Abstract
Key message
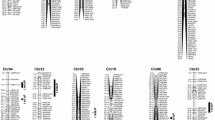
QTLs for fiber length mapped in three generations of advanced backcross populations derived from crossing Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium mustelinum showed opportunities to improve elite cottons by introgression from wild relatives.
Abstract
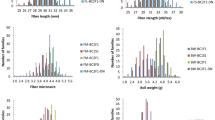
The molecular basis of cotton fiber length in crosses between Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium mustelinum was dissected using 21 BC3F2 and 12 corresponding BC3F2:3 and BC3F2:4 families. Sixty-five quantitative trait loci (QTLs) were detected by one-way analysis of variance. The QTL numbers detected for upper-half mean length (UHM), fiber uniformity index (UI), and short fiber content (SFC) were 19, 20, and 26 respectively. Twenty-three of the 65 QTLs could be detected at least twice near adjacent markers in the same family or near the same markers across different families/generations, and 32 QTLs were detected in both one-way variance analyses and mixed model-based composite interval mapping. G. mustelinum alleles increased UHM and UI and decreased SFC for five, one, and one QTLs, respectively. In addition to the main-effect QTLs, 17 epistatic QTLs were detected which helped to elucidate the genetic basis of cotton fiber length. Significant among-family genotypic effects were detected at 18, 16, and 16 loci for UHM, UI, and SFC, respectively. Six, two, and two loci showed genotype × family interaction for UHM, UI and SFC, respectively, illustrating complexities that might be faced in introgression of exotic germplasm into cultivated cotton. Co-location of many QTLs for UHM, UI, and SFC accounted for correlations among these traits, and selection of these QTLs may improve the three traits simultaneously. The simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers associated with G. mustelinum QTLs will assist breeders in transferring and maintaining valuable traits from this exotic source during cultivar development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alves M, Barroso P, Ciampi A, Hoffmann L, Azevedo V, Cavalcante U (2013) Diversity and genetic structure among subpopulations of Gossypium mustelinum (Malvaceae). Genet Mol Res 12:597–609
Borém A, Freire EC, Penna JCV, Barroso PAV (2003) Considerations about cotton gene escape in Brazil: a review. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 3:315–332
Burow MD, Starr JL, Park CH, Simpson CE, Paterson AH (2014) Introgression of homeologous quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for resistance to the root-knot nematode [Meloidogyne arenaria (Neal) Chitwood] in an advanced backcross-QTL population of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Mol Breed 34:393–406
Chee P, Draye X, Jiang CX, Decanini L, Delmonte TA, Bredhauer R, Smith CW, Paterson AH (2005a) Molecular dissection of interspecific variation between Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense (cotton) by a backcross-self approach: I. Fiber elongation. Theor Appl Genet 111:757–763
Chee P, Draye X, Jiang CX, Decanini L, Delmonte TA, Bredhauer R, Smith CW, Paterson AH (2005b) Molecular dissection of phenotypic variation between Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense (cotton) by a backcross-self approach: III. Fiber length. Theor Appl Genet 111:772–781
Chen H, Khan MKR, Zhou Z, Wang X, Cai X, Ilyas MK, Wang C, Wang Y, Li Y, Liu F, Wang K (2015) A high-density SSR genetic map constructed from a F2 population of Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium darwinii. Gene 574:273–286
