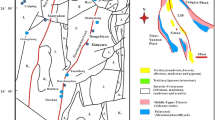
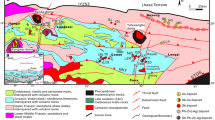
Abstract
Analyses of sphalerite minerals from the characteristic brecciated Zn–Pb ores of the main ore body in the giant Dongshengmiao deposit have revealed variations in δ66Zn from 0.17 to 0.40‰ and in δ56Fe from −1.78 to −0.35‰. Further, the investigated pyrrhotite samples have iron that is isotopically similar to that of associated sphalerite minerals. The most distinctive pattern revealed by the zinc and iron isotope data is the lateral trend of increasing δ66Zn and δ56Fe values from southwest to northeast within the main ore body. The lead isotopic homogeneity of ore sulfides from the main ore body suggests that there is only one significant source for metal, thus precluding the mixing of multiple metal sources as the key factor controlling spatial variations of zinc and iron isotopes. The most likely control on spatial variations is Rayleigh fractionation during hydrothermal fluid flow, with lighter Zn and Fe isotopes preferentially incorporated into the earliest sulfides to precipitate from fluids. Precipitations of sphalerite and pyrrhotite have played vital roles in the Zn and Fe isotopic variations, respectively, of the ore-forming system. Accordingly, the larger isotopic variability for Fe than Zn within the same hydrothermal system perhaps resulted from a larger proportion of precipitation for pyrrhotite than for sphalerite. The lateral trend pattern revealed by the zinc and iron isotope data is consistent with the occurrence of a cystic-shaped breccia zone, which is characterized by marked elevation in Cu. The results further confirm that Zn and Fe isotopes can be used as a vectoring tool for mineral prospecting.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albarède F (2004) The stable isotope geochemistry of copper and zinc. Rev Mineral Geochem 55:409–427
Archer C, Vance D (2002) Large fractionations in Fe, Cu, and Zn isotopes associated with Archean mircrobially-mediated sulfides. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66(15):26
Archer C, Vance D, Butler IB (2004) Abiotic Zn isotope fractionations associated with ZnS precipitation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:A325
Butler IB, Archer C, Vance D, Oldroyd A, Rickard D (2005) Fe isotope fractionation on FeS formation in ambient aqueous solution. Earth Planet Sci Lett 236(1–2):430–442
Dekov VM, Cuadros J, Kamenov GD, Weiss D, Arnold T, Basak C, Rochette P (2010) Metalliferous sediments from the HMS challenger voyage (1872–1876). Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74(17):5019–5038
Ding TP, Jiang SY (2000) Stable isotope study of the Langshan polymetallic mineral district, Inner Mongolia, China. Resour Geol 50:25–38
Duan JL, Tang JX, Li YB, Liu SA, Wang Q, Yang C, Wang YY (2016a) Copper isotopic signature of the Tiegelongnan high-sulfidation copper deposit, Tibet: implications for its origin and mineral exploration. Mineral Deposita 51:591–602
Duan JL, Tang JX, Lin B (2016b) Zinc and lead isotope signatures of the Zhaxikang Pb-Zn deposit, South Tibet: implications for the source of the ore-forming metals. Ore Geol Rev 78:58–68
Gagnevin D, Boyce AJ, Barrie CD, Menuge JF, Blakeman RJ (2012) Zn, Fe and S isotope fractionation in a large hydrothermal system. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 88:183–198
Guilbaud R, Butler IB, Ellam RM, Rickard D (2010) Fe isotope exchange between Fe(II)(aq) and nanoparticulate mackinawite (FeSm) during nanoparticle growth. Earth Planet Sci Lett 300(1–2):174–183
Hu CS, Li WB, Xu C, Zhong RC, Zhu F, Qiao XY (2015) Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Permian granitoids in the northwestern margin of the North China craton: insights from the Dongshengmiao pluton, Inner Mongolia. Int Geol Rev 57(14):1843–1860