Draye X, Chee P, Jiang CX, Decanini L, Delmonte TA, Bredhauer R, Smith CW, Paterson AH (2005) Molecular dissection of interspecific variation between Gossypium hirsutum and G. barbadense (cotton) by a backcross-self approach: II. Fiber fineness. Theor Appl Genet 111:764–771
Fulop D, Ranjan A, Ofner I, Covington MF, Chitwood DH, West D, Ichihashi Y, Headland L, Zamir D, Maloof JN, Sinha NR (2016) A new advanced backcross tomato population enables high resolution leaf QTL mapping and gene identification. G3-Genes Genom Genet 6:3169–3184
Haas M, Menke J, Chao S, Steffenson BJ (2016) Mapping quantitative trait loci conferring resistance to a widely virulent isolate of Cochliobolus sativus in wild barley accession PI 466423. Theor Appl Genet 129:1–12
Hou MY, Cai CP, Zhang SW, Guo WZ, Zhang TZ, Zhou BL (2013) Construction of microsatellite-based linkage map and mapping of nectarilessness and hairiness genes in Gossypium tomentosum. J Genet 92:445–459
Jiang CX, Wright RJ, El-Zik KM, Paterson AH (1998) Polyploid formation created unique avenues for response to selection in Gossypium (cotton). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4419–4424
Kalladan R, Worch S, Rolletschek H, Harshavardhan VT, Kuntze L, Seiler C, Sreenivasulu N, Roder MS (2013) Identification of quantitative trait loci contributing to yield and seed quality parameters under terminal drought in barley advanced backcross lines. Mol Breed 32:71–90
Khan MKR, Chen H, Zhou Z, Ilyas MK, Wang X, Cai X, Wang C, Liu F, Wang K (2016) Genome wide SSR high density genetic map construction from an interspecific cross of Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium tomentosum. Front Plant Sci 7:436
Kim SM, Suh JP, Qin Y, Noh TH, Reinke RF, Jena KK (2015) Identification and fine-mapping of a new resistance gene, Xa40, conferring resistance to bacterial blight races in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 128:1933–1943
Kinkade MP, Foolad MR (2013) Validation and fine mapping of lyc12.1, a QTL for increased tomato fruit lycopene content. Theor Appl Genet 126:2163–2175
Kroymann J, Mitchell-Olds T (2005) Epistasis and balanced polymorphism influencing complex trait variation. Nature 435:95–98
Kuang XQ, Yu CW (2015) Generating cotton fiber length probability density function from fiber length parameters by finite mixture model. J Text I 106:655–662
Lacape JM et al (2010) Meta-analysis of cotton fiber quality QTLs across diverse environments in a Gossypium hirsutum x G. barbadense RIL population. BMC Plant Biol 10:132
Lawrence CA (2003) Fundamentals of spun yarn technology. CRC Press, Boca Raton
McCouch S, Cho Y, Yano M, Paul E, Blinstrub M, Morishima H, Kinoshita T (1997) Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet Newsl 14:11
Nagata K et al (2015) Advanced backcross QTL analysis reveals complicated genetic control of rice grain shape in a japonica x indica cross. Breed Sci 65:308–318
Naz AA, Klaus M, Pillen K, Leon J (2015) Genetic analysis and detection of new QTL alleles for Septoria tritici blotch resistance using two advanced backcross wheat populations. Plant Breed 134:514–519
Paterson AH, Deverna JW, Lanini B, Tanksley SD (1990) Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci using selected overlapping recombinant chromosomes, in an interspecies cross of tomato. Genetics 124:735–742
Paterson AH et al (2004) Reducing the genetic vulnerability of cotton. Crop Sci 44:1900–1901
Paterson AH et al (2012) Repeated polyploidization of Gossypium genomes and the evolution of spinnable cotton fibres. Nature 492:423–427
Rong JK et al (2004) A 3347-locus genetic recombination map of sequence-tagged sites reveals features of genome organization, transmission and evolution of cotton (Gossypium). Genetics 166:389–417