Jiang XQ (1993) Geological characteristics of the Dongshengmiao pyrite-polymetallic sulfide deposit, Inner Mongolia. China Academic Journal Electronic Publishing House 27(28):103–115
Jiang XQ (1994) Evidence for contemporaneous faults in the Dongshengmiao sulfide polymetallic ore district in Inner Mongolia and the genesis of the ore deposit. Mineral Deposits 13:49–60
John SG, Rouxel OJ, Craddock PR, Engwall AM, Boyle EA (2008) Zinc stable isotopes in seafloor hydrothermal vent fluids and chimneys. Earth Planet Sci Lett 269:17–28
Johnson CM, Beard BL, Roden EE, Newman DK, Nealson KH (2004) Isotopic constraints on biogeochemical cycling of Fe. In: Johnson CM, Beard BL, Albarède F (eds) Geochemistry of Non-Traditional Stable Isotopes 359–408. Rev Mineral Geochem 55 Mineralogical Society of America and Geochemical Society, Washington, DC
Kelley KD, Wilkinson JJ, Chapman JB, Crowther HL, Weiss DJ (2009) Zinc isotopes in sphalerite from base metal deposits on the red dog district, northern Alaska. Econ Geol 104:767–773
Li JJ, Zhai YS, Sang HQ, Li HM, Zhang YS, Liu SY, Wang SG, Sun ZP, Liu XX (2010b) Metallogenic epoch of the Oubulage copper-gold deposit in the Alax area, Inner Mongolia autonomous region. Bull Mineral Petrol Geochem 29:323–327
Li JJ, Zhai YS, Yang YQ, Wang YB, Li CD, Cui LW, Zhou HY, Liu XY, Liu XX, Li S (2010c) Re-discussion on the metallogenic age of Zhulazhaga gold deposit in the Alax area, Inner Mongolia: evidence from zircon U-Pb SHRIMP age. Earth Science Frontiers 17:178–184
Li QL, Chen FK, Guo JH, Li XH, Yang YH, Siebel W (2007) Zircon ages and Nd-Hf isotopic composition of the Zhaertai group (Inner Mongolia): evidence for early Proterozoic evolution of the northern North China craton. J Asian Earth Sci 30:573–590
Li SZ, Zhu XK, Tang SH, He XX, Cai JJ (2008) The application of MC-ICP-MS to high-precision measurement of Zn isotope ratios. Acta Petrol Mineral 27:273–278
Li WQ, Jackson SE, Pearson NJ, Graham S (2010a) Copper isotopic zonation in the Northparkes porphyry Cu-Au deposit, SE Australia. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74(14):4078–4096
Li ZL, Xu WD, Pang WZ (1986) S, Pb, C and O isotopic compositions and ore genesis of the stratabound polymetallic sulfide deposits in middle Inner Mongolia, China. Geochimica 1:13–22
Long LZ (2009) Geological characteristics and genesis analysis of the Dongshengmiao lead-zinc ore deposit in the Inner Mongolia. Central South University, Dissertation
Maréchal CN, Télouk P, Albarède F (1999) Precise analysis of copper and zinc isotopic compositions by plasma–source mass spectrometry. Chem Geol 156:251–273
Markl G, Von Blanckenburg F, Wagner T (2006) Iron isotope fractionation during hydrothermal ore deposition and alteration. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:3011–3030
Mason TFD, Weiss DJ, Chapman JB, Wilkinson JJ, Tessalina SG, Spiro B, Horstwood MSA, Spratt J, Coles BJ (2005) Zn and Cu isotopic variability in the Alexandrinka volcanic-hosted massive sulfide (VHMS) ore deposit, Urals, Russia. Chem Geol 221:170–187
Mason TFD, Weiss DJ, Horstwood M, Parrish RR, Russell SS, Mullance E, Coles JB (2004a) High–precision Cu and Zn isotope analysis by plasma source mass spectrometry: part 1 spectral interferences and their correction. J Anal Atom Spectrom 19:209–217
Mason TFD, Weiss DJ, Horstwood M, Parrish RR, Russell SS, Mullance E, Coles JB (2004b) High-precision Cu and Zn isotope analysis by plasma source mass spectrometry: part 2 correction for mass discrimination effects. J Anal Atom Spectrom 19:218–226
Mathur R, Dendas M, Titley S, Philips A (2010) Patterns in the copper isotope composition of minerals in porphyry copper deposits in southwestern United States. Econ Geol 105:1457–1467