Said JI, Song M, Wang H, Lin Z, Zhang X, Fang DD, Zhang J (2015) A comparative meta-analysis of QTL between intraspecific Gossypium hirsutum and interspecific G. hirsutum × G. barbadense populations. Mol Genet Genomics 290:1003–1025
SAS Institute (1999) SAS/STAT user’s guide, version 8, vol 2. SAS Institute, Cary
Self SG, Liang K-Y (1987) Asymptotic properties of maximum likelihood estimators and likelihood ratio tests under nonstandard conditions. J Am Stat Assoc 82:605–610
Shi YZ et al (2015) Constructing a high-density linkage map for Gossypium hirsutum x Gossypium barbadense and identifying QTLs for lint percentage. J Integr Plant Biol 57:450–467
Swamy BPM, Kaladhar K, Rani NS, Prasad GSV, Viraktamath BC, Reddy GA, Sarla N (2012) QTL analysis for grain quality traits in 2 BC2F2 populations derived from crosses between Oryza sativa cv Swarna and 2 accessions of O. nivara. J Hered 103:442–452
Tang SY et al (2015) Construction of genetic map and QTL analysis of fiber quality traits for Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Euphytica 201:195–213
Tanksley S, Nelson J (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis: a method for the simultaneous discovery and transfer of valuable QTLs from unadapted germplasm into elite breeding lines. Theor Appl Genet 92:191–203
Testore F, Minero G (1988) A study of the fundamental parameters of some fancy yarns. J Text I 79:606–619
Trachsel S, Sun D, SanVicente FM, Zheng H, Atlin GN, Suarez EA, Babu R, Zhang X (2016) Identification of QTL for early vigor and stay-green conferring tolerance to drought in two connected advanced backcross populations in tropical maize (Zea mays L.). PLoS ONE 11(3):e0149636
van der Knaap E et al (2014) What lies beyond the eye: the molecular mechanisms regulating tomato fruit weight and shape. Front Plant Sci 5:227
Waghmare VN, Rong JK, Rogers CJ, Pierce GJ, Wendel JF, Paterson AH (2005) Genetic mapping of a cross between Gossypium hirsutum (cotton) and the Hawaiian endemic, Gossypium tomentosum. Theor Appl Genet 111:665–676
Wang B, Chee PW (2010) Application of advanced backcross quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis in crop improvement. J Plant Breed Crop Sci 2:221–232
Wang FR, Gong YC, Zhang CY, Liu GD, Wang LM, Xu ZZ, Zhang J (2011) Genetic effects of introgression genomic components from Sea Island cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) on fiber related traits in upland cotton (G. hirsutum L.). Euphytica 181:41–53
Wang B, Nie YC, Lin ZX, Zhang XL, Liu JJ, Bai J (2012) Molecular diversity, genomic constitution, and QTL mapping of fiber quality by mapped SSRs in introgression lines derived from Gossypium hirsutum x G. darwinii Watt. Theor Appl Genet 125:1263–1274
Wang XQ, Yu Y, Li W, Guo HL, Lin ZX, Zhang XL (2013) Association analysis of yield and fiber quality traits in Gossypium barbadense with SSRs and SRAPs. Genet Mol Res 12:3353–3362
Wang B, Draye X, Zhang Z, Zhuang Z, May OL, Paterson AH, Chee PW (2016a) Advanced backcross QTL analysis of fiber elongation in a cross between Gossypium hirsutum and G. mustelinum. Crop Sci 56:1760–1768
Wang B, Liu L, Zhang D, Zhuang Z, Guo H, Qiao X, Wei L, Rong J, May OL, Paterson AH, Chee PW (2016b) A genetic map between Gossypium hirsutum and the Brazilian endemic G. mustelinum and its application to QTL mapping. G3-Genes Genomics Genet 6:1673–1685
Wendel JF, Grover CE (2015) Taxonomy and evolution of the cotton genus, Gossypium. In: Fang DD, Percy RG (ed) Cotton, 2nd edn. American Society of Agronomy, Inc., Crop Science Society of America, Inc., and Soil Science Society of America, Inc, Madison.
Wickneswari R, Bhuiyan MAR, Kalluvettankuzhy S, Lim LS, Thomson MJ, Narimah MK, Abdullah MZ (2012) Identification and validation of quantitative trait loci for agronomic traits in advanced backcross breeding lines derived from Oryza rufipogon x Oryza sativa cultivar MR219. Plant Mol Biol Rep 30:929–939
Yang J, Hu CC, Hu H, Yu RD, Xia Z, Ye XZ, Zhu J (2008) QTLNetwork: mapping and visualizing genetic architecture of complex traits in experimental populations. Bioinformatics 24:721–723
Yu JW, Yu SX, Gore M, Wu M, Zhai HH, Li XL, Fan SL, Song MZ, Zhang JF (2013a) Identification of quantitative trait loci across interspecific F2, F2:3 and testcross populations for agronomic and fiber traits in tetraploid cotton. Euphytica 191:375–389
Yu JW, Zhang K, Li SY, Yu SX, Zhai HH, Wu M, Li XL, Fan SL, Song MZ, Yang DG, Li YH, Zhang JF (2013b) Mapping quantitative trait loci for lint yield and fiber quality across environments in a Gossypium hirsutum x Gossypium barbadense backcross inbred line population. Theor Appl Genet 126:275–287
Yu J, Jung S, Cheng CH, Ficklin SP, Lee T, Zheng P, Jones D, Percy RG, Main D (2014a) CottonGen: a genomics, genetics and breeding database for cotton research. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D1229–D1236
Yu JZ, Ulloa M, Hoffman SM, Kohel RJ, Pepper AE, Fang DD, Percy RG, Burke JJ (2014b) Mapping genomic loci for cotton plant architecture, yield components, and fiber properties in an interspecific (Gossypium hirsutum L. x G. barbadense L.) RIL population. Mol Genet Genomics 289:1347–1367
Zhang HB, Li Y, Wang B, Chee PW (2008) Recent advances in cotton genomics. Int J Plant Genomics 2008:742304
Zhang ZS, Rong JK, Waghmare VN, Chee PW, May OL, Wright RJ, Gannaway JR, Paterson AH (2011) QTL alleles for improved fiber quality from a wild Hawaiian cotton, Gossypium tomentosum. Theor Appl Genet 123:1075–1088
Zhang JF, Yu JW, Pei WF, Li XL, Said J, Song MZ, Sanogo S (2015a) Genetic analysis of Verticillium wilt resistance in a backcross inbred line population and a meta-analysis of quantitative trait loci for disease resistance in cotton. BMC Genomics 16:577
Zhang TZ, Hu Y, Jiang WK, Fang L, Guan XY, Chen JD, Zhang JB, Saski CA, Scheffler BE, Stelly DM, Hulse-Kemp AM, Wan Q, Liu BL, Liu CX, Wang S, Pan MQ, Wang YK, Wang DW, Ye WX, Chang LJ, Zhang WP, Song QX, Kirkbride RC, Chen XY, Dennis E, Llewellyn DJ, Peterson DG, Thaxton P, Jones DC, Wang Q, Xu XY, Zhang H, Wu HT, Zhou L, Mei GF, Chen SQ, Tian Y, Xiang D, Li XH, Ding J, Zuo QY, Tao LN, Liu YC, Li J, Lin Y, Hui YY, Cao ZS, Cai CP, Zhu XF, Jiang Z, Zhou BL, Guo WZ, Li RQ, Chen ZJ (2015b) Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat Biotechnol 33:531–537
Acknowledgements
We appreciate financial help from the National Science Foundation (PFI award IIP 0917856; AIR award IIP 1127755), Cotton Incorporated, and Key Research and Development Project of Jiangsu Province, China (Modern Agriculture, BE2015353). We thank Jennifer McCurdy for help in field work and Cornelia Lemke for technical assistance in the lab.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Joshua A. Udall.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Draye, X., Zhuang, Z. et al. QTL analysis of cotton fiber length in advanced backcross populations derived from a cross between Gossypium hirsutum and G. mustelinum . Theor Appl Genet 130, 1297–1308 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2889-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-017-2889-1