Mathur R, Munk L, Nguyen M, Gregory M, Annell H, Lang J (2013) Modern and paleofluid pathways revealed by Cu isotope compositions in surface waters and ores of the pebble porphyry Cu-Au-Mo deposit, Alaska. Econ Geol 108:529–541
Mathur R, Titley S, Barra F, Brantley S, Wilson M, Phillips A, Munizaga F, Maksaev V, Vervoort J, Hart G (2009) Exploration potential of Cu isotope fractionation in porphyry copper deposits. J Geochem Explor 102:1–6
Peng RM, Zhai YS (1997) The confirmation of the metamorphic double-peaking volcanic rocks in Langshan Group of the Dongshengmiao ore district, Inner Mongolia and its significance. Earth Sci J China Univ Geosci 22:589–594
Peng RM, Zhai YS (2004) The characteristics of hydrothermal exhalative mineralization of the Langshan–Zhaertai belt, Inner Mongolia. China Earth Science Frontiers 11:257–268
Peng RM, Zhai YS, Han XF, Wang JP, Wang ZG, Qin JW (2007) Magmatic hydrothermal overprinting in the Mesoproterozoic Dongshengmiao deposit, Inner Mongolia: geological and fluid inclusion evidences. Acta Petrol Sin 23:145–152
Peng RM, Zhai YS, Wang ZG (2000) Ore-controlling synchronous faults of Mesoproterozoic Dongshengmiao and Jiashengpan SEDEX-type ore deposits, Inner Mongolia. Earth Science, Journal of China University of Geosciences 4:404–410
Peng RM, Zhai YS, Wang ZG, Han XF, Qin JW, Wang JP, Mei JM (2006) Characteristics and exploration of submarine sedex deposits in the Langshan-Zhaertai ore concentration area, Inner Mongolia. Mineral Deposits 25:221–224
Pi QH, Zhong RC, Hu RZ (2015) Tracing the ore-formation history of the shear-zone-controlled Huogeqi Cu-Pb-Zn deposit in Inner Mongolia, northern China, using H, O, S, and Fe isotopes. Ore Geol Rev 71:263–272
Rui ZY, Shi LD, Fang RH (1994) Geology of nonferrous metallic deposits in the northern margin of the North China landmass and its adjacent area. Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Sun J, Zhu XK, Chen YL, Fang N (2013) Iron isotopic constraints on the genesis of Bayan obo ore deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Precambrian Res 235:88–106
Tang SH, Zhu XK, Cai JJ, Li SZ, He XX, Wang JH (2006) Chromatographic separation of Cu, Fe and Zn using AGMP–1 anion exchange resin for isotope determination by MC–ICP–MS. Rock and Mineral Analysis 25:5–8
Teng FZ (2017) Magnesium isotope geochemistry. Rev Mineral Geochem 82:219–287
Wang Y, Zhu XK, Cheng YB (2015) Fe isotope behaviours during sulfide-dominated skarn-type mineralization. J Asian Earth Sci 103:374–392
Wang Y, Zhu XK, Mao JW, Li ZH, Cheng YB (2011) Iron isotope fractionation during skarn-type metallogeny: a case study of Xinqiao Cu-S-Fe-Au deposit in the middle-lower Yangtze valley. Ore Geol Rev 43:194–202
Wilkinson JJ, Weiss DJ, Mason TFD, Coles BJ (2005) Zinc isotope variation in hydrothermal systems: preliminary evidence from the Irish midlands ore field. Econ Geol 100:583–590
Wilkinson JJ (2014) Sediment-hosted zinc-lead mineralization: processes and perspectives. In: Scott SD (ed) Treatise on geochemistry 2nd ed. Elsevier 13: Geochemistry of Mineral Deposits:219–249
Xia XH (1992) Ore-forming characteristics and genetic discussion of the Dongshengmiao polymetallic pyrite deposits in the Langshan metallogenic belt, Inner Mongolia. Mineral Deposits 11:374–383
Xia XH, Zhao X (1990) Origin of brecciated-type ores of the Dongshengmiao polymetallic sulfide deposit, Inner Mongolia. Geology and Prospecting 26(7):30–41
Xiu SY (1987) Origin of the Tanyaokou-Dongshengmiao polymetallic sulfide deposits. Geology of Chemical Minerals 02:1–12
Zhai YS, Peng RM, Chen CX, Cai KQ, Deng J, Chen XM, Cheng XJ, Wang JP (2008) Genesis and structure of major metallogenic series of China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Zhao XM, Zhang HF, Zhu XK, Tang SH, Yan B (2012) Iron isotope evidence for multistage melt-peridotite interactions in the lithospheric mantle of eastern China. Chem Geol 292–293:127–139
Zhong RC, Li WB (2016) The multistage genesis of the giant Dongshengmiao Zn-Pb-Cu deposit in western Inner Mongolia, China: syngenetic stratabound mineralization and metamorphic remobilization. Geosci Front 7(3):529–542
Zhong RC, Li WB, Chen YJ, Huo HL (2012) Ore-forming conditions and genesis of the Huogeqi Cu-Pb-Zn-Fe deposit in the northern margin of the North China craton: evidence from ore petrologic characteristics. Ore Geol Rev 44:107–120
Zhong RC, Li WB, Chen YJ, Ji JQ, Yang YF, Hu CS (2015) Significant Zn-Pb-Cu remobilization of a syngenetic stratabound deposit during regional metamorphism: a case study in the giant Dongshengmiao deposit, northern China. Ore Geol Rev 64:89–102
Zhong RC, Li WB, Chen YJ, Yue DC, Yang YF (2013) P-T-X conditions, origin, and evolution of Cu-bearing fluids of the shear zone-hosted Huogeqi Cu-(Pb-Zn-Fe) deposit, northern China. Ore Geol Rev 50:83–97
Zhou CX, Zhang YG, Tang PZ, Chen YM, Wang SL, Qi YH, Yang Q (2012) A discussion on genesis and ore prospecting of Dongshengmiao deposit, Inner Mongolia. J Jilin Univ (Earth Sci Ed) 42:1656–1664
Zhou JX, Huang ZL, Zhou MF, Zhu XK, Gao JG, Mirnejad H (2014a) Geology, isotope geochemistry and ore genesis of the Shanshulin carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit, Southwest China. Ore Geol Rev 63:209–225
Zhou JX, Huang ZL, Zhou MF, Zhu XK, Muchez P (2014b) Zinc, sulfur and lead isotopic variations in carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn sulfide deposits, Southwest China. Ore Geol Rev 58:41–54
Zhu XK, O’Nions RK, Guo Y, Belshaw NS, Rickard D (2000) Determination of natural Cu isotope variation by plasmas source mass spectrometry: implications for use as geochemical tracers. Chem Geol 163:139–149
Zhu XK, Guo Y, Williams RJP, O’Nions RK, Matthews A, Belshaw NS, Canters GW, Waal ECD, Weser U, Burgess BK, Salvato B (2002) Mass fractionation processes of transition metal isotopes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 200:47–62
Zhu XK, Li ZH, Tang SH, Li YH (2008a) Fe isotope characteristics of early Precambrian pyrite deposits and their geological significance: examples from Shandong and Hebei provinces. Acta Petrol Mineral 27(5):429–434
Zhu XK, Li ZH, Zhao XM, Tang SH, He XX, Belshaw NS (2008b) High-precision measurements of Fe isotopes using MC-ICP-MS and Fe isotope compositions of geological reference materials. Acta Petrol Mineral 27(4):263–272
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the China Geological Survey (No. 12120113015700) and CAGS Research Fund (No. YYWF201603). We gratefully acknowledge support from the Dongshengmiao Mining Co. Ltd. during fieldwork. Thanks are given to Mr. Binglin Wang for allowing access to their mining tunnels and properties. We would like to thank Zhihong Li, Jin Li, and Shizhen Li for their meticulous guidance during the chemical and instrumental experiments at CAGS, and we thank Kan Zhang, Dan Wang, Yuan He, Yue Wang, Zilong Zhou, and Yu Zhang for helpful comments. Comments by the Editor-in-Chief Bernd Lehmann, the Associate Editor Shao-Yong Jiang, Prof. Ryan Mathur, and one anonymous reviewer have improved the manuscript significantly.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: S.-Y. Jiang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Z., Zhu, X., Sun, J. et al. Spatial evolution of Zn-Fe-Pb isotopes of sphalerite within a single ore body: A case study from the Dongshengmiao ore deposit, Inner Mongolia, China. Miner Deposita 53, 55–65 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-017-0724-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-017-0724-